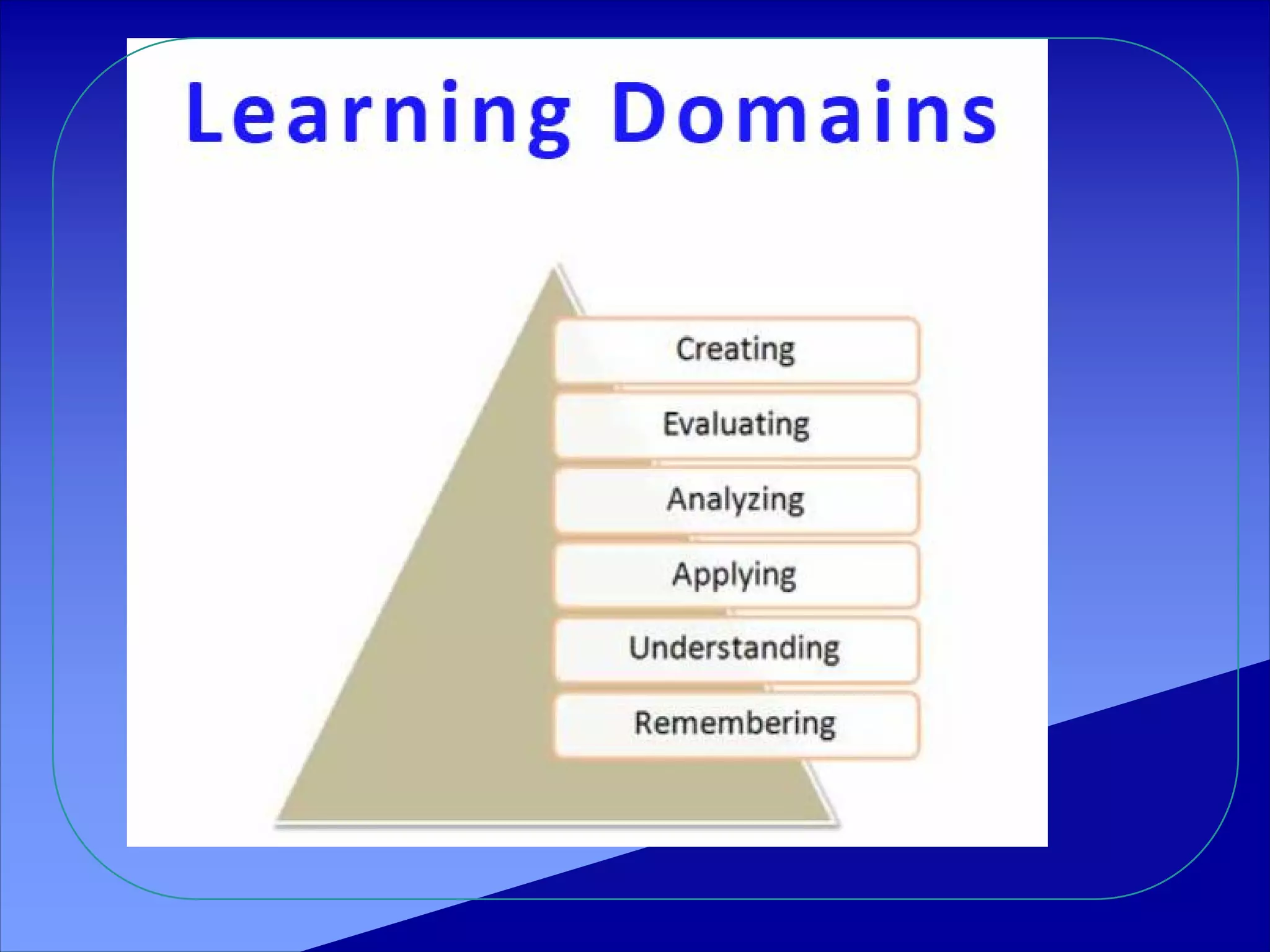
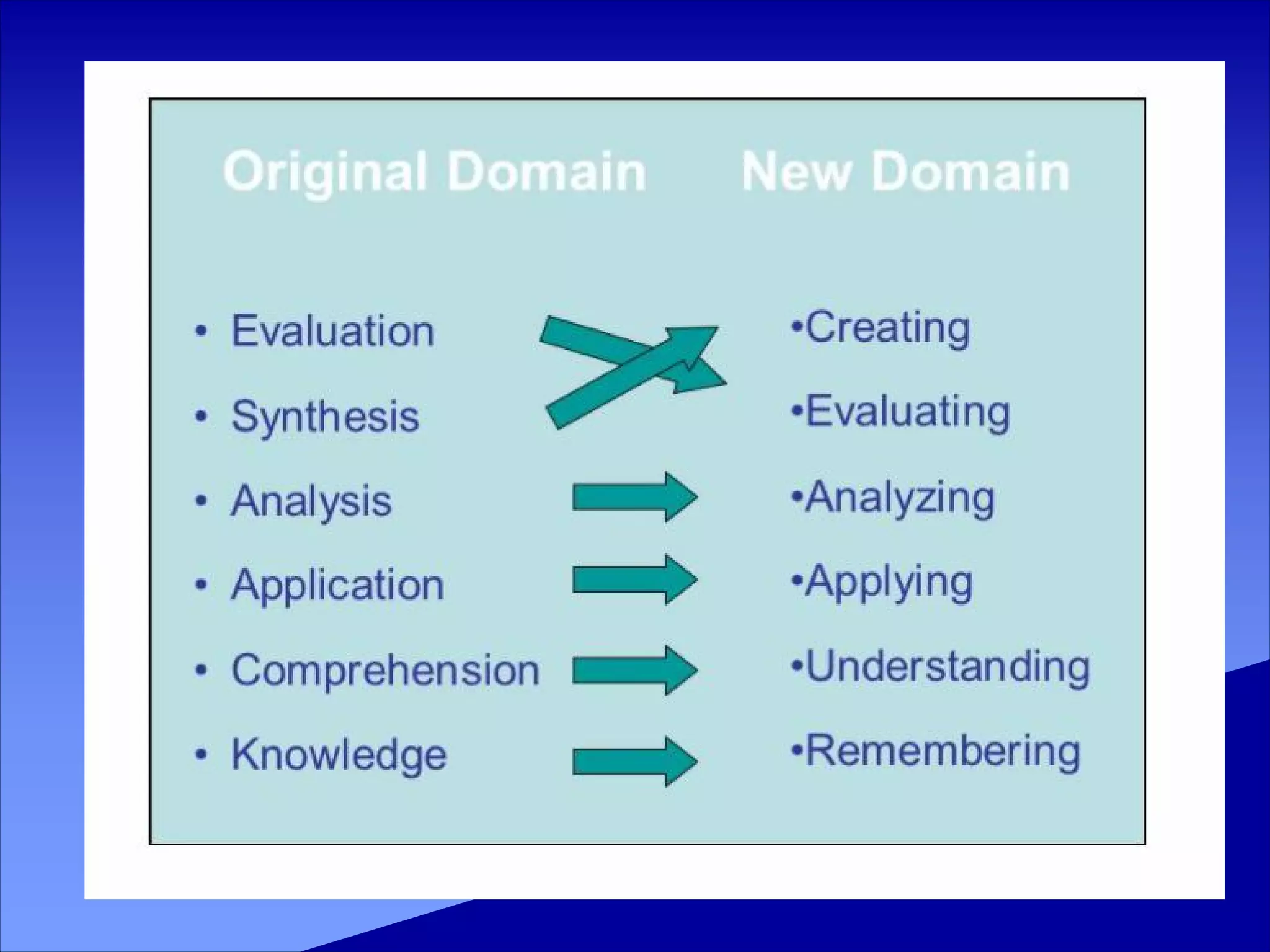
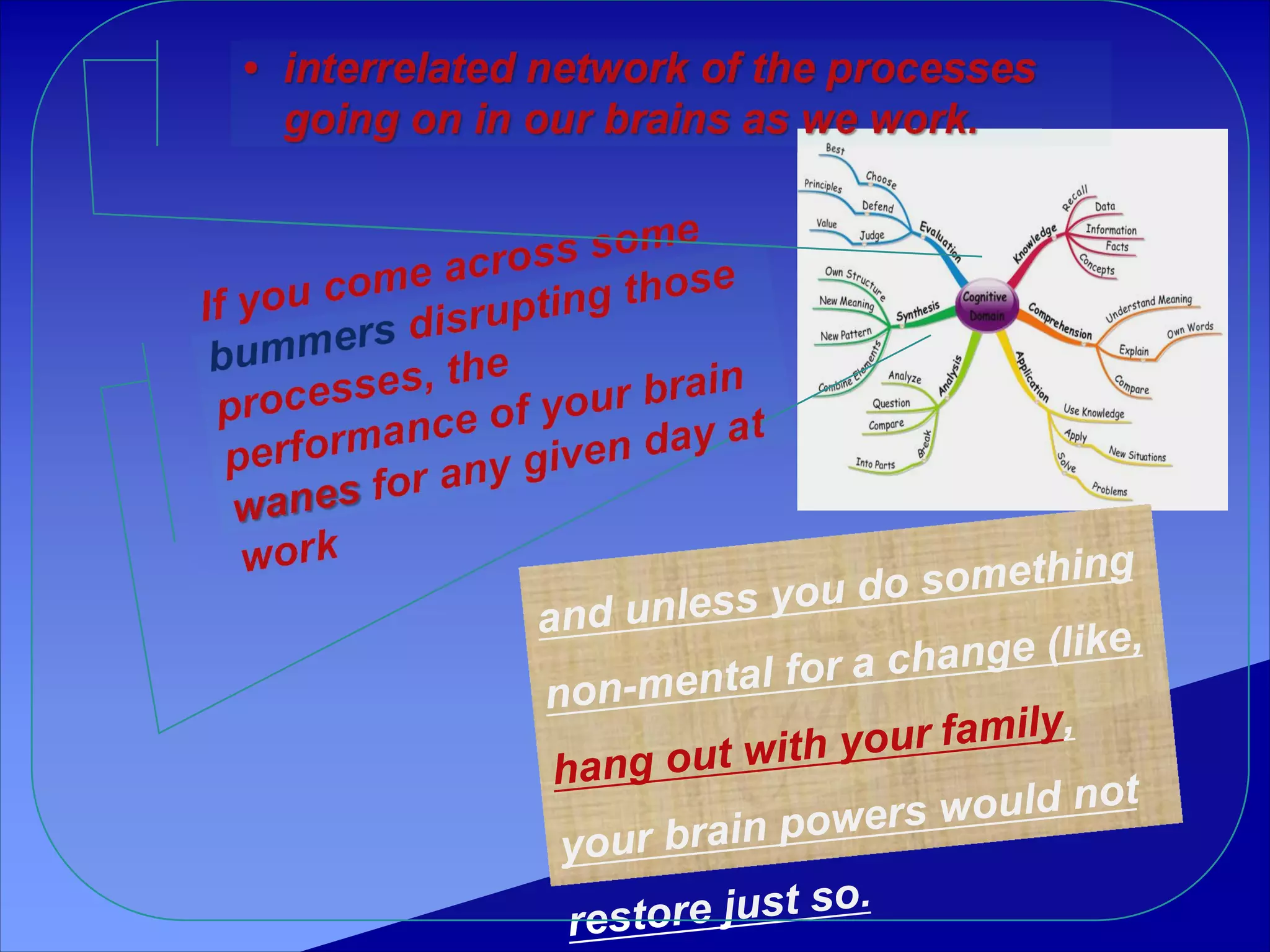
Bloom's taxonomy categorizes levels of learning into six major categories from simplest to most complex: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. Each category provides examples of verbs and learning activities. The categories move from recalling facts to creating new structures or solutions. The taxonomy provides a framework for setting learning objectives and assessing learning outcomes.