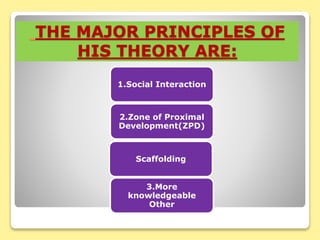
The document discusses Lev Vygotsky's constructivist theory of cognitive development, which asserts that social interaction and learning from more knowledgeable others contributes to children's cognitive development. Key aspects of Vygotsky's theory include the zone of proximal development, scaffolding provided by more knowledgeable others to help children learn, and that social learning precedes individual development.