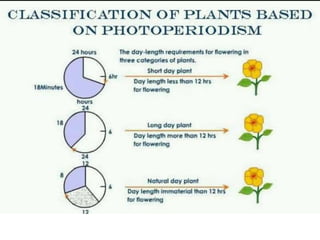
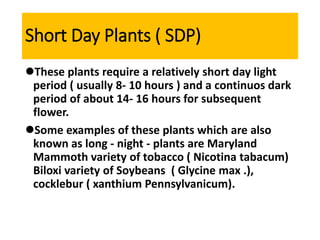
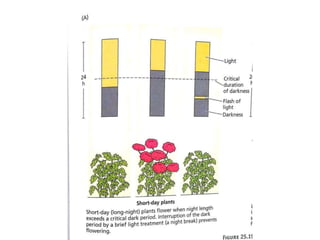
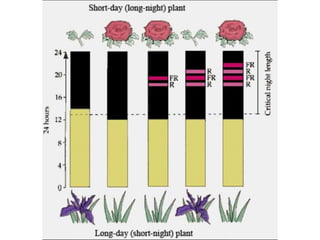
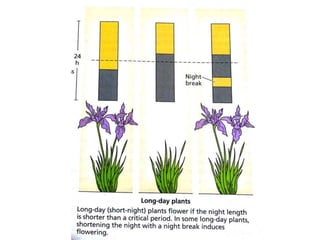
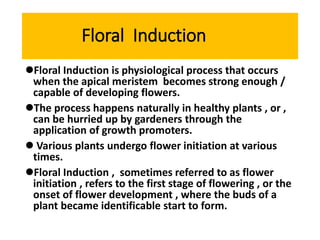
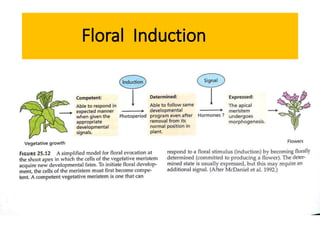
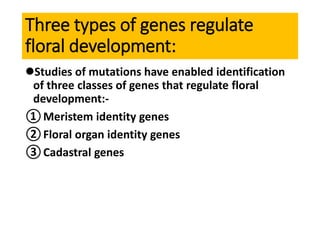
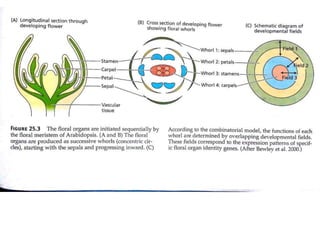
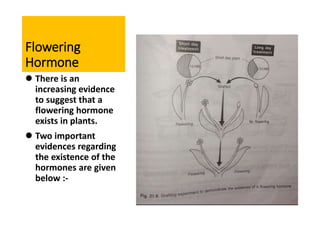
The document discusses photoperiodism, the response of plants to changes in day length, which is crucial for flowering. It classifies plants into short day, long day, and day neutral categories based on their light requirements for flowering. The document also touches on floral induction, the genes regulating floral development, and the possible existence of a flowering hormone.