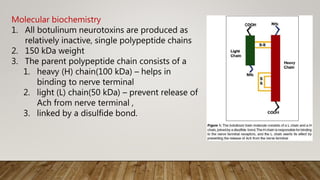
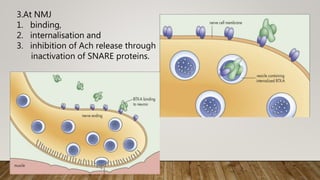
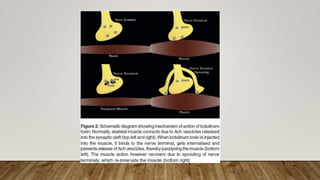
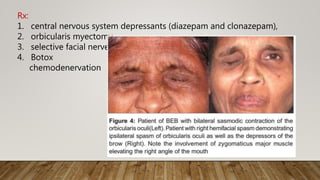
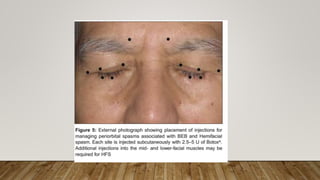
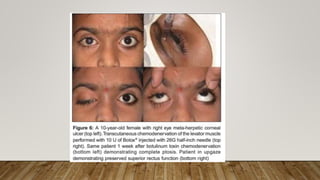
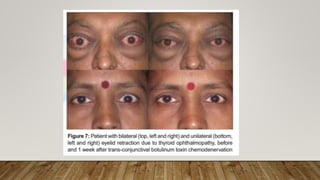
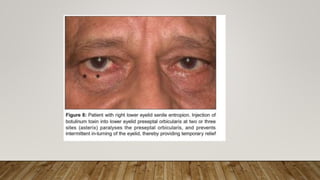
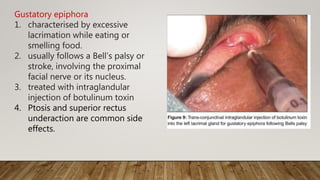
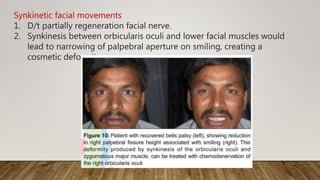
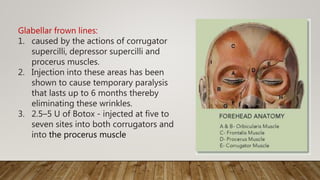
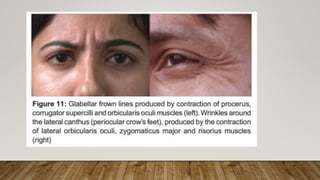
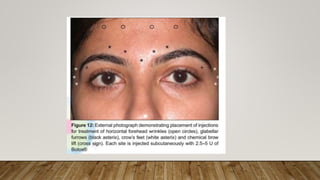
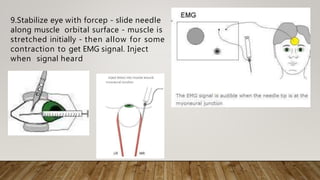
Botulinum toxin in ophthalmology
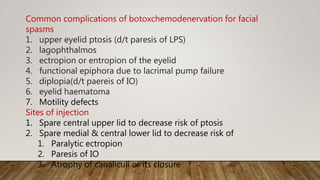
Botulinum toxin type A (Botox) is produced by Clostridium botulinum and effectively treats strabismus and other eye muscle disorders by temporarily paralyzing muscles. It works by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction, preventing nerve impulses from being transmitted to muscles. Common uses in ophthalmology include treating blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm, dry eye, and strabismus, with the effects lasting 2-4 months before the muscle function returns.