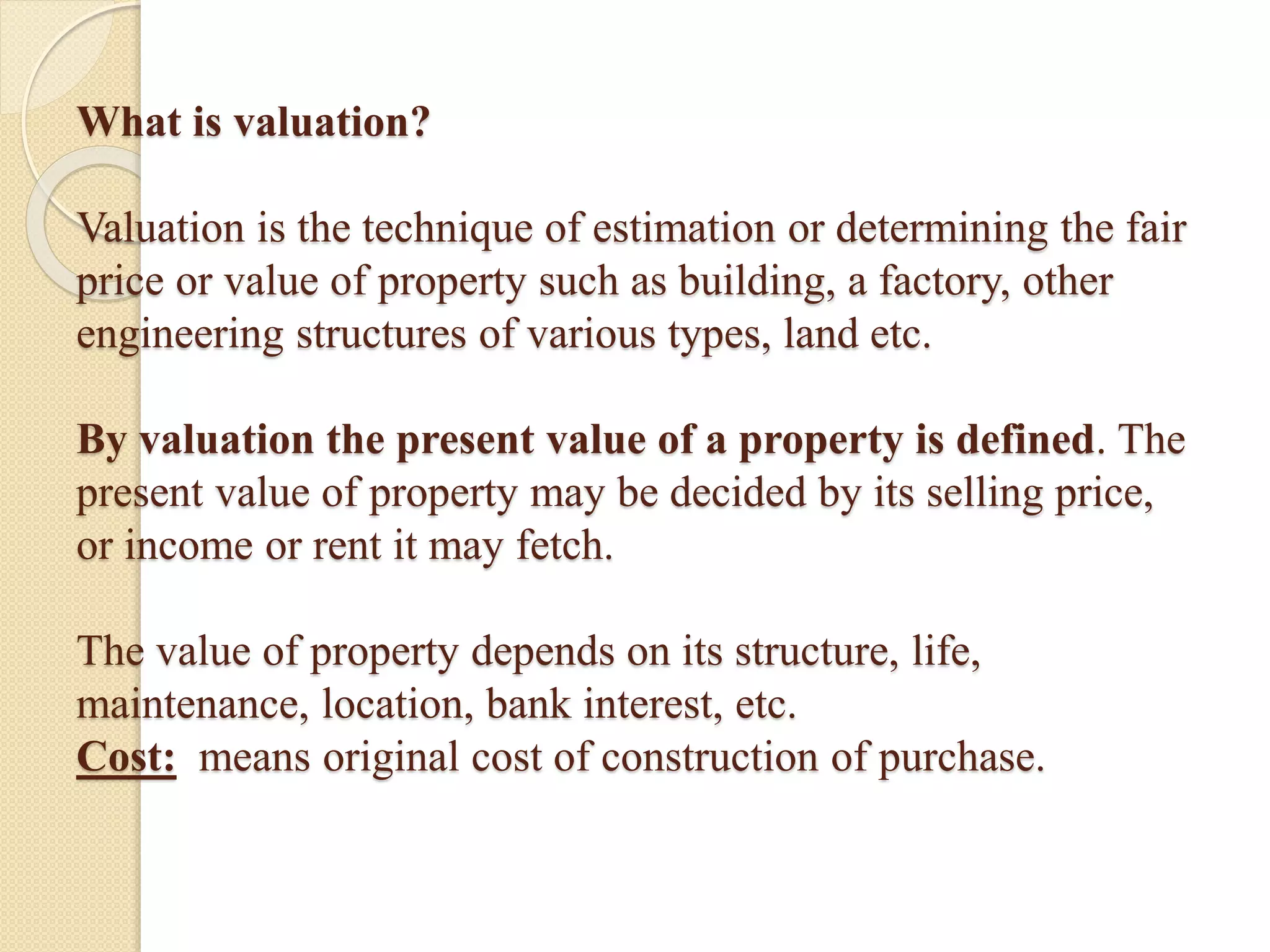
Valuation is determining the fair price or value of a property like buildings, land, etc. It considers factors like construction cost, age, maintenance, location, and income generated. Common valuation methods are rental method, comparing recent sale prices, and depreciation method. Rent is usually fixed as a percentage of valuation, with allowances for expenses like repairs, taxes, and management costs. Depreciation and obsolescence reduce value over time. Various terms related to valuation are defined, like gross income, net income, salvage value, sinking fund, and years purchase.














