Embed presentation








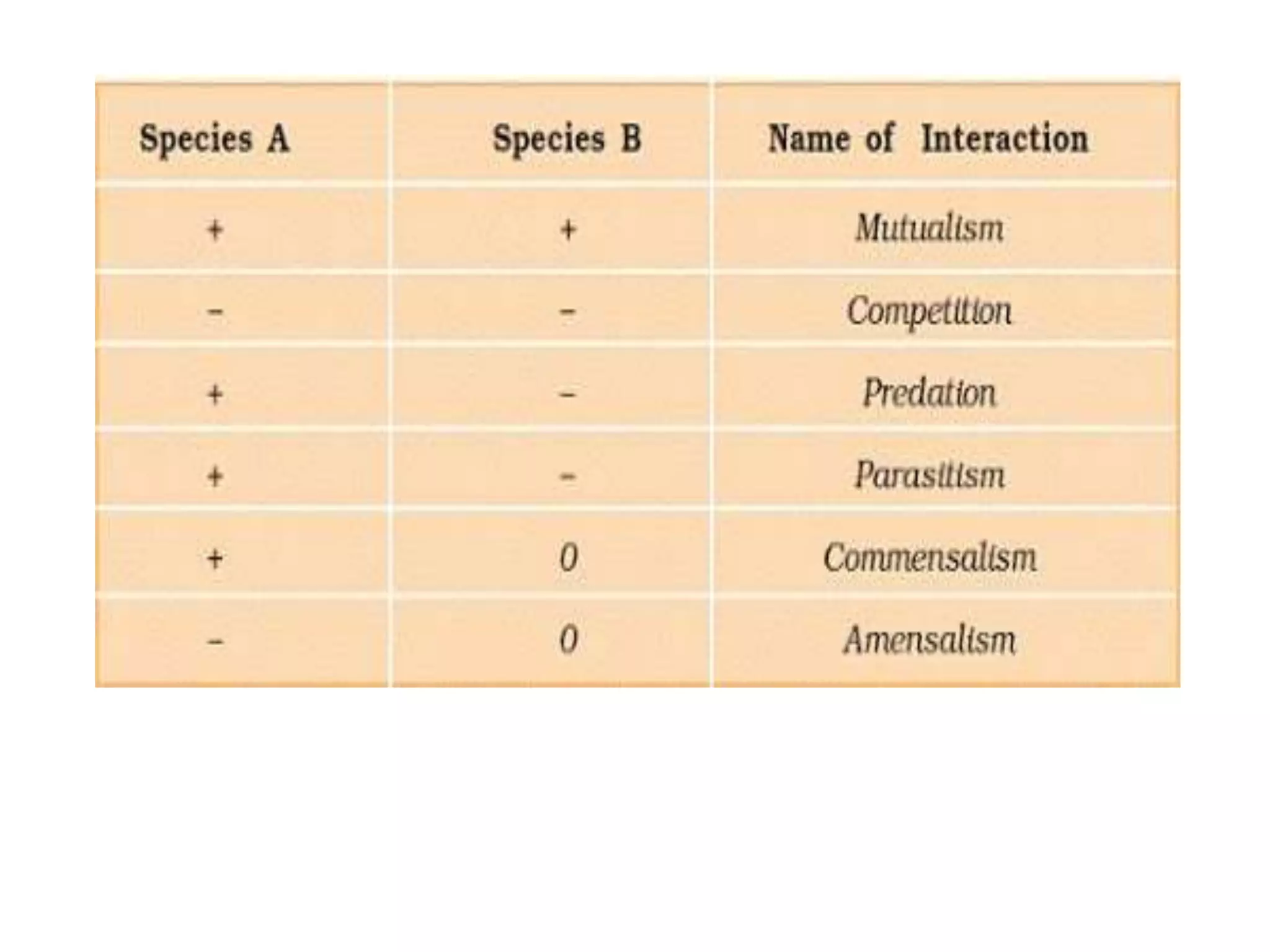











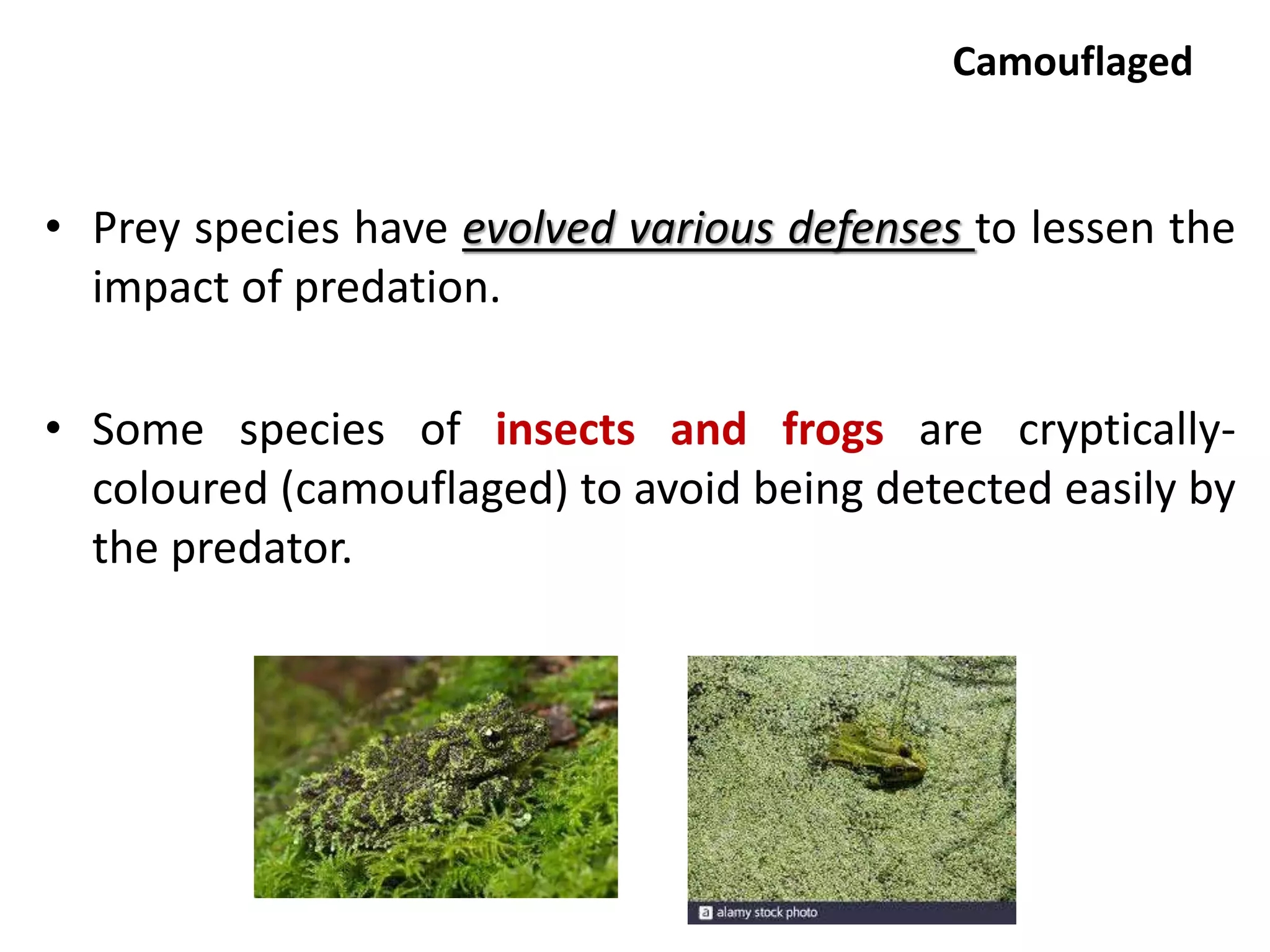




















The document discusses life history variation and population interactions, emphasizing the importance of predation and competition in ecosystems. It explains how species adapt their reproductive strategies and defenses against predators, and how interspecific interactions can affect community dynamics. Additionally, it highlights Gause's competitive exclusion principle and resource partitioning as mechanisms that enable species coexistence despite competition for resources.







































