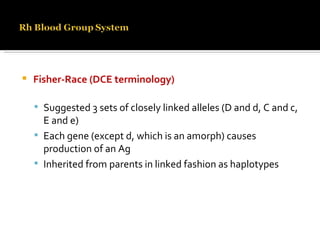
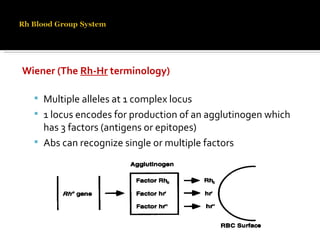
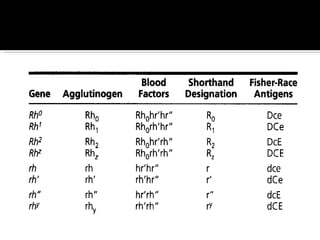
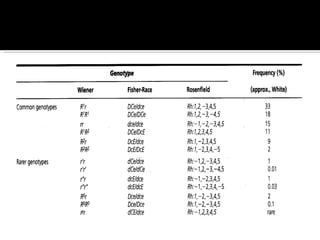
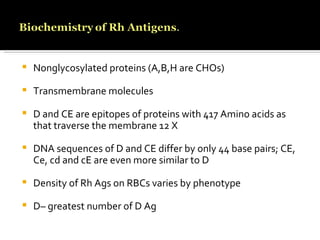
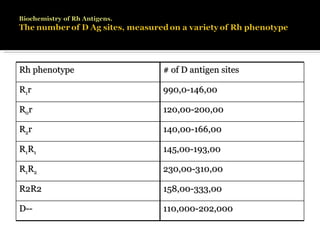
The Rh blood group system involves a complex of antigens encoded by genes at a single locus. There are several terminologies used to describe the Rh system based on proposed genetic mechanisms or presence/absence of antigens. The most widely used terminology describes antigens as products of alleles at the locus (e.g. D, C, E, c, e) and their combinations in haplotypes determine phenotypes. Anti-D is the most immunogenic antibody and causes hemolytic disease of the newborn when a Rh-negative mother is sensitized during pregnancy with a Rh-positive baby. Testing for Rh involves detection of D and other antigens through agglutination assays.