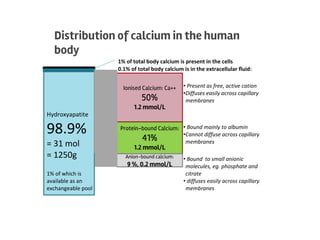
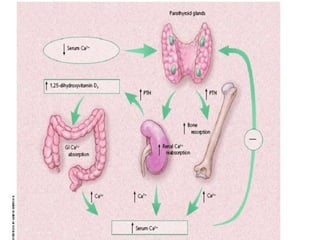
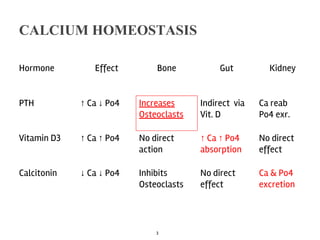
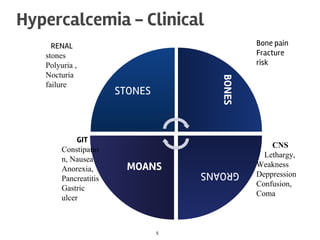
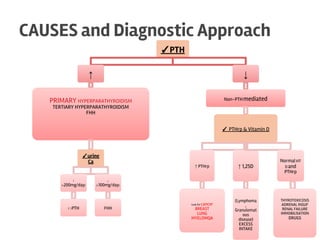
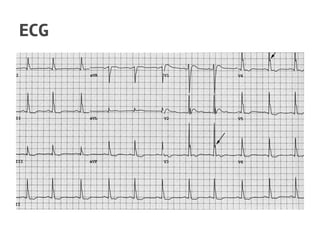
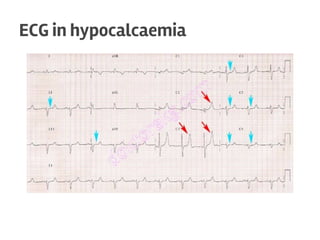
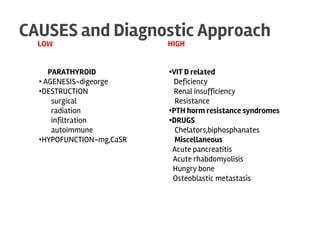
The document discusses calcium homeostasis in the human body. It notes that 98.9% of calcium in the body is found in bones and teeth in the form of hydroxyapatite. The remaining 1.1% is divided between the extracellular fluid and cells. Extracellular calcium is present as ionized calcium and protein-bound or anion-bound forms, while intracellular calcium is primarily protein-bound. The document also summarizes calcium regulation by parathyroid hormone, vitamin D, and calcitonin, as well as causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia.