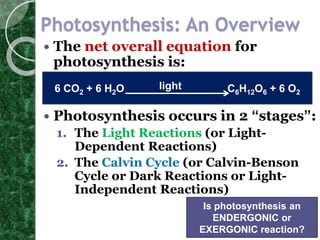
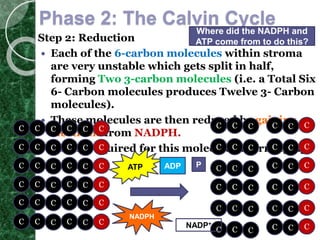
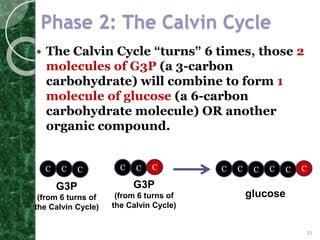
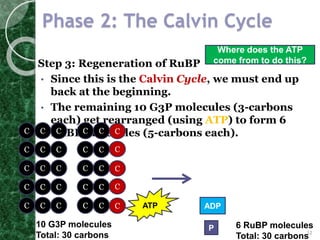
The Calvin cycle occurs in two stages: carbon fixation and reduction. During carbon fixation, the enzyme RuBisCO incorporates carbon from CO2 into RuBP to form unstable 6-carbon compounds. These 6-carbon compounds are then split into two 3-carbon molecules which are reduced using electrons from NADPH and energy from ATP. The 3-carbon molecules are then rearranged to regenerate RuBP, completing the cycle. The Calvin cycle uses energy from the light reactions in the form of ATP and NADPH along with CO2 to produce organic compounds like glucose.