This document summarizes different types of biotic interactions in an ecosystem:
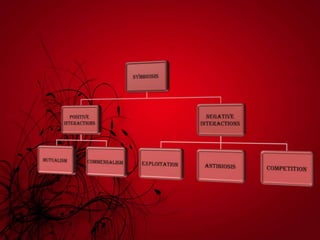
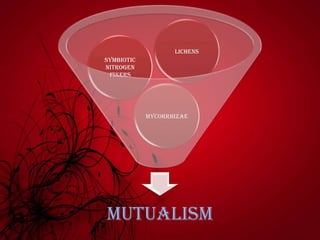
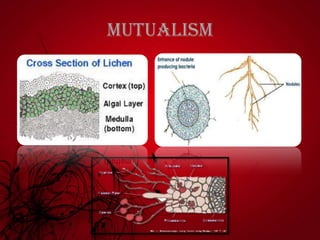
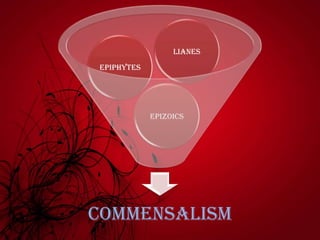
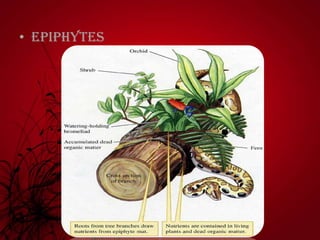
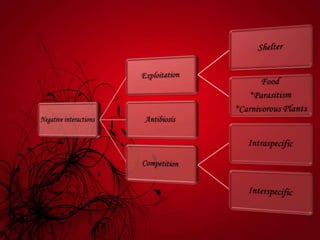
Mutualism includes relationships like mycorrhizal fungi and plant roots, nitrogen-fixing bacteria and legumes, and lichens. Commensalism includes epiphytic plants, lianas that climb trees, and epizoic algae on animal fur. Negative interactions include exploitation like parasites on plants and animals and carnivorous plants. Antibiosis refers to inhibition or death of one organism by another through metabolic toxins. Competition occurs when organisms seek inadequate resources and can be intraspecific between members of a species or interspecific between different species.