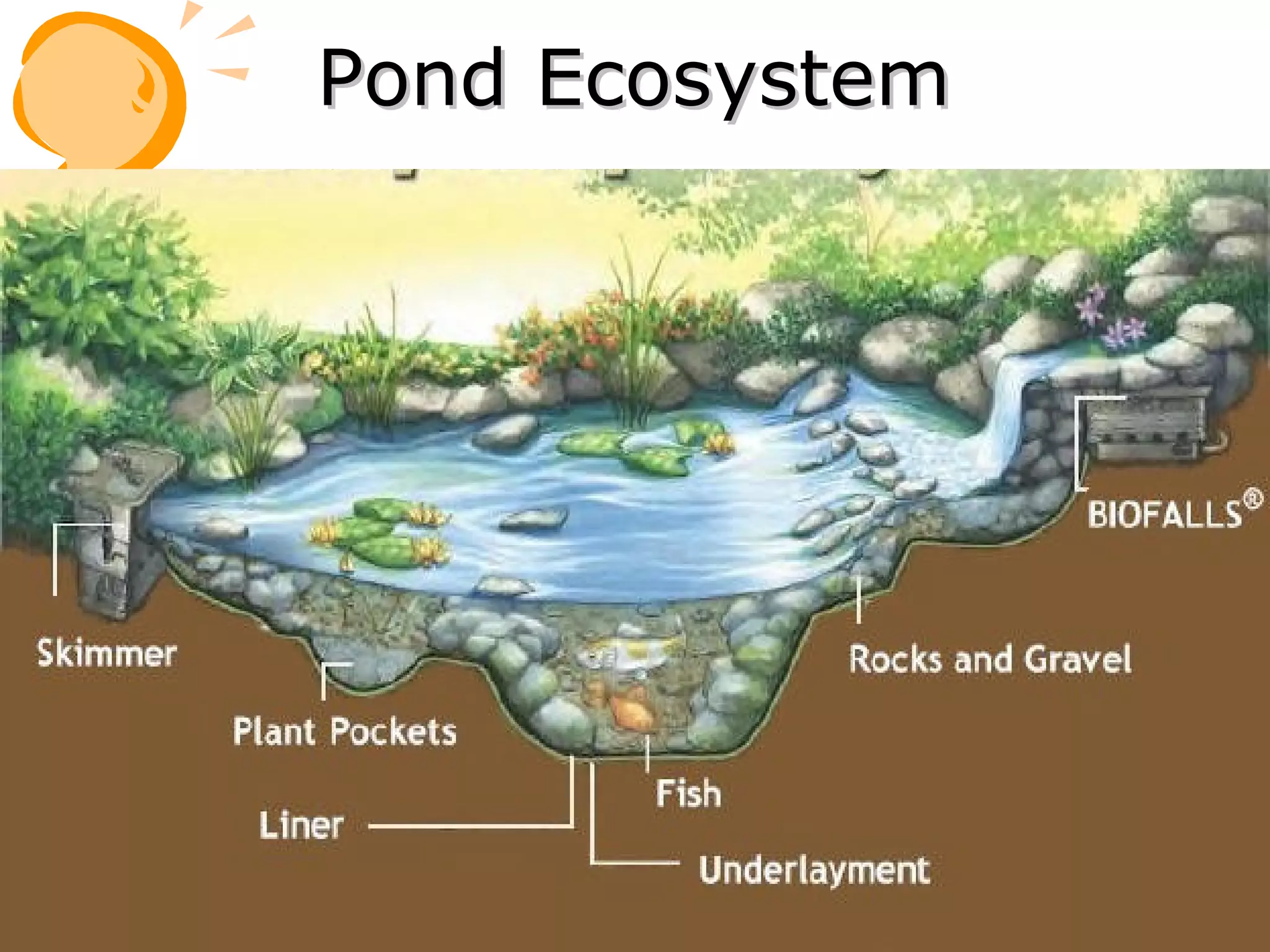
