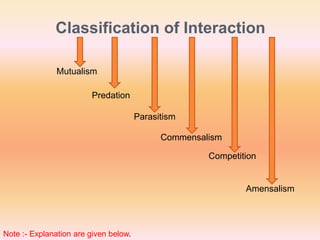
The document describes different types of interspecific interactions:
1. Mutualism benefits both species, like the relationship between fungi and plants in mycorrhizae.
2. Predation benefits the predator species while harming the prey species, such as insects flushed out by cattle being eaten by egrets.
3. Parasitism benefits the parasite while harming the host, for example tapeworms living inside the intestines of another organism.
4. Commensalism benefits one species without affecting the other, like orchids growing on trees.
5. Competition harms both species as they contend for the same limited resources, as seen with flamingoes and fish competing for z