The document describes how to prepare an acetate buffer using two methods: 1) Titration of acetic acid with sodium hydroxide and 2) Using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. For the titration method, acetic acid is titrated with sodium hydroxide and the pH is monitored to determine the pKa. For the Henderson-Hasselbalch method, the desired pH, pKa, and concentrations are used to calculate the ratios of acetic acid and sodium acetate needed to make a 0.1M buffer at pH 4.86. The solutions are then mixed and the final pH is checked to ensure it is as desired.


![Buffers
Mammalian tissues in the resting state have a pH
of about 7.4
In order to maintain the required pH in an invitro
biochemical experiment a buffer is always used
The pH of a buffer is given by Handerson-
Hasselbalch equation:
pH= pKa + log [A-]
[HA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffer-230131113807-0ed2c45b/85/BUFFER-ppt-3-320.jpg)
![Buffers
pKa= -log Ka
Ka is the dissociation constant of the acid
[A-] is the concentration of the base
[HA] is the concentration of the acid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffer-230131113807-0ed2c45b/85/BUFFER-ppt-4-320.jpg)

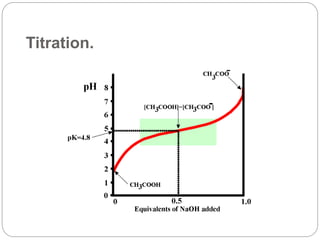
![Buffers
If acid (H+) is added, it will be buffered by another
reaction, this time using the salt (CH3COO-):
CH3COO- + H+ CH3COOH
The pH will not alter significantly because the
CH3COOH
formed is a weak acid
• Addition of more base increases A- and
decreases (HA) and this doesn’t alter the pH
much until [A-]>>>>[HA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffer-230131113807-0ed2c45b/85/BUFFER-ppt-6-320.jpg)
















![•
Use the pKa value nearest your desired pH and the ratio
will refer to the acid-base conjugate pair that
correspond
to that pKa.
HH Equation:
pH = pKa + log ([Base]/[Acid])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffer-230131113807-0ed2c45b/85/BUFFER-ppt-24-320.jpg)
![ The desired molarity of the buffer is the sum of
[Acid] + [Base].
For a 1 M buffer, [Base] + [Acid] = 1 and
[Base] = 1 - [Acid]
By substituting this into the ratio equation, from
step 2, you get:
==> [Acid]= value
b. Substitute for [Base]and Solve for [Acid]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffer-230131113807-0ed2c45b/85/BUFFER-ppt-25-320.jpg)
![c. Solve for [Base]
Using the equation: [Base] = 1 - [Acid], you can
calculate that:
[Base] = value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffer-230131113807-0ed2c45b/85/BUFFER-ppt-26-320.jpg)
