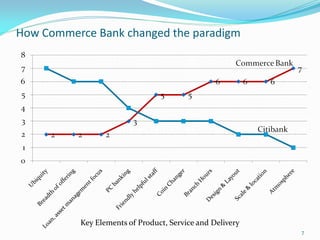
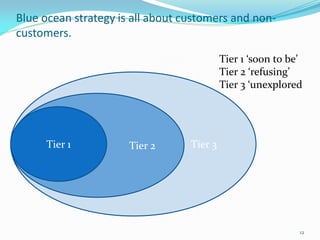
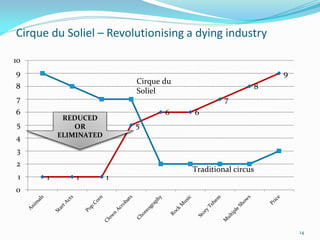
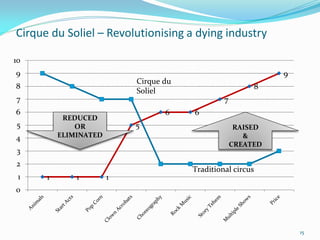
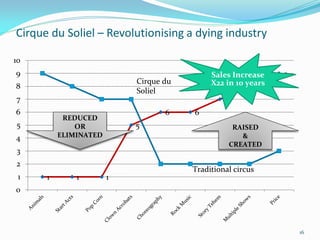
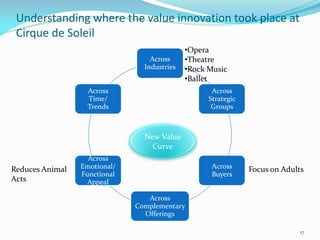
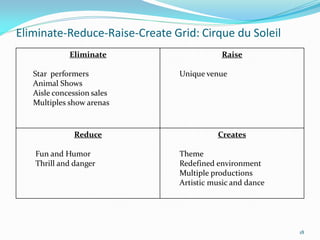
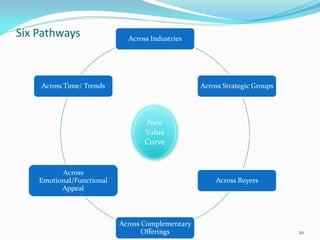
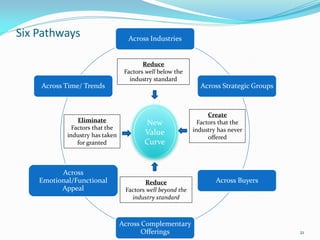
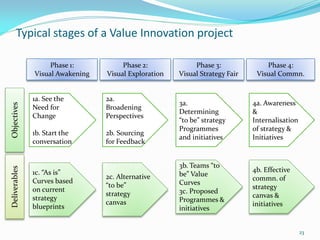
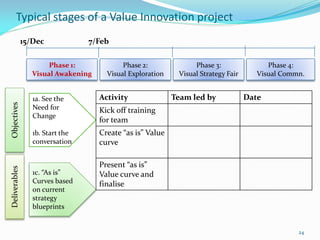
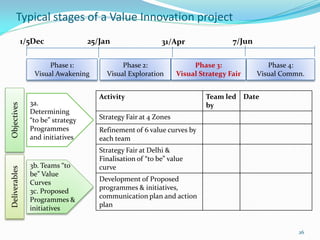
Between 1975 and 1995, 60% of Fortune 500 companies were replaced, showing that markets and competitors are constantly changing. Industries and companies continuously rise and fall, so there are no permanently dominant players. Strategic moves that continuously create new value for customers allow companies to stay at the top. Value innovation aims to substantially raise customer value rather than focus only on new technologies. By identifying and serving overall customer needs through an unparalleled value proposition, companies can dominate their market.