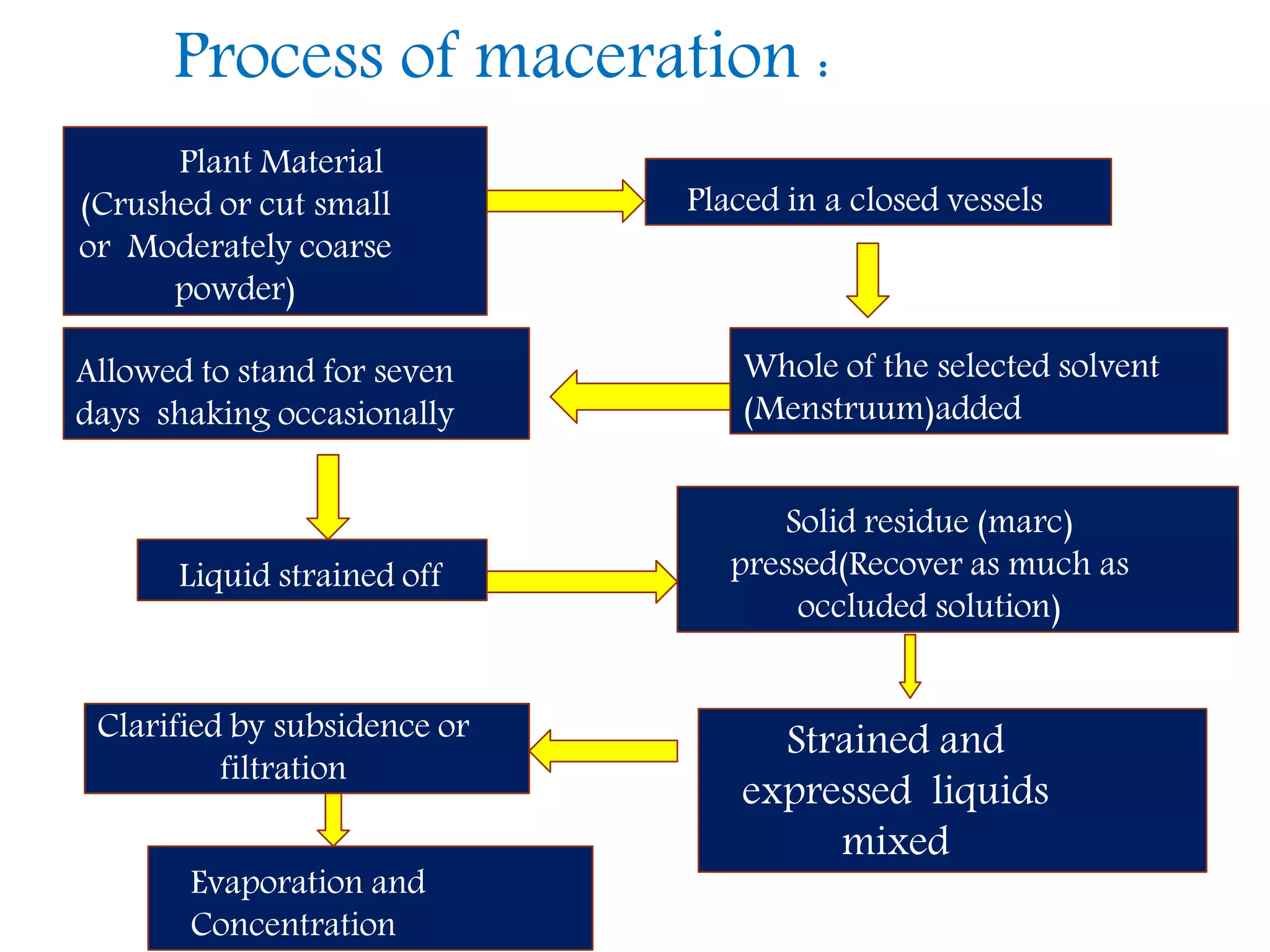
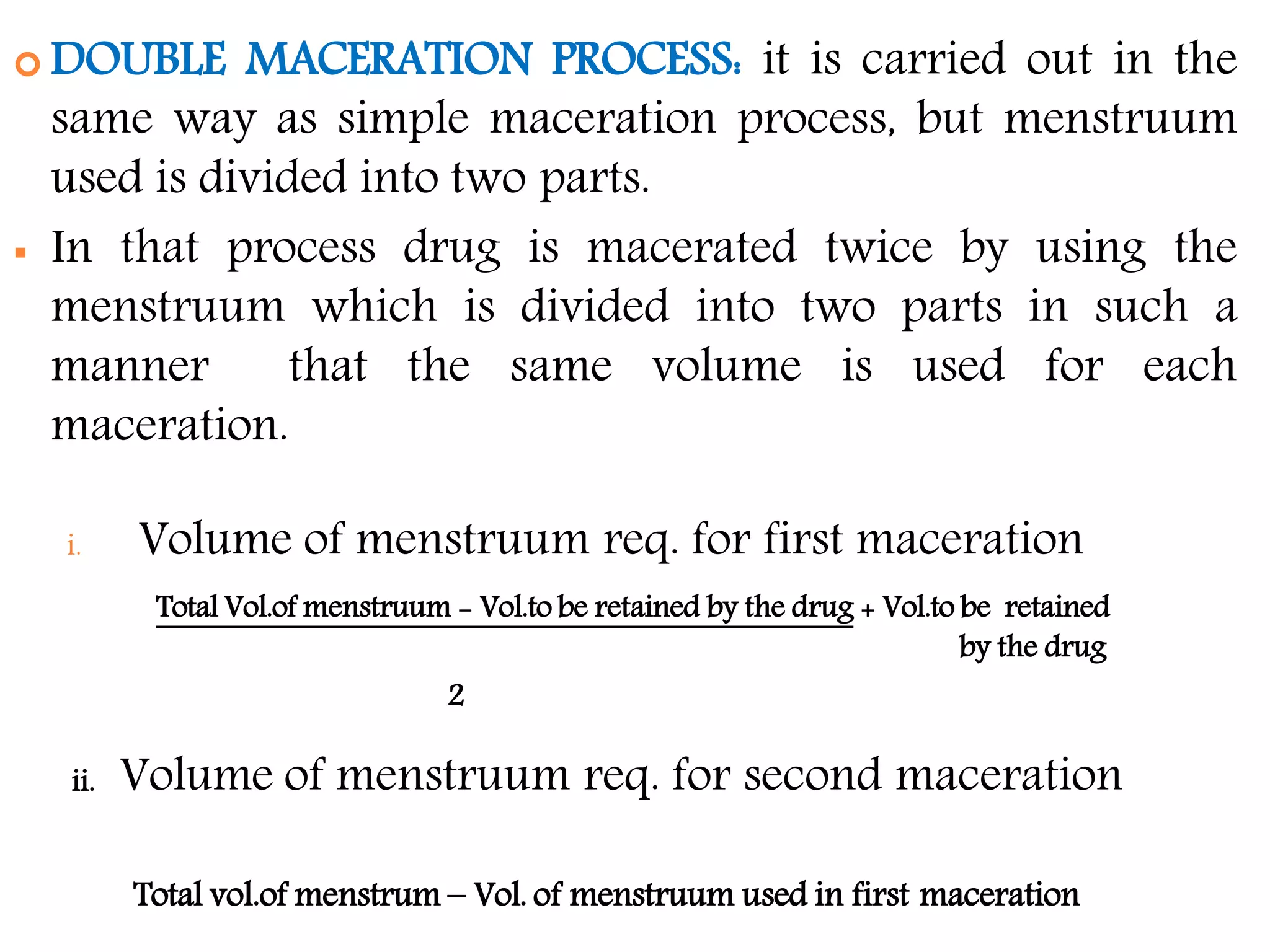
