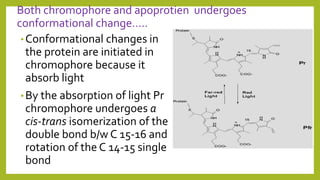
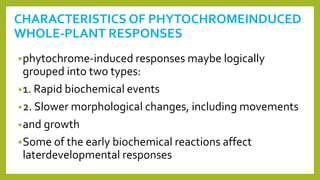
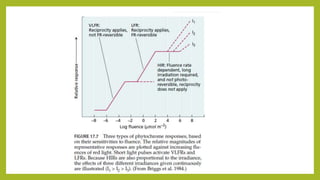
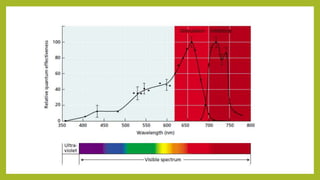
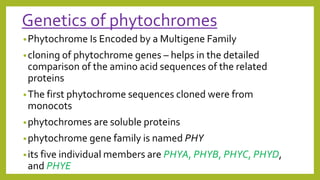
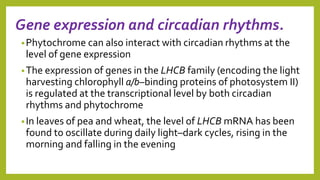
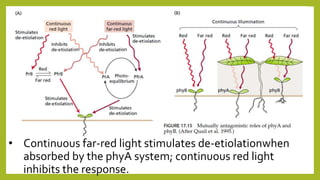
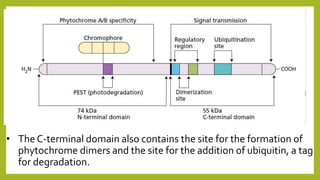
1. Photomorphogenesis refers to the response of plants to light and is central to plant development. Plants have photosensory systems including photoreceptors that detect different wavelengths of light.
2. The main photoreceptors are phytochromes, cryptochromes, phototropins, and UV-B receptors. Phytochromes absorb red and far-red light and have major roles in development from germination to flowering.
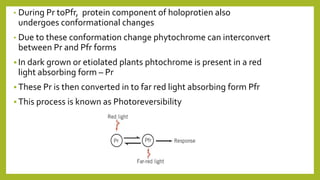
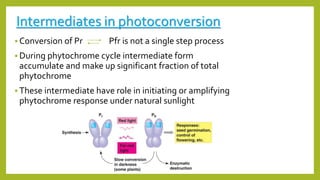
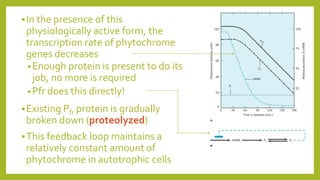
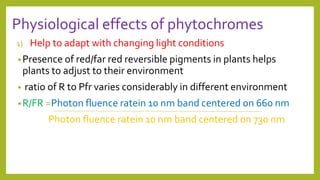
3. Photoreceptors undergo conformational changes when absorbing light, which triggers signal transduction pathways controlling photomorphogenic responses. The physiologically active form of phytochrome that triggers responses is Pfr, converted from Pr by red light absorption.