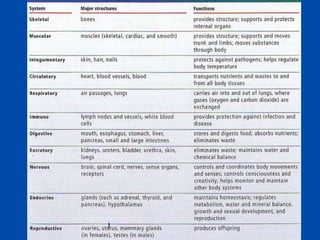
1. Homeostasis is the maintenance and regulation of the internal environment within the body through feedback mechanisms that keep conditions within a narrow range.
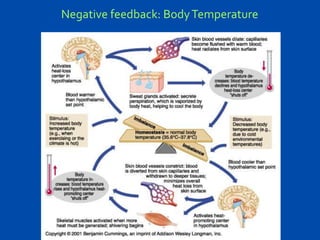
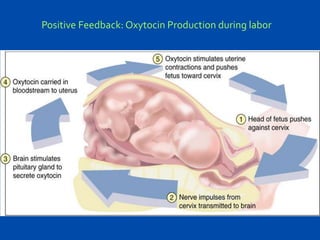
2. Feedback mechanisms can be negative, which counteracts changes away from normal conditions, or positive, which increases the rate of change away from normal. Negative feedback is more common in the body.
3. When homeostasis is disrupted in the short term by things like exercise or illness, the body uses feedback mechanisms to return conditions to normal; however, long term disruptions like diabetes can cause lasting damage throughout the body if not regulated.