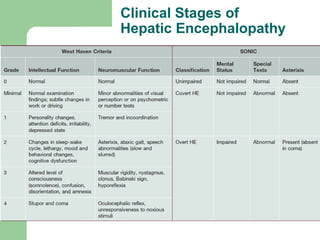
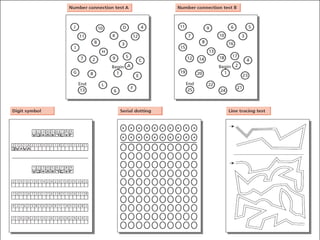
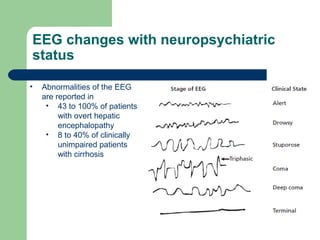
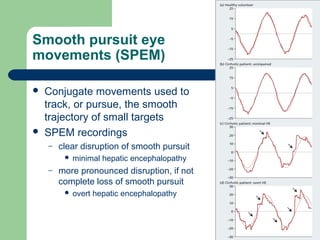
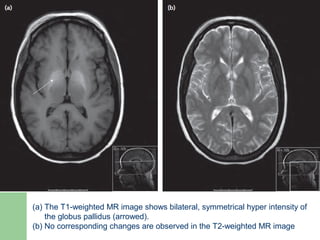
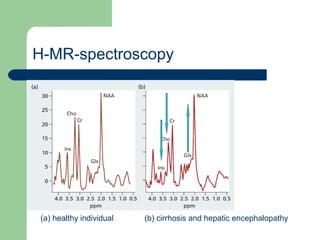
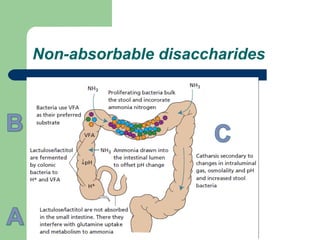
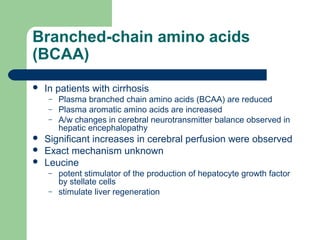
Hepatic encephalopathy is a neuropsychiatric syndrome caused by liver dysfunction and portosystemic shunting of blood flow. The leading theories for its cause are ammonia toxicity, inflammation, and imbalances in neurotransmitters. It ranges from mild cognitive impairment to coma. Treatment involves identifying and treating precipitants, a low-protein diet, non-absorbable disaccharides to reduce ammonia, and antibiotics to suppress gut bacteria. For persistent cases, additional therapies include branched-chain amino acids, probiotics, and transplantation for severe cases.