1) Human blood contains red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, an iron-rich protein that gives blood its red color.
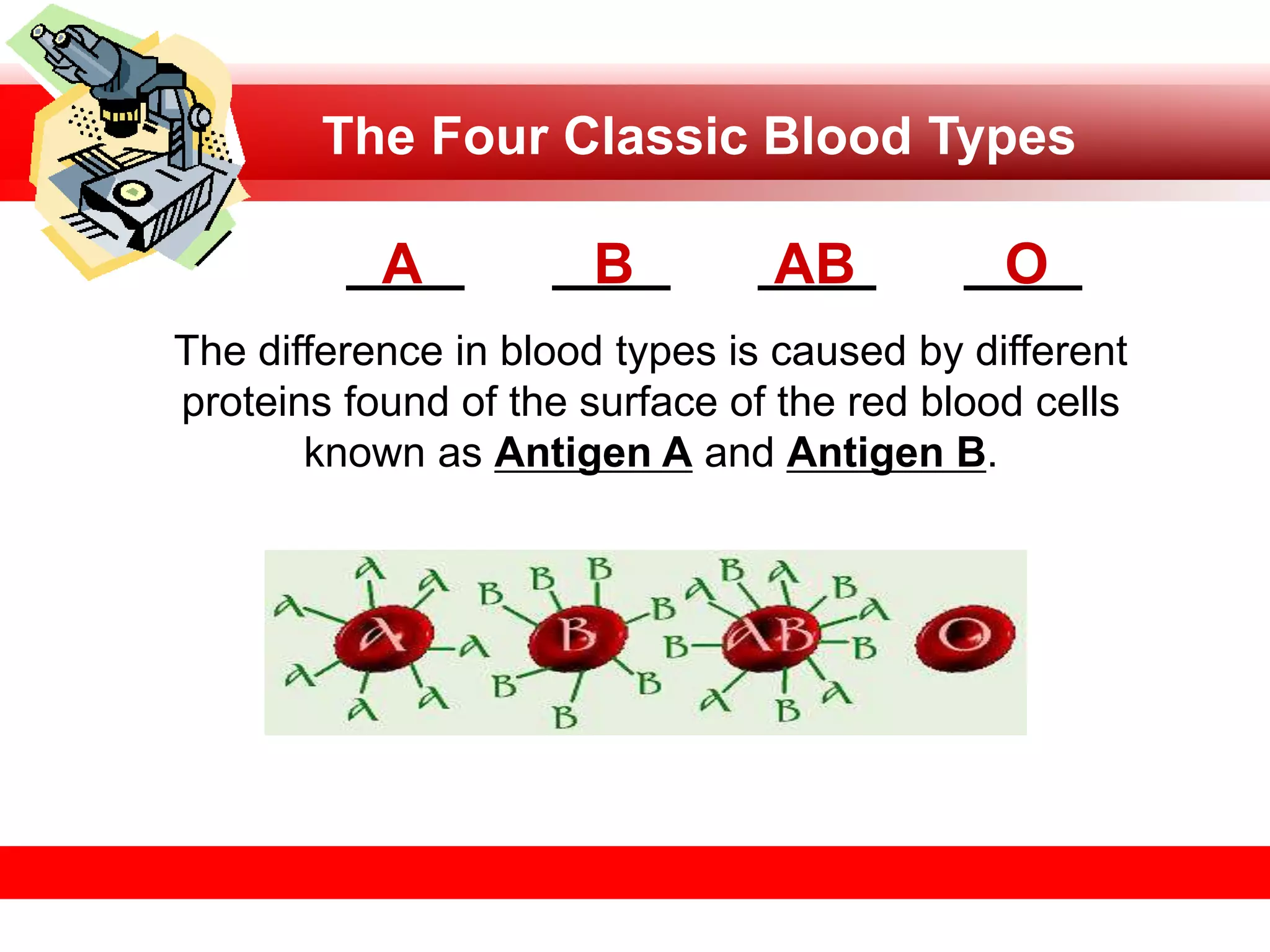
2) Dr. Karl Landsteiner discovered the four main blood types (A, B, AB, and O) in 1900 while observing incompatible blood transfusions. The differences in blood types are due to proteins called antigens on the surface of red blood cells.
3) A person's blood type is determined by the presence or absence of antigens A and B. Those with type O blood lack both antigens, while types A, B, and AB have antigen A, B, or both, respectively.