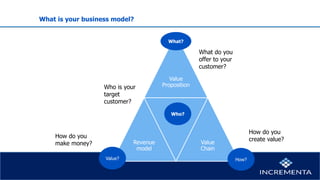
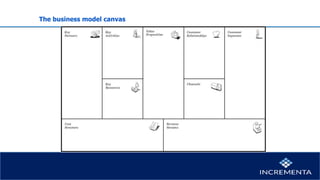
This document discusses business models and their key components. It defines a business model as the story that explains how an enterprise works by answering fundamental questions about who the customer is, what value is provided to the customer, and how the business generates revenue. It then discusses the key components of a business model canvas including value proposition, customer segments, channels, customer relationships, key activities, key resources, key partners, revenue streams, and cost structure. It emphasizes understanding these components to create a tangible business model and addresses considering external forces like competition and substitutes that may impact the business model.