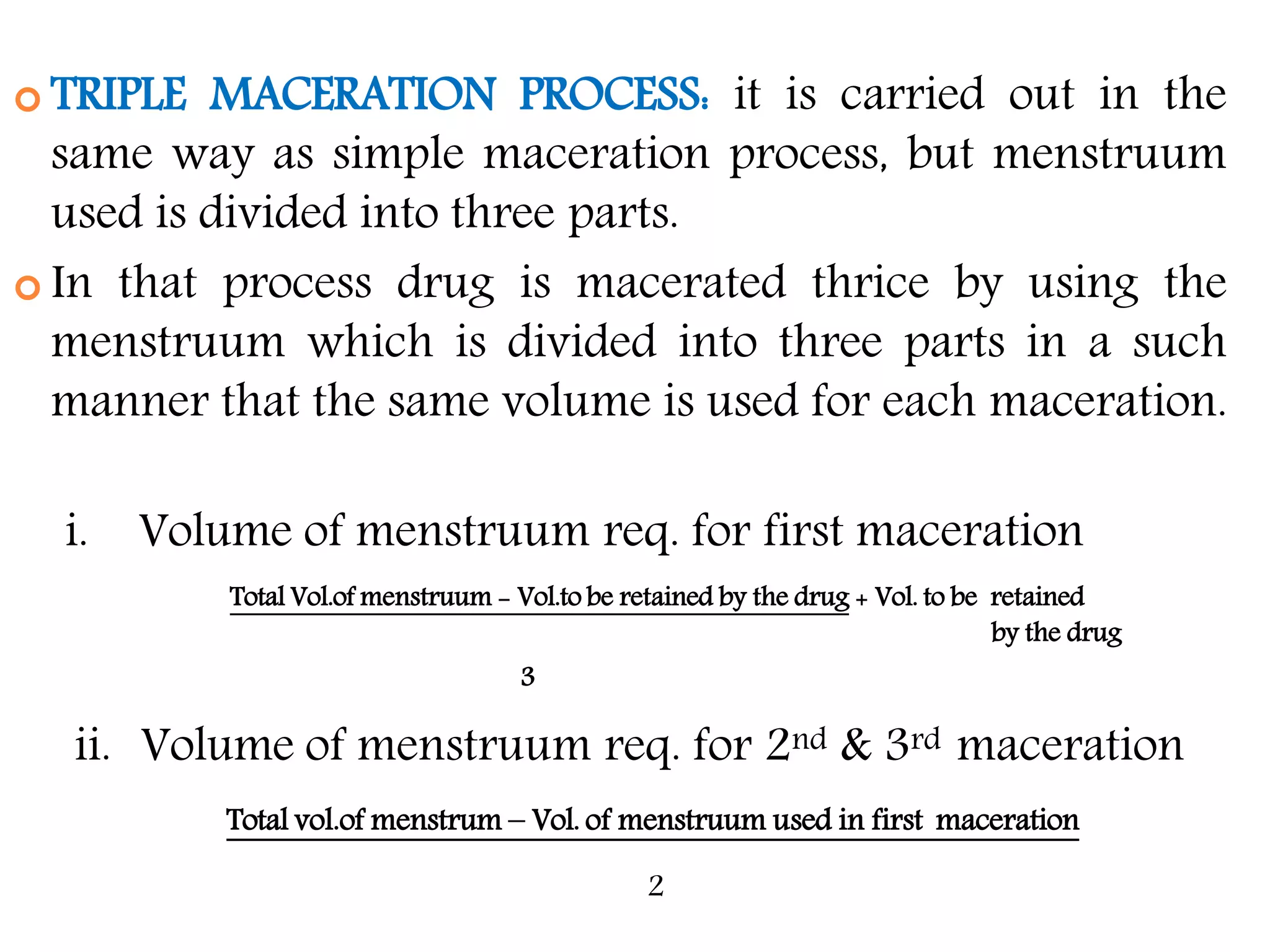
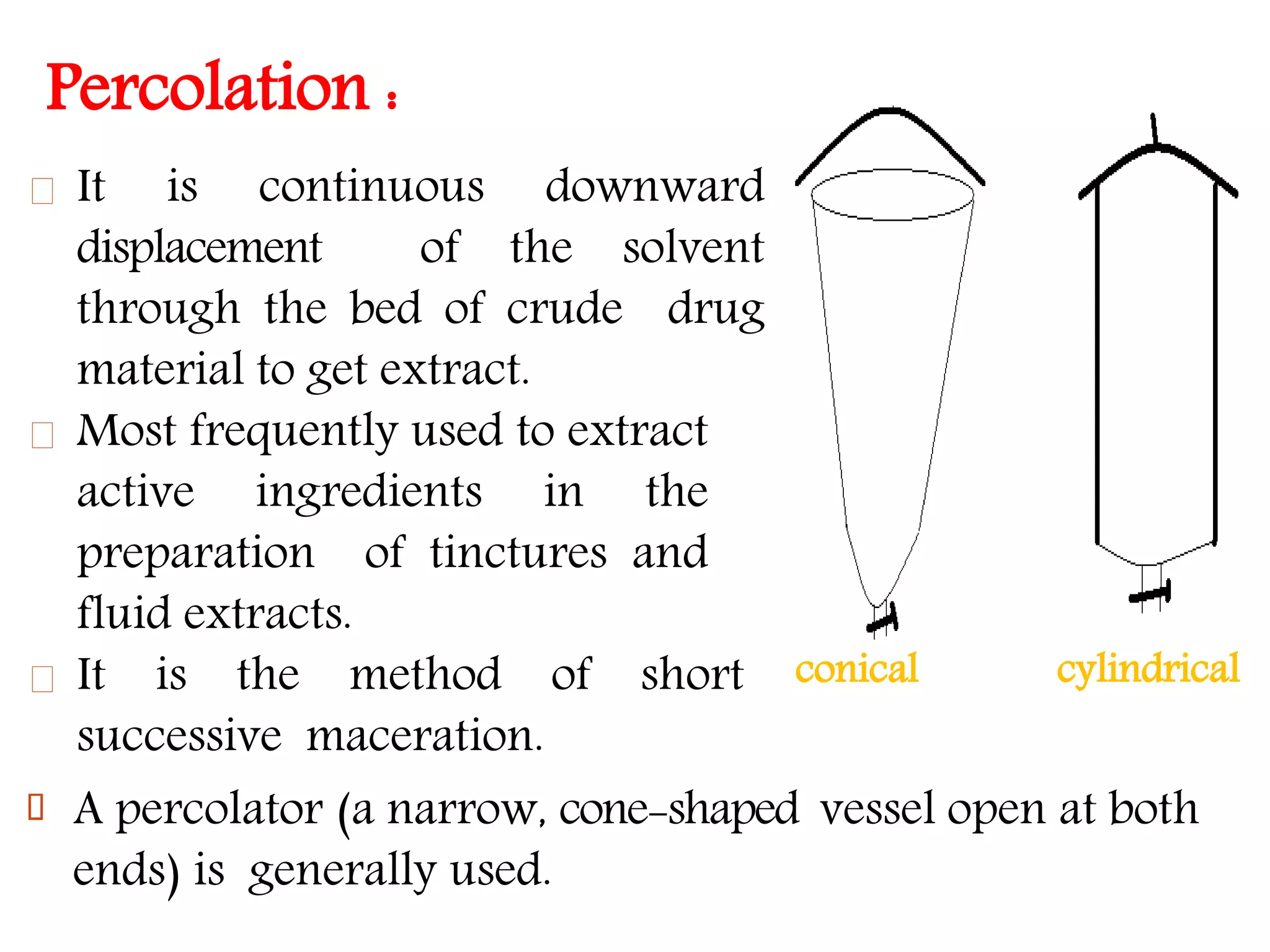
