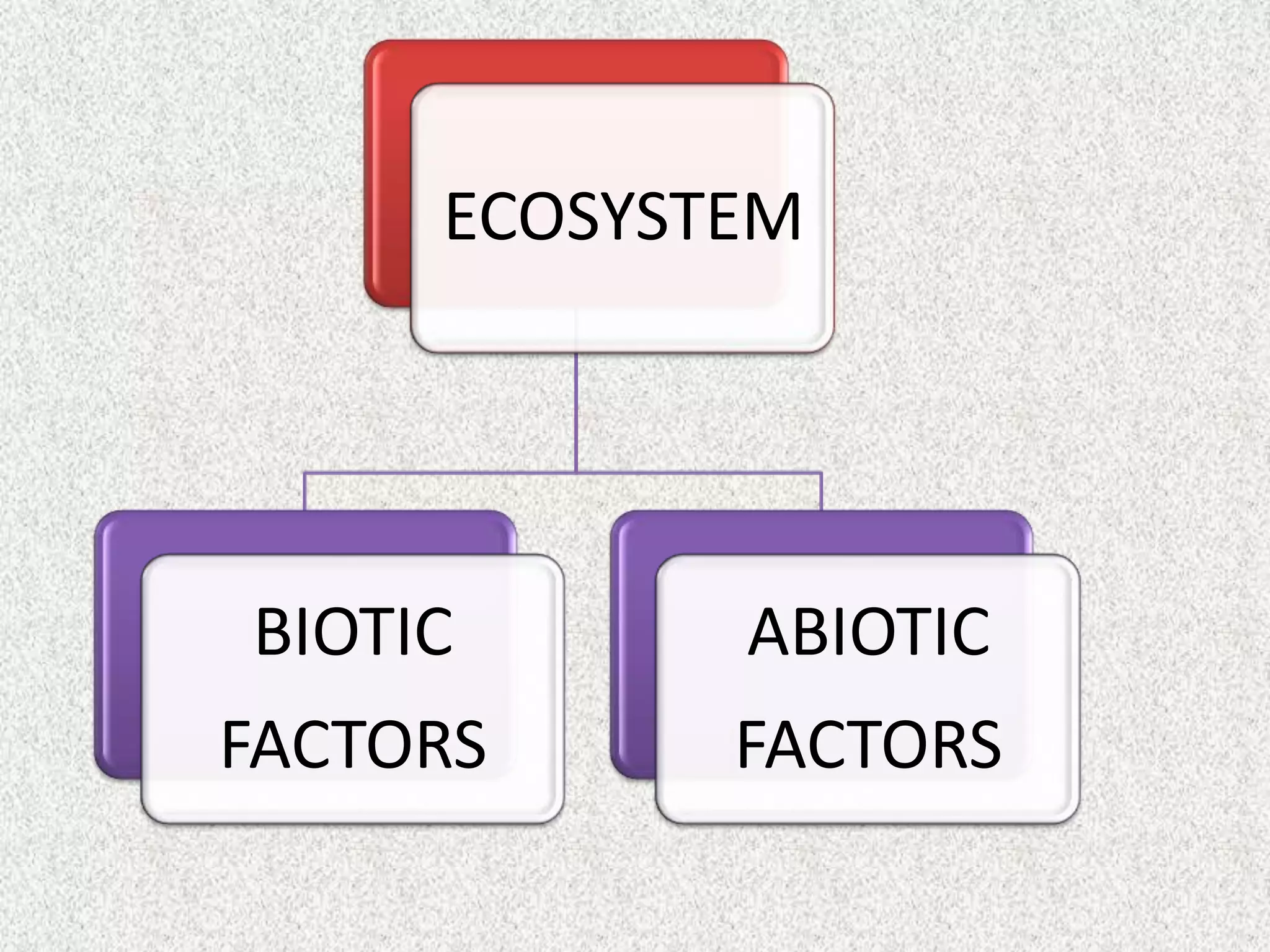
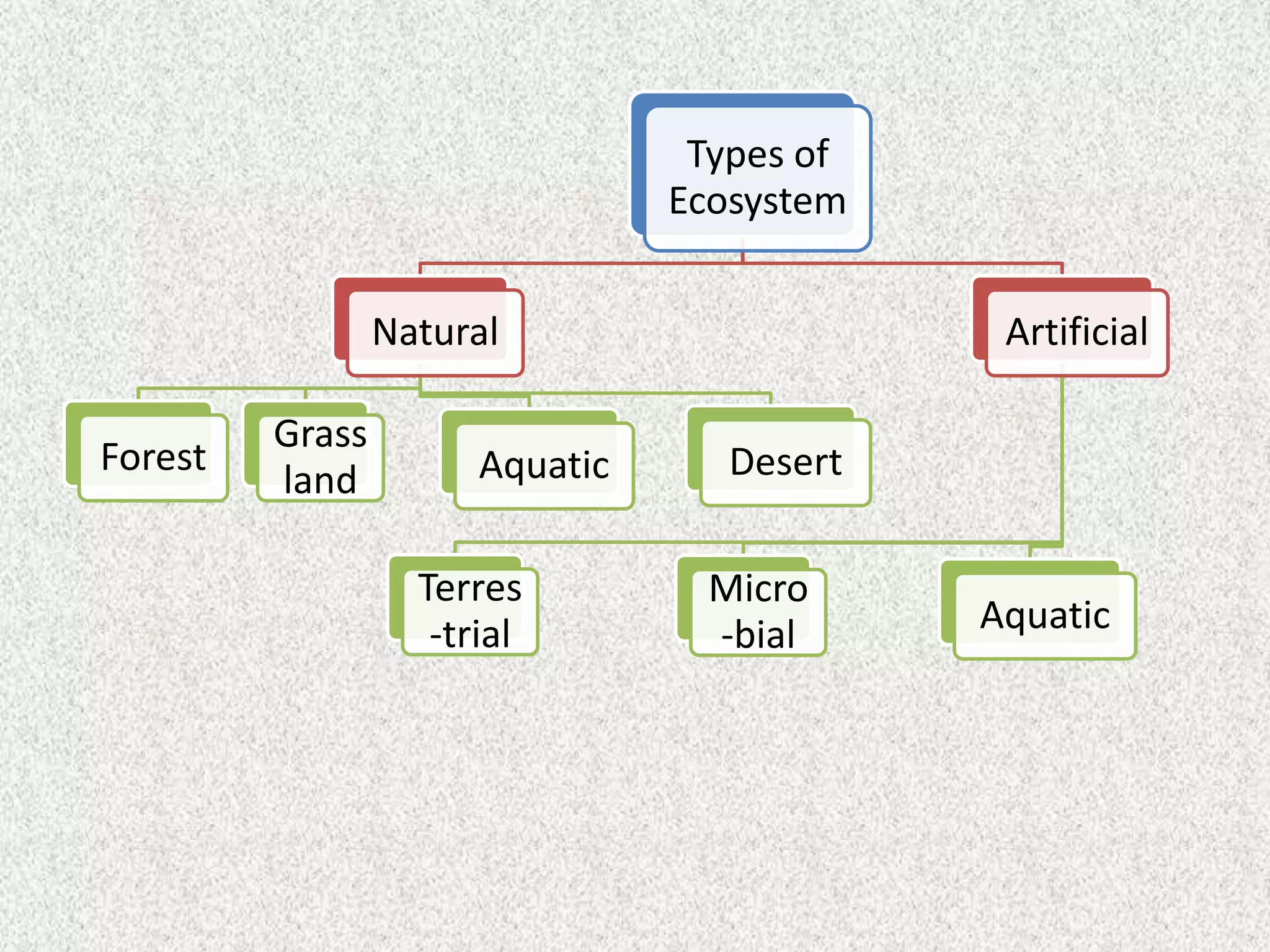
There are four major types of ecosystems: grassland, forest, aquatic, and desert. Each ecosystem is defined by its biotic and abiotic factors. Biotic factors include living organisms, while abiotic factors include non-living elements like air, soil, water, and sunlight. Ecosystems are classified based on these factors and provide important functions such as purifying water, recycling nutrients, and supporting biodiversity.