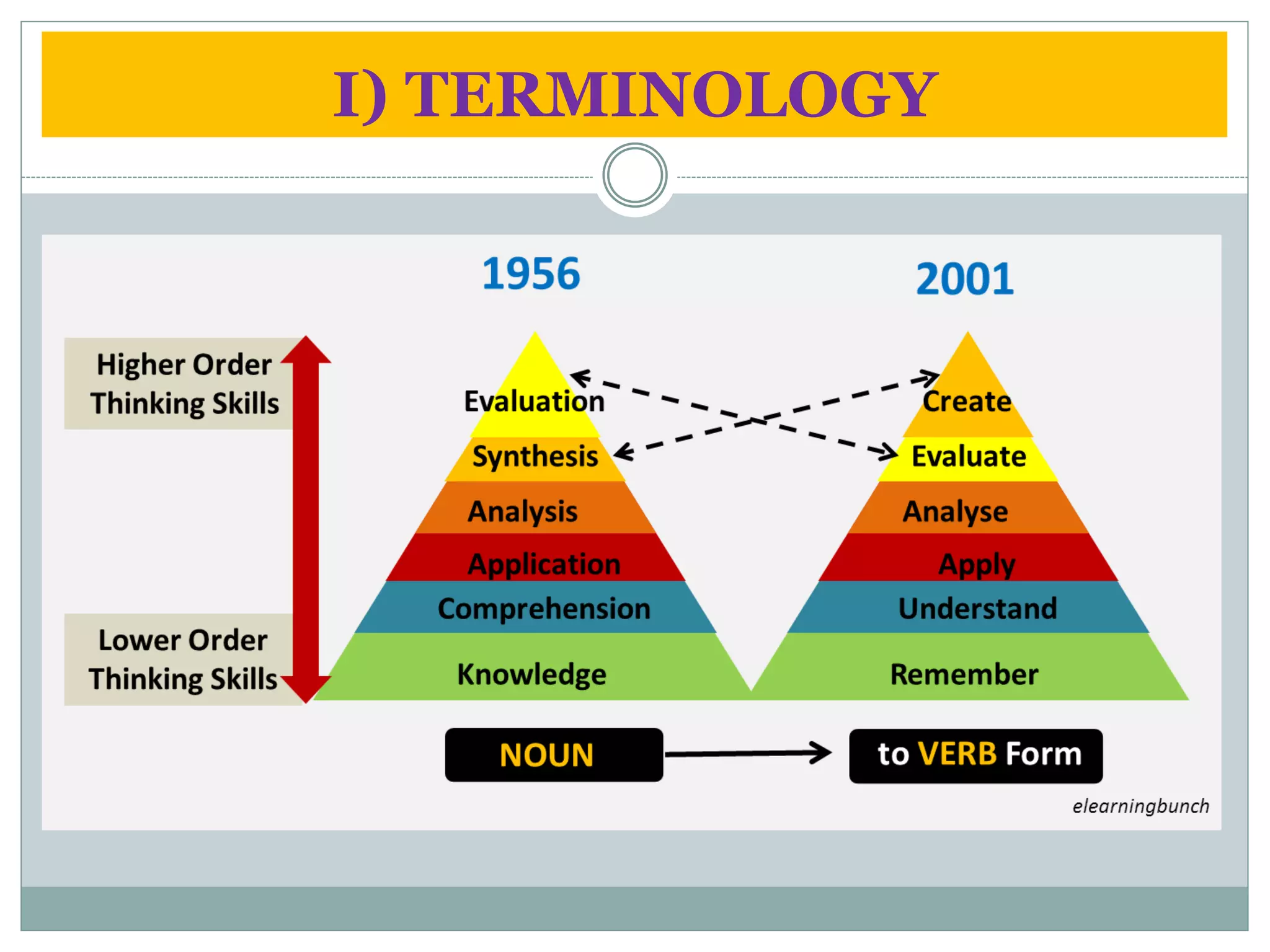
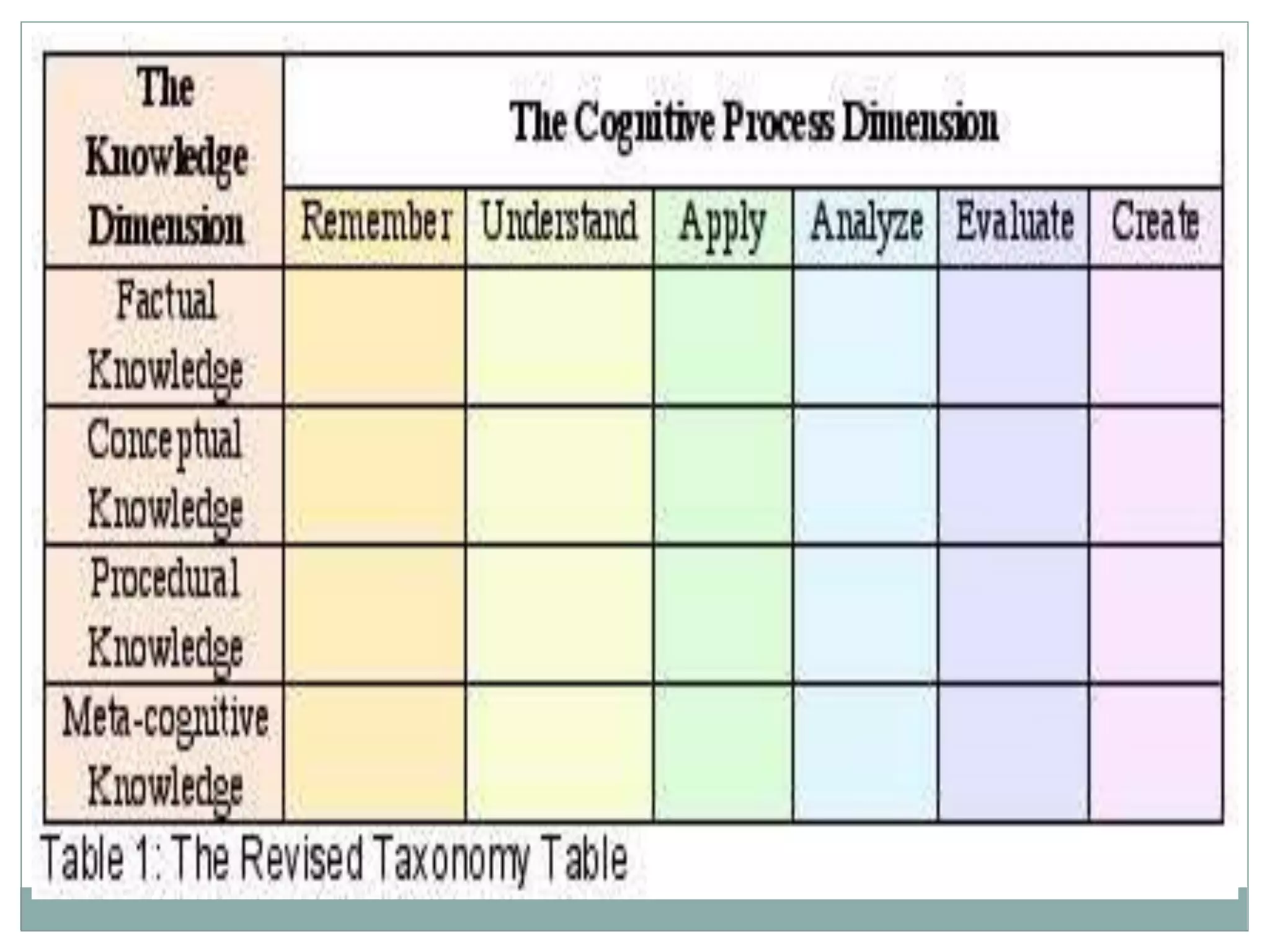
This document compares and contrasts Bloom's original taxonomy of learning with the revised version by Anderson and Krathwohl. The revised taxonomy has three main differences: terminology, structure, and emphasis. In terms of terminology, it uses different words than Bloom's original version. Its structure is two-dimensional rather than one-dimensional, and it reorders some levels. Finally, the revised taxonomy places more emphasis on describing subcategories of learning and being applicable to higher levels of education.