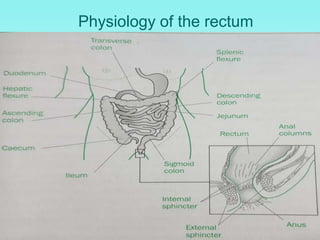
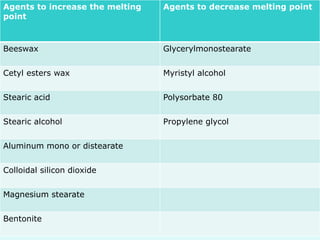
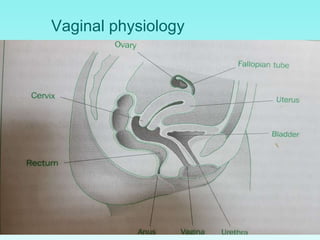
This document discusses rectal and vaginal dosage forms, including suppositories. It provides details on the physiology of the rectum and vagina, as well as formulations, manufacturing processes, and advantages and disadvantages of various rectal and vaginal dosage forms. Specifically, it describes the components, production processes, and quality control testing for suppositories manufactured via fusion or compression molding on an industrial scale. It also discusses other rectal and vaginal dosage forms such as creams, ointments, gels, solutions, and capsules.