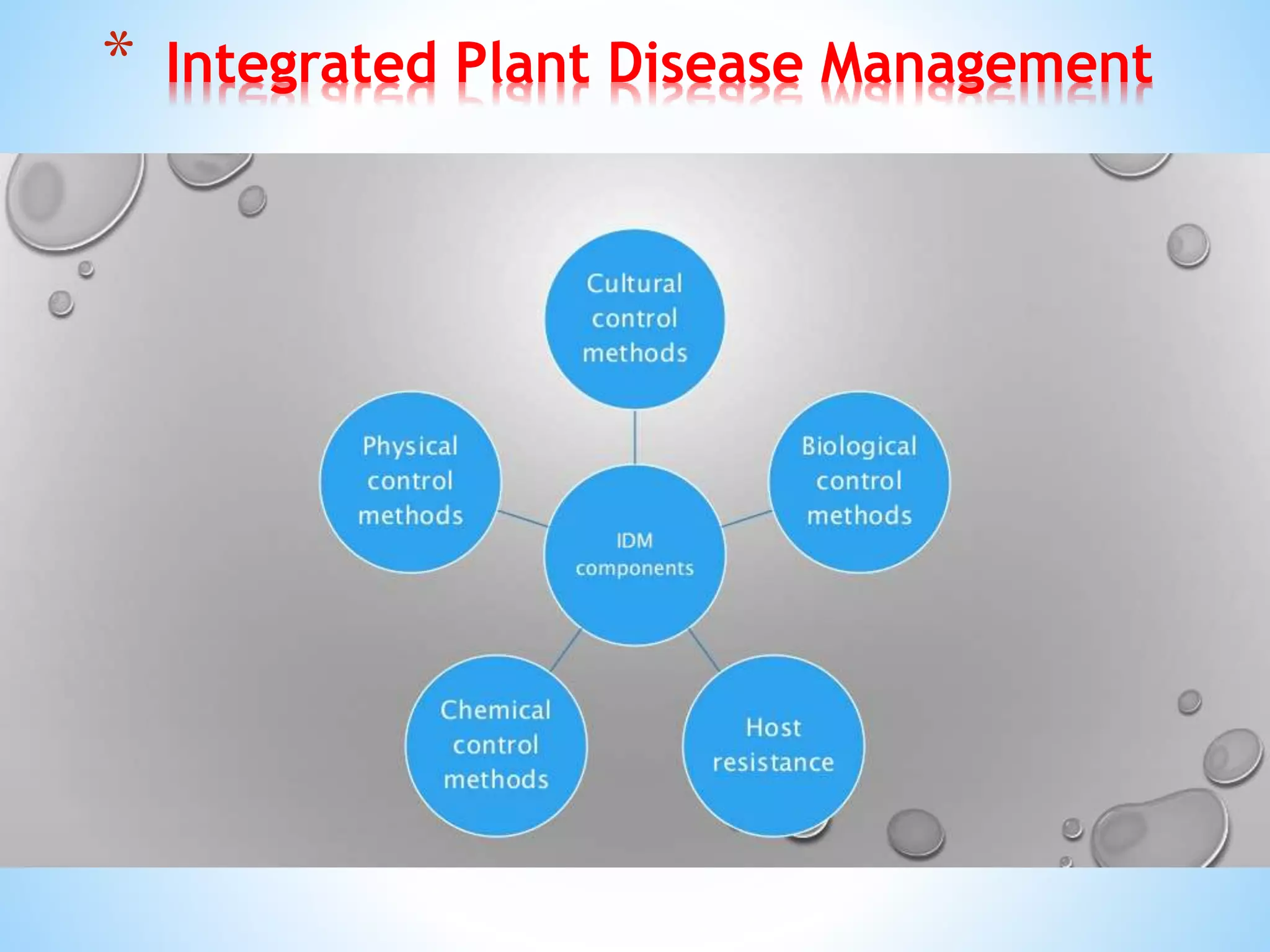
Integrated Plant Disease Management (IDM) utilizes multiple control methods to manage crop diseases efficiently while minimizing environmental impact. It encompasses principles such as avoidance, exclusion, eradication, protection, resistance, and therapy, along with various components like cultural control, biological control, and chemical control. IDM promotes sustainable practices, reduces reliance on pesticides, and enhances overall farm health by integrating diverse management strategies.