This document provides an overview of various common building materials used in civil engineering projects. It discusses the composition, properties, uses and testing procedures for water, concrete, cement, aggregates, paints/coatings, bricks, stones, metals/steel, timber and glass. For each material, key details are given around its history, ingredients, strengths and applications in construction. Standards and quality measures are also outlined. The document serves as a basic introduction to the principal materials that civil engineers work with.














![Stones: A stone is a small piece of rock.
History: The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during
which stone was widely used to make implements with an edge, a
point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted roughly 3.4 million
years, and ended between 8700 BCE] and 2000 BCE with the advent
of Metal working.
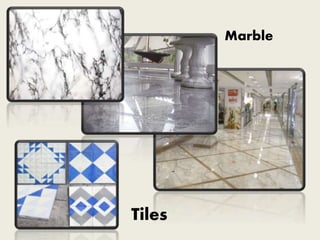
Marbleis a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized
carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble
may be foliated Geologists use the term "marble" to refer to
metamorphosed limestone & is use as a building material.
A Tileis a manufactured piece of hard-wearing material such
as ceramic, stone, metal, or even glass, generally used for covering
roofs, floors, walls, showers, or other objects such as tabletop
Types:
1)Igneous (Born of Fire) 2) Sedimentary (Cementing of Grains)
3)Metamorphic (Changed in Structure)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingmaterialsgroup7-170319105506/85/Building-Materials-17-320.jpg)