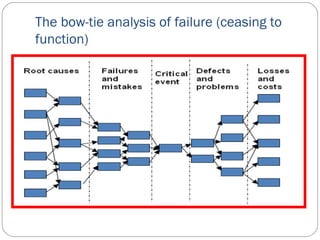
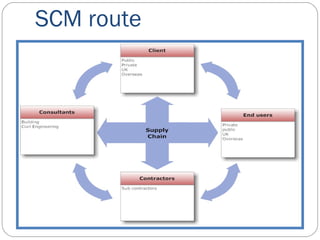
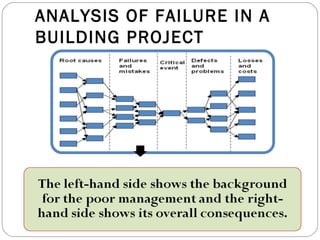
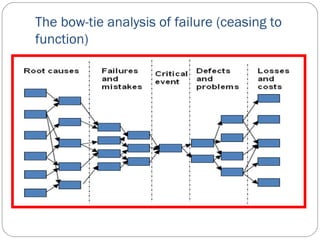
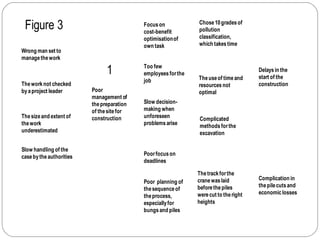
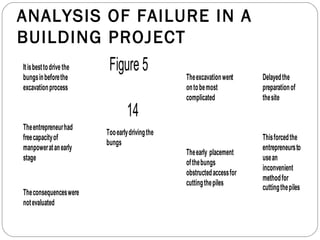
The document describes an analysis of failures in a building project using a bow-tie analysis method. The analysis identified several causes for delays and complications in the project, including poor site preparation management, an incompetent project manager, unexpected pollution in the ground requiring more classification, and improperly sequenced work like laying crane tracks before piles were cut. The bow-tie diagrams show how these initial failures and delays led to downstream effects throughout the construction process, compounding issues and further delays.