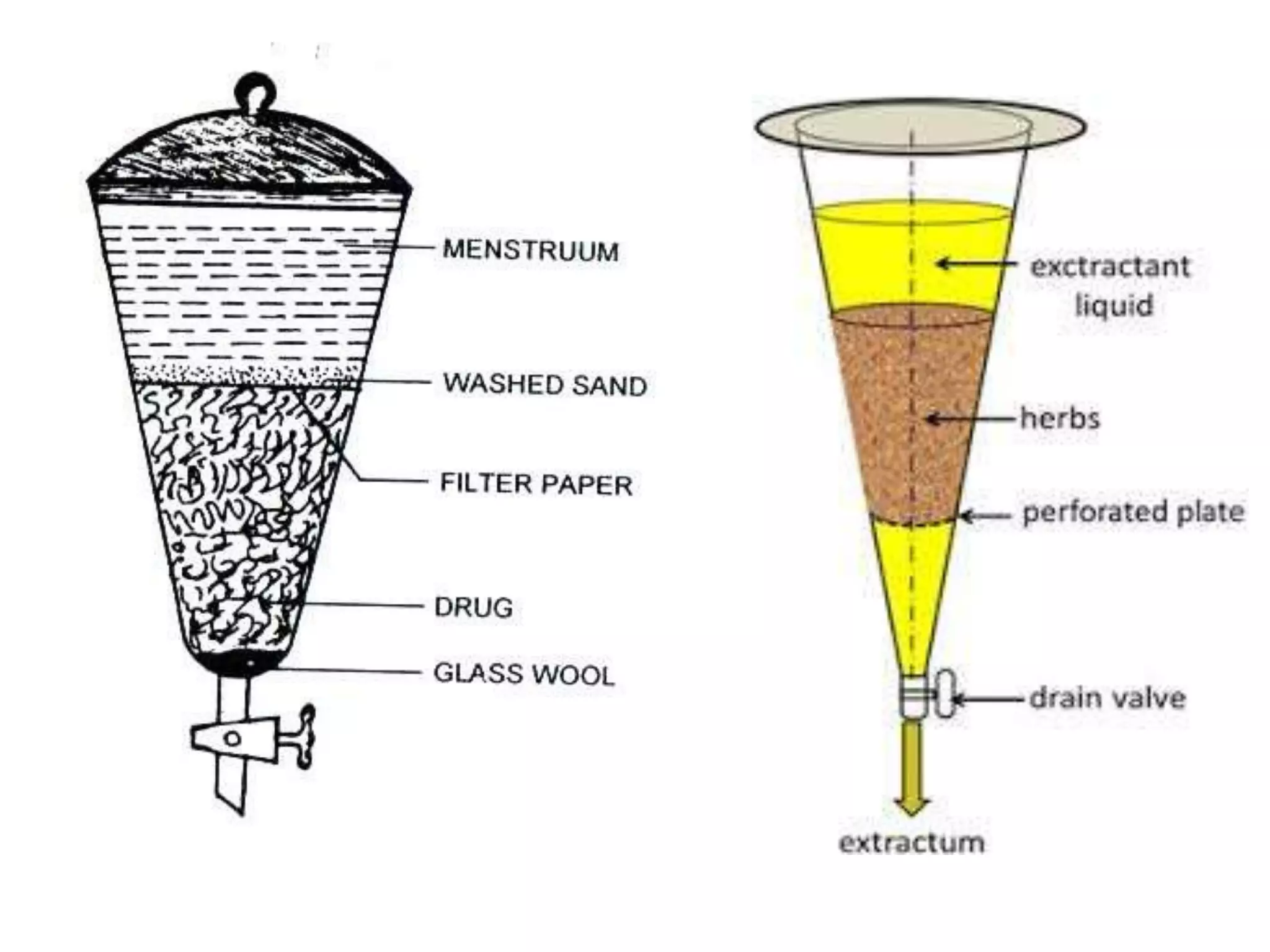
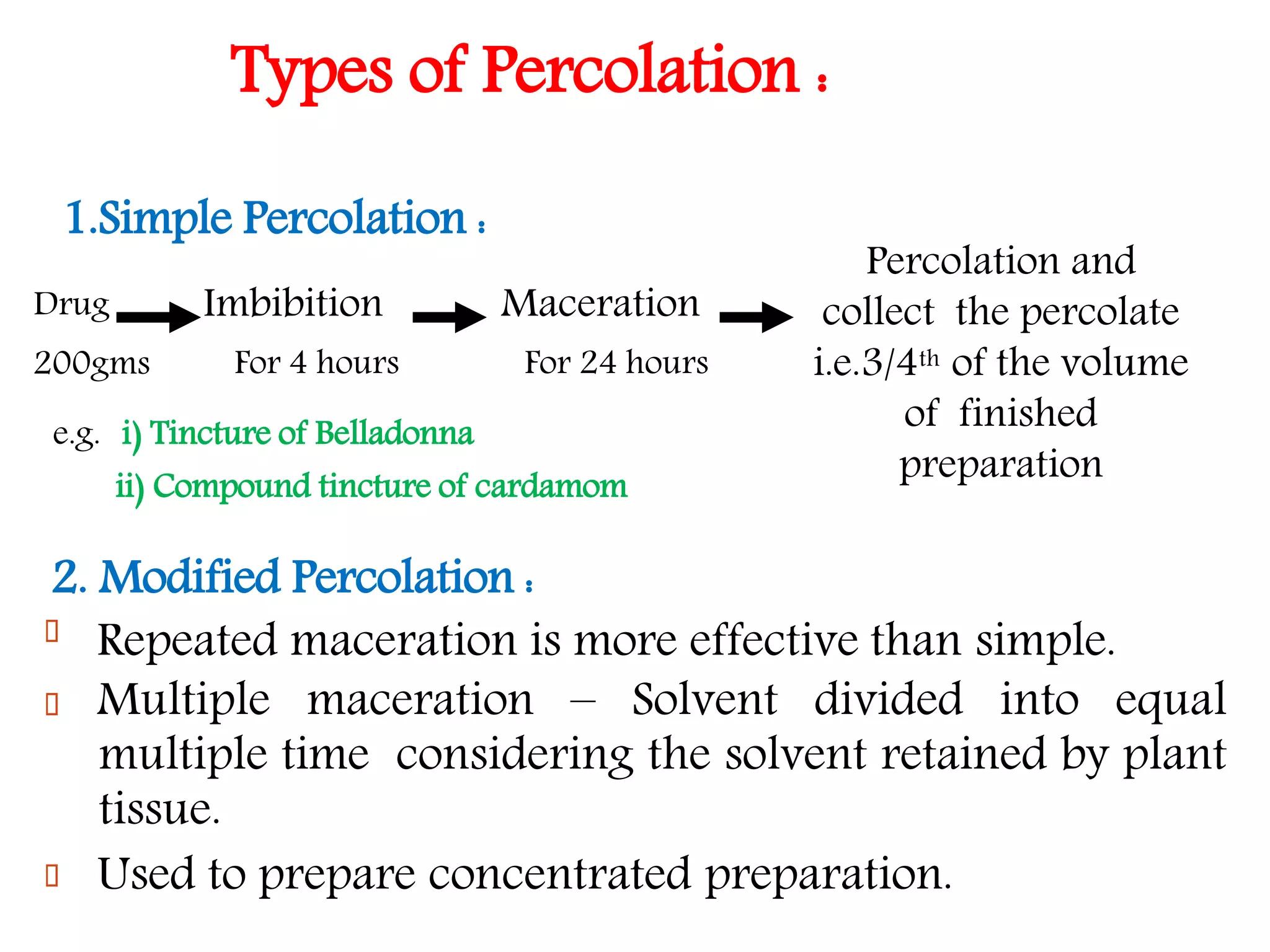
