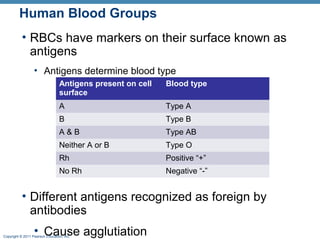
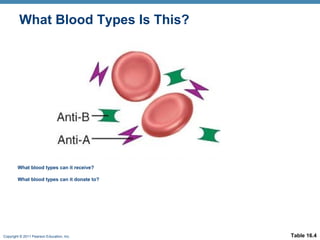
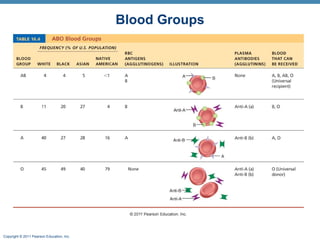
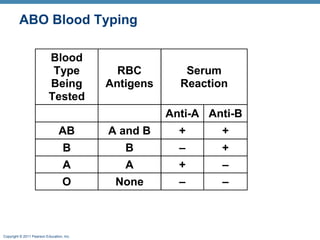
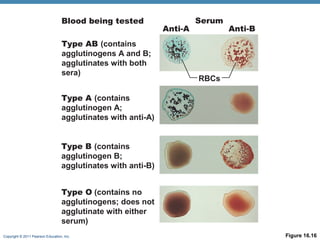
This document discusses human blood groups and types. It explains that blood types are determined by the presence or absence of antigens on red blood cells, specifically the A, B, and Rh antigens. People have one of four main blood types - A, B, AB, or O - depending on which antigens are present. It also describes how blood typing works by testing a blood sample against various antibodies to detect agglutination. The Rh factor further divides blood types into positive or negative based on the presence of the Rh antigen. Understanding blood groups is important for blood transfusions and preventing diseases like erythroblastosis fetalis.