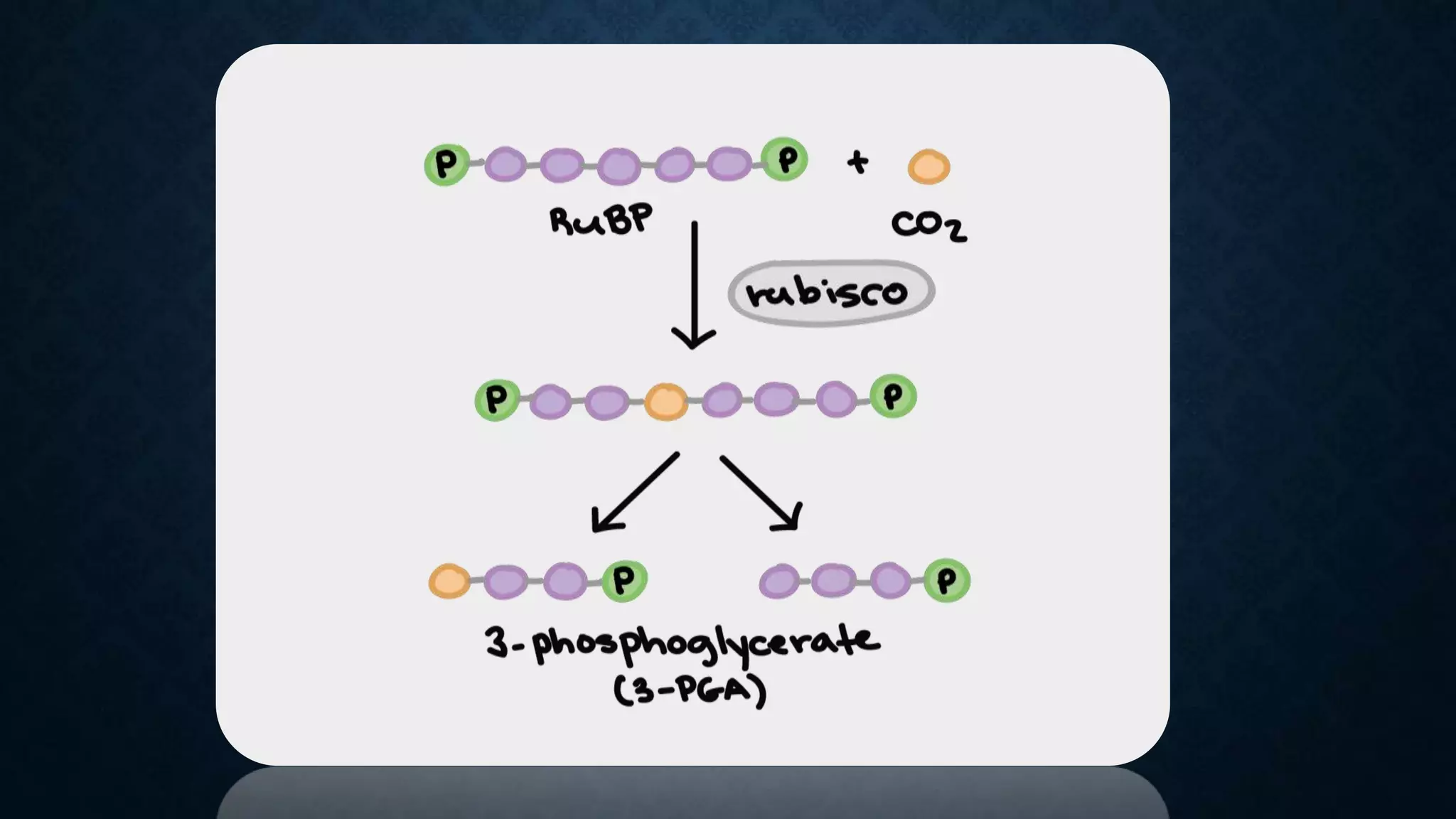
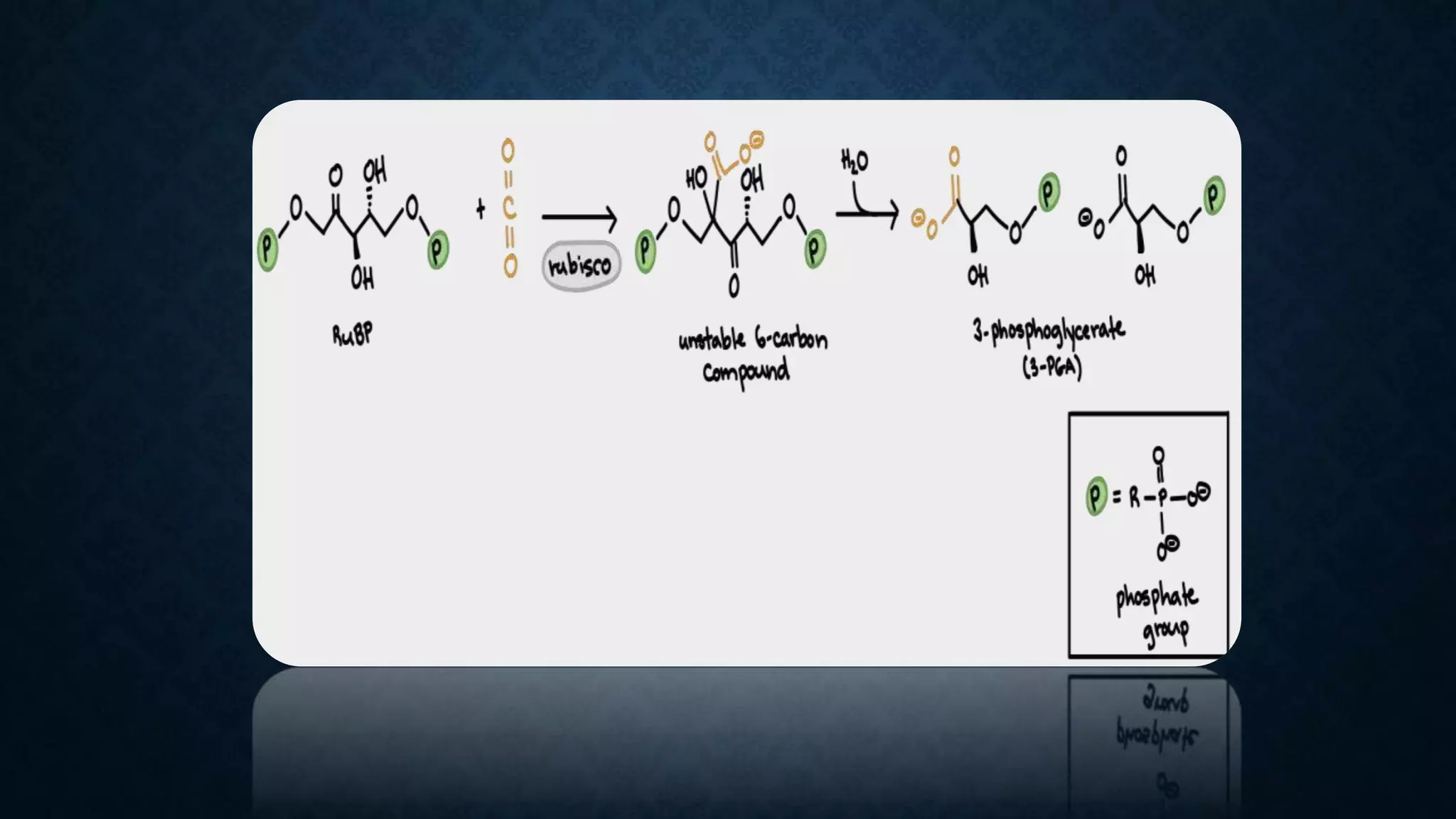
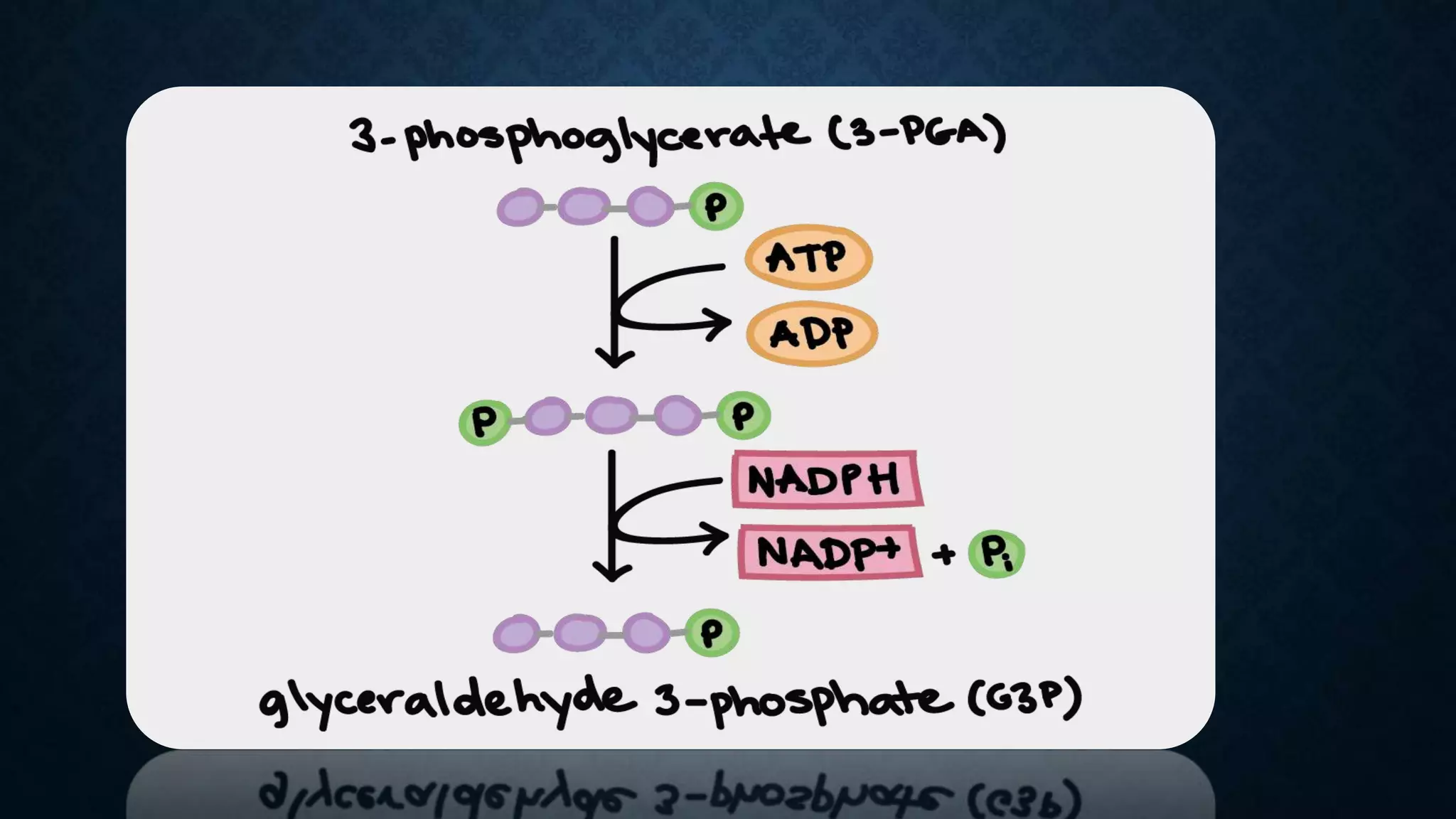
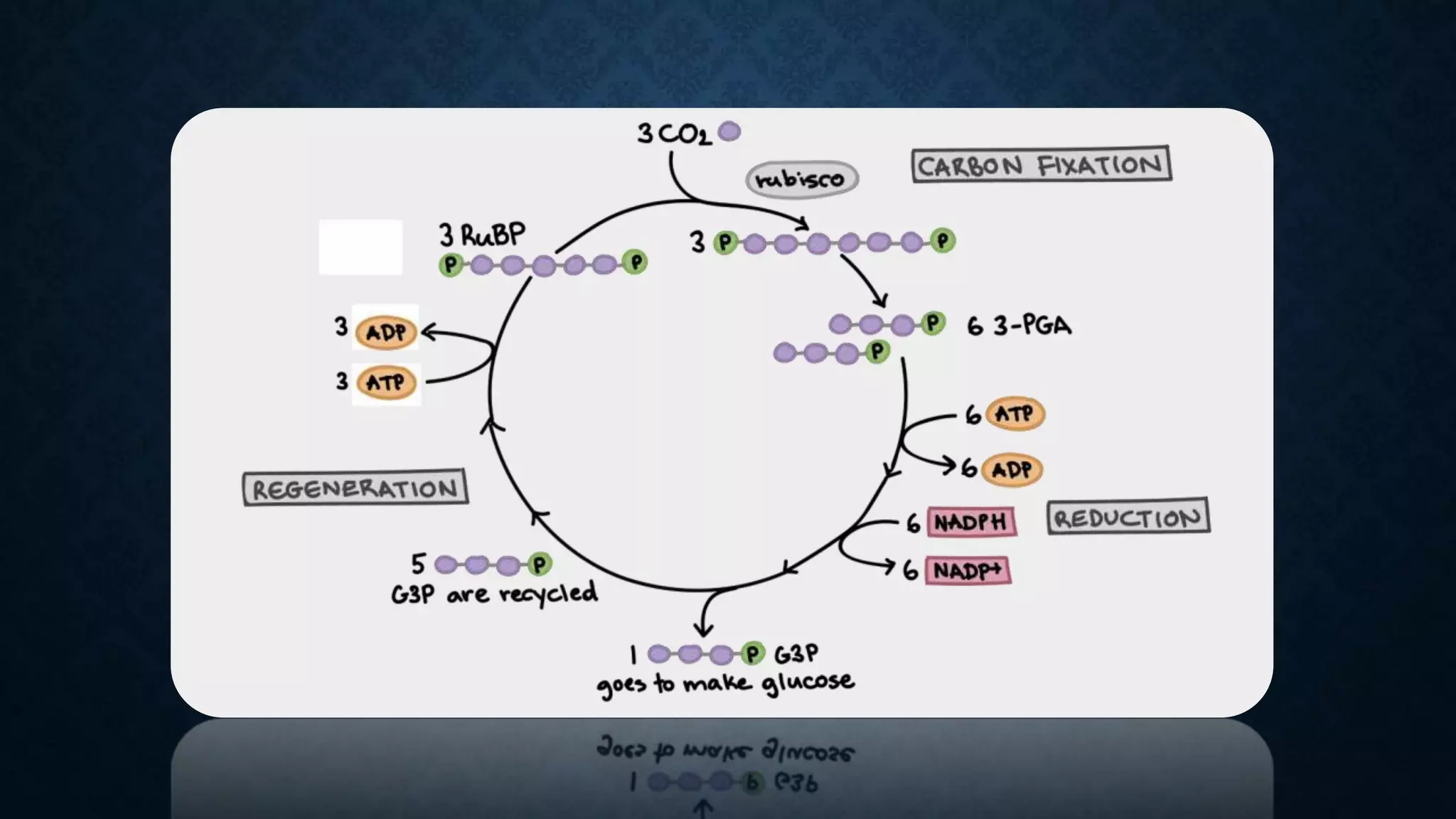
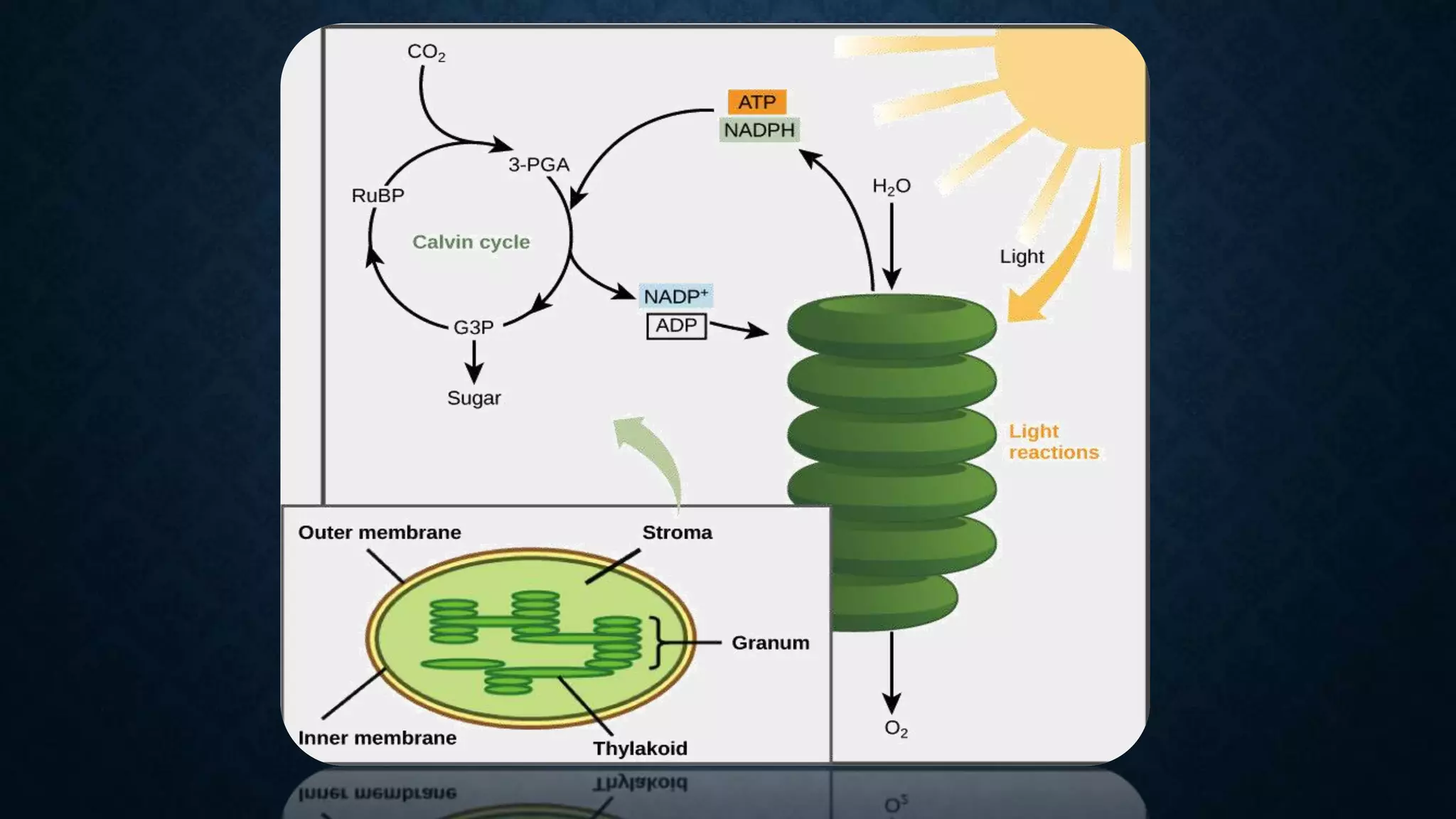
The Calvin cycle is a cyclic process that occurs in the dark phase of photosynthesis and fixes carbon dioxide into sugars. It was discovered by Melvin Calvin in the 1940s using radioactive carbon-14 isotopes to track the path of carbon in photosynthesis. The cycle has three main stages: carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration. In carbon fixation, the enzyme rubisco incorporates CO2 into ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). The resulting six-carbon compound then splits into two three-carbon molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3PGA). In reduction, ATP and NADPH are used to convert the 3PGA into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P). Some G3P molecules


![• Other names for Calvin Cycle :
• 1) Dark reactions
• 2)C3 Cycle
• 3) Reductive Pentose phosphate Cycle
• 4) Calvin Cycle
• 5) Photosynthetic Carbon Reduction Cycle [ PCR ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calvincyclec3-pathway-220820155618-f24e8d3d/75/CALVIN-CYCLE-C3-PATHWAY-pptx-3-2048.jpg)