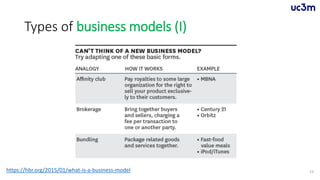
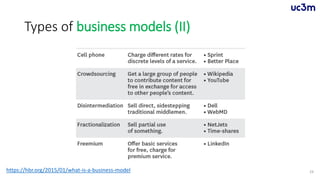
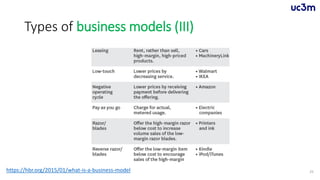
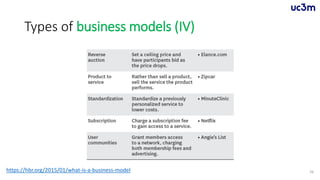
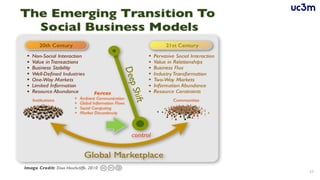
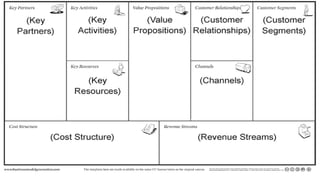
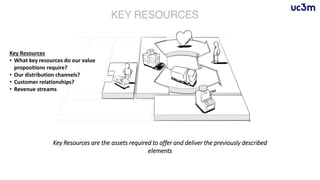
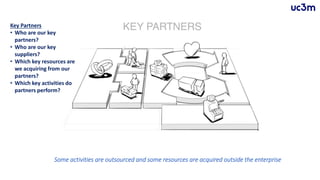
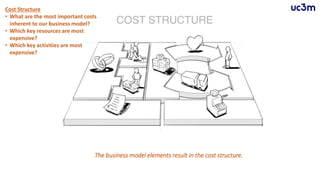
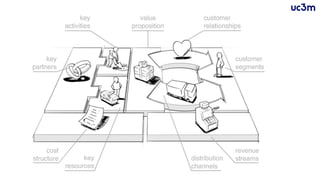
The document provides guidelines for preparing a startup pitch, emphasizing the importance of storytelling, time management, and clarity in presenting core business elements like the product, market opportunity, and revenue model. It outlines a recommended structure for a pitch, including comprehensive elements such as business problems, market expectations, competition analysis, and financial viability. Additionally, it lists critical questions to address during the pitch related to the team, product, competition, marketing strategy, and financial projections.