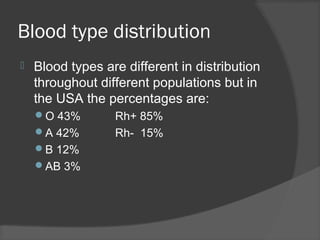
This document discusses blood typing and composition. It explains that blood is made up of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The two major blood type systems are A, B, AB, and O, and Rh+ and Rh-. Blood types vary in distribution between populations, with O+ being the most common in the USA at 36.55% of the population. Blood typing is determined by antigens on red blood cells and the presence or absence of agglutination reactions between blood cells and specific anti-A and anti-B antibodies.