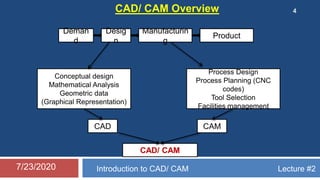
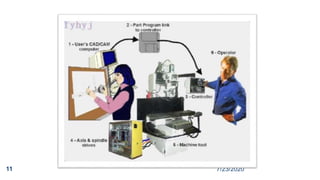
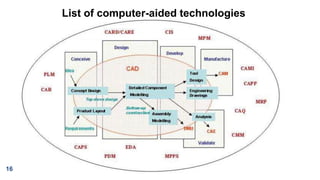
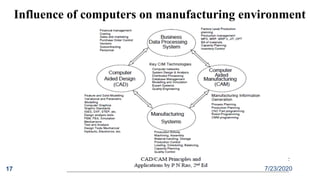
The document discusses computer aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM). It begins by introducing CAD as using computers to assist in design processes like defining geometry, analysis, and optimization. CAM uses computers to plan, manage, and control manufacturing operations. The benefits of CAD/CAM over manual drafting include increased accuracy, easier modification, storage, and sharing of designs. CAD systems require hardware like workstations, computers, and output devices. Graphics software is used for modeling, drafting, analysis and optimization. Computers have influenced manufacturing by allowing for computer monitoring and control of processes as well as manufacturing support applications.