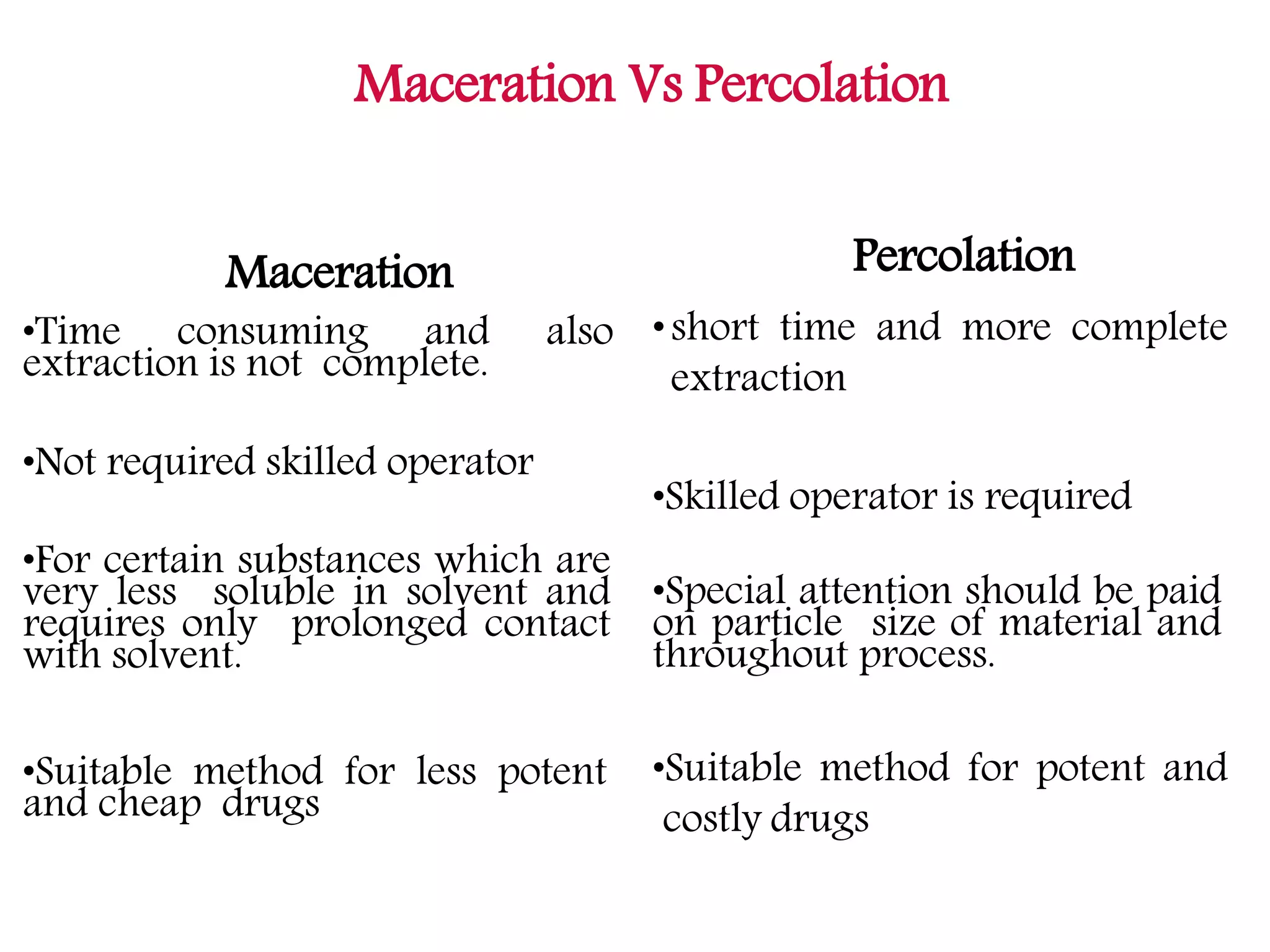