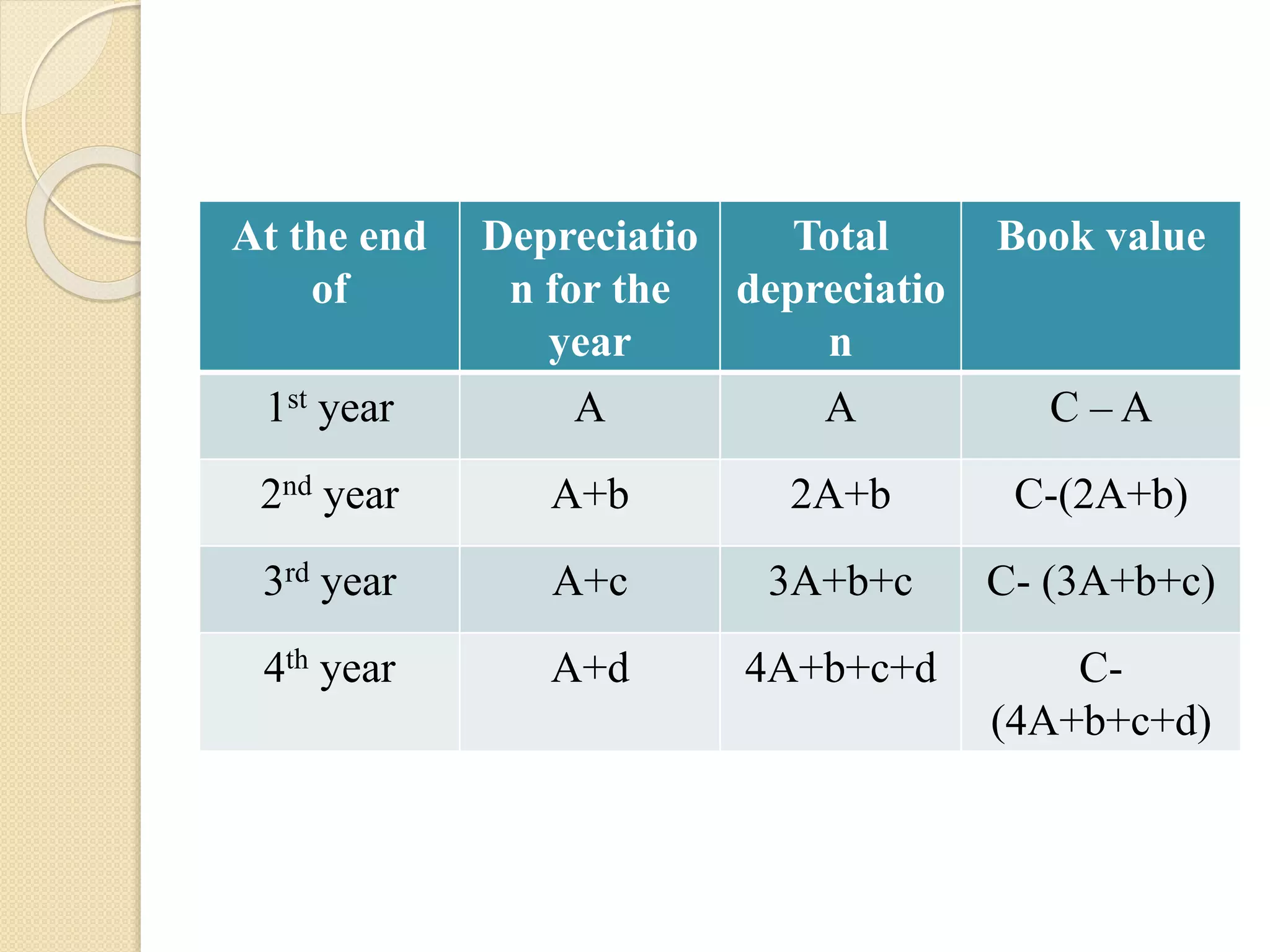









![6) Depreciation method of
valuation.
According to this method the depreciated value of the
property on the present day rates is calculated by the
formula:
D = P[(100 – rd)/100]n
Where,
D – depreciated value
P – cost at present market rate
rd – fixed percentage of depreciation (r stands for rate
and d for depreciation)
n – The number of years the building had been
constructed.
To find the total valuation of the property, the present value of
land, water supply, electric and sanitary fitting etc; should
be added to the above value.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/valuationunitv-170327073004/75/Valuation-part-of-Building-27-2048.jpg)












