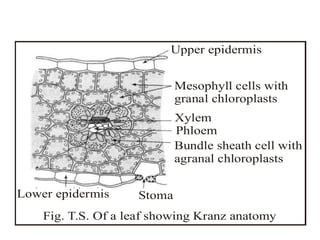
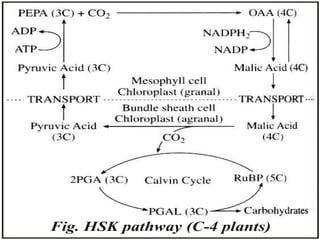
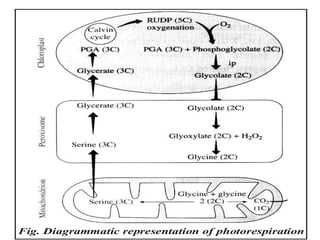
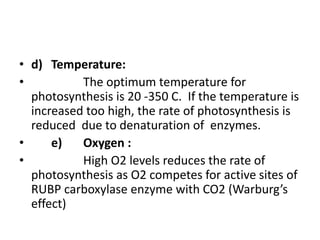
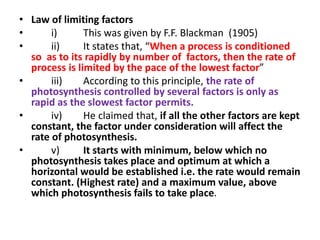
The document discusses the C4 pathway and Kranz anatomy in plants, highlighting the structural and functional aspects of C4 plants such as sugar cane. It outlines the processes of photosynthesis, including the fixation of CO2 and the significance of the C4 pathway in adapting to low CO2 and water scarcity. Additionally, the document covers the factors affecting photosynthesis, including light, carbon dioxide, water, temperature, and internal plant factors, along with the law of limiting factors that governs the rate of photosynthesis.