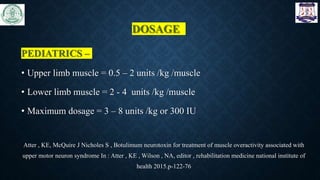
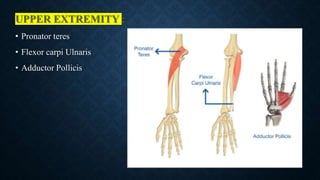
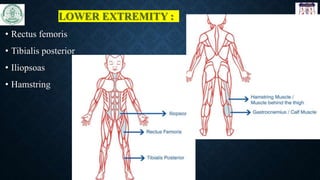
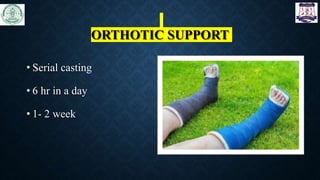
The document discusses the use of botulinum toxin (Botox) for treating spasticity, particularly in children with cerebral palsy, outlining its mechanism of action, dosage, injection technique, and effects. It highlights the indications for treatment, potential side effects, and the importance of post-injection physiotherapy management to improve muscle function and joint mobility. The document concludes with references to relevant literature on the combined benefits of Botox and rehabilitation programs.