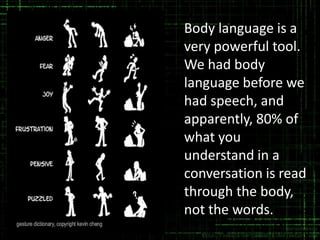
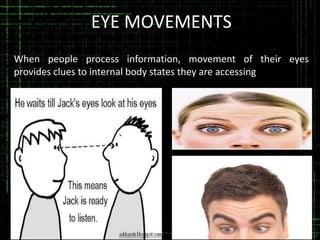
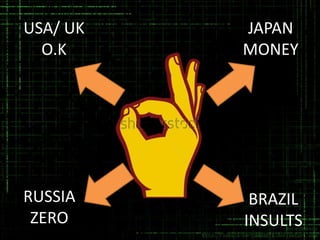
This document discusses the importance of body language in the workplace. It provides advice to managers on how understanding body language can help in different work settings and across cultures. The authors have extensive experience in management consulting and training. The document outlines positive and negative body language signals and how body language is used in various work contexts like meetings, presentations, interviews and negotiations. It emphasizes that body language is a powerful communication tool that can often convey true meaning beyond words. Cultural differences in common gestures are also addressed.