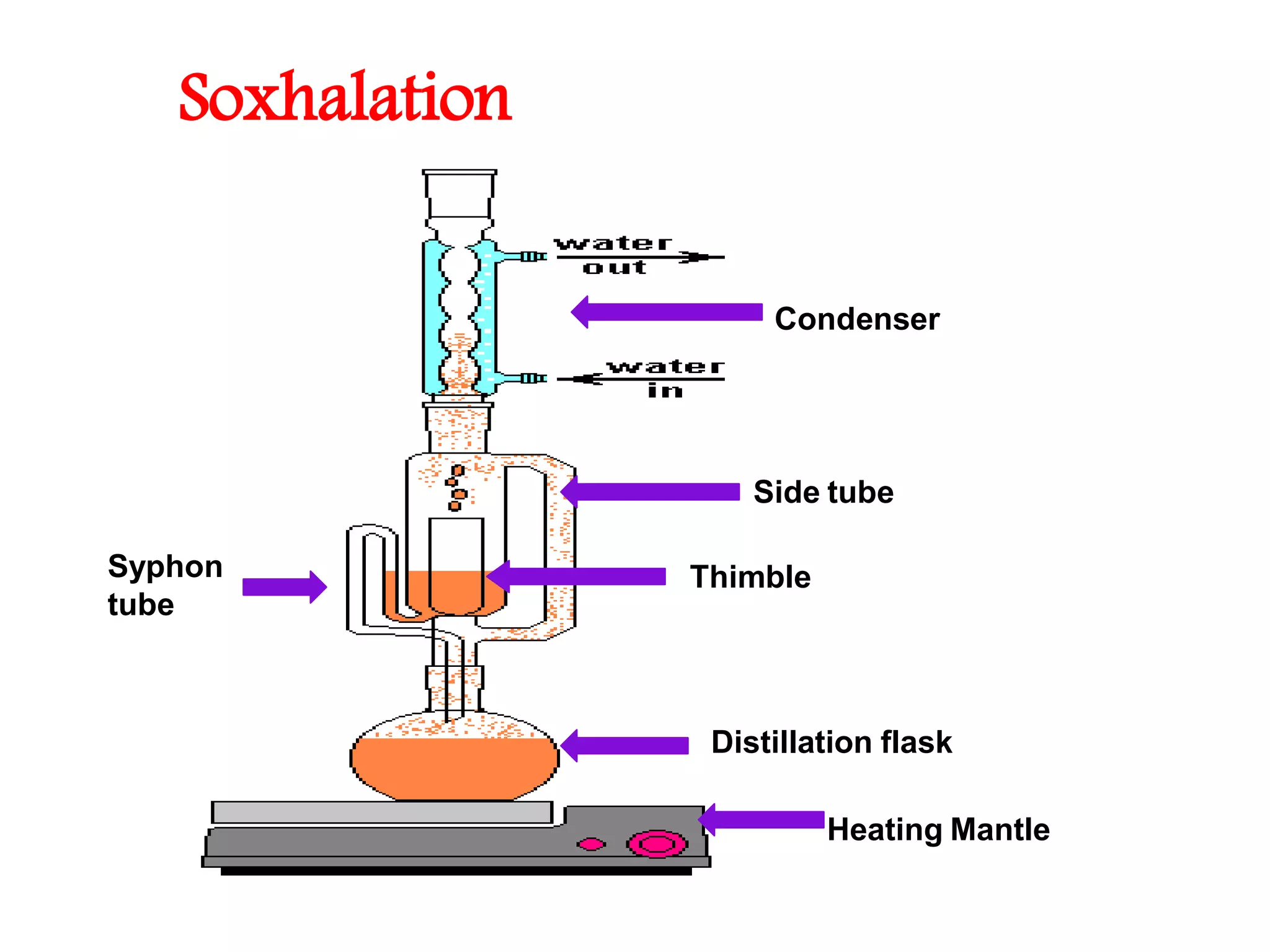
1. Extraction is the process of removing active constituents from plant or animal tissues using a solvent. Common extraction methods include maceration, percolation, digestion, decoction, and infusion.
2. Galenicals refer to medicinal preparations produced by extraction methods. Common galenicals include tinctures, extracts, and spirits.
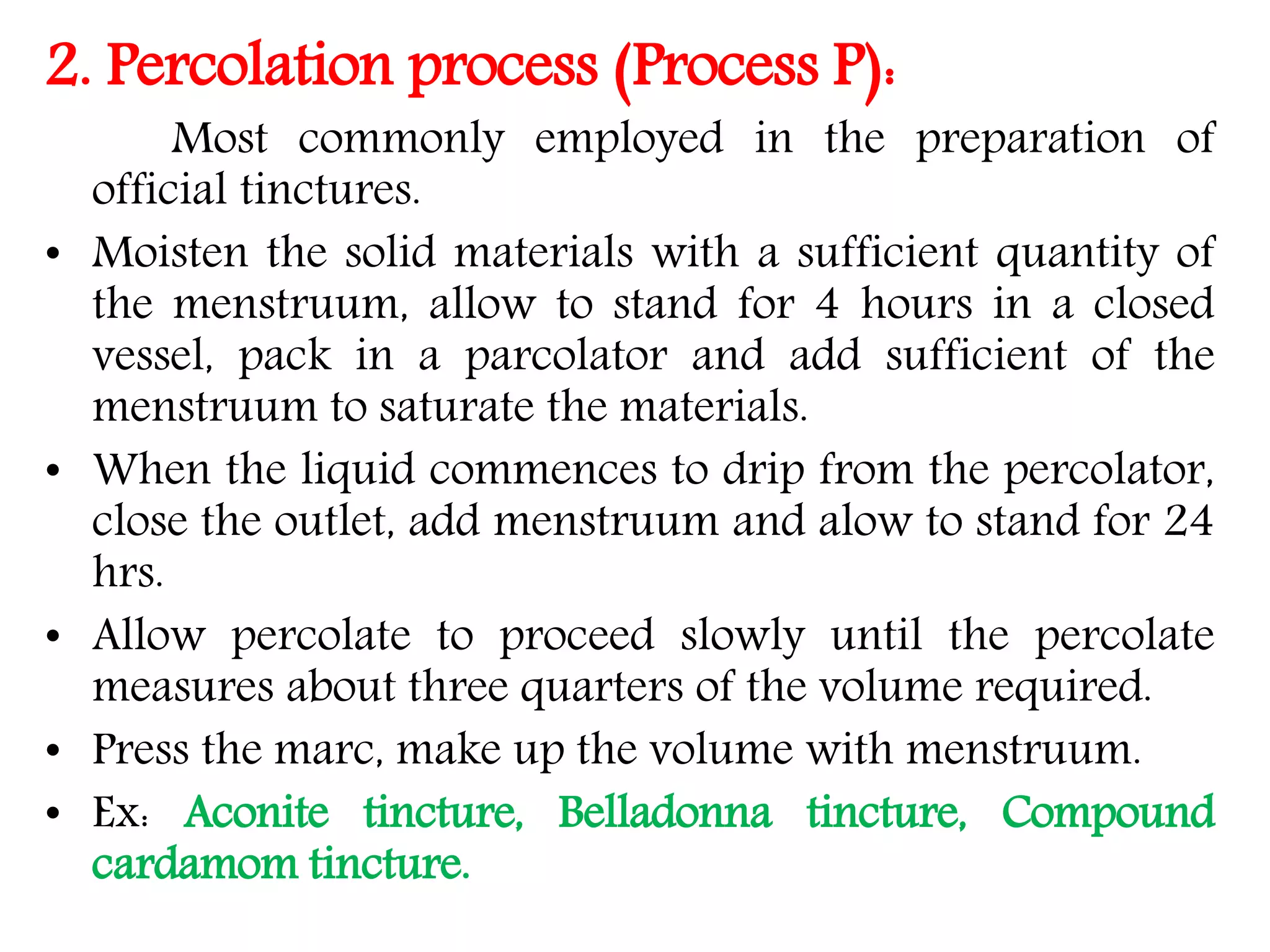
3. Tinctures are alcoholic or hydroalcoholic solutions of plant or animal materials. They are typically produced by maceration or percolation to extract active constituents from the raw materials.