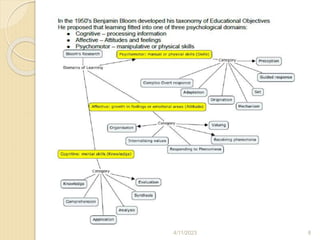
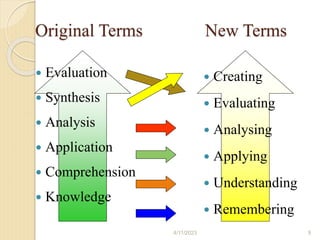
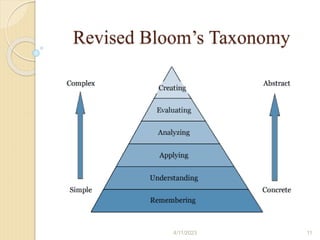
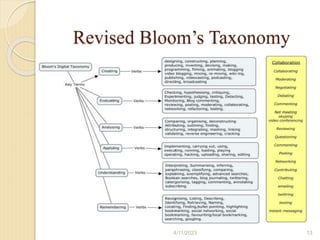
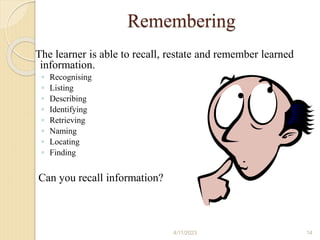
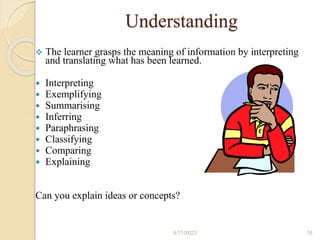
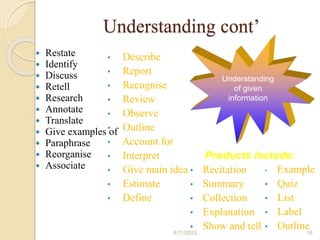
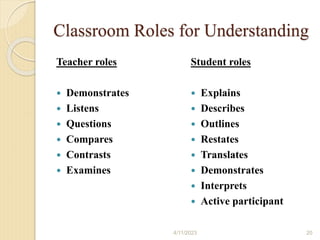
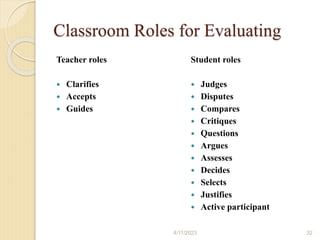
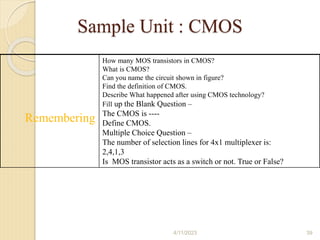
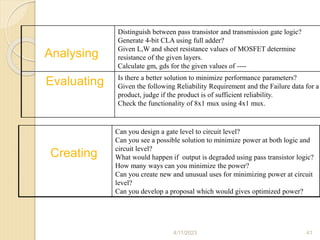
Bloom's Taxonomy is a framework for categorizing levels of thinking skills that was created by educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom in 1956. It divides thinking skills into six categories moving from basic recall or recognition of facts through increasingly more complex and abstract mental levels of comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. The document provides details on the origins and development of Bloom's Taxonomy, including its domains of cognitive, affective, and psychomotor skills. It also explains the categories within each domain and provides classroom examples of activities and assessments for each thinking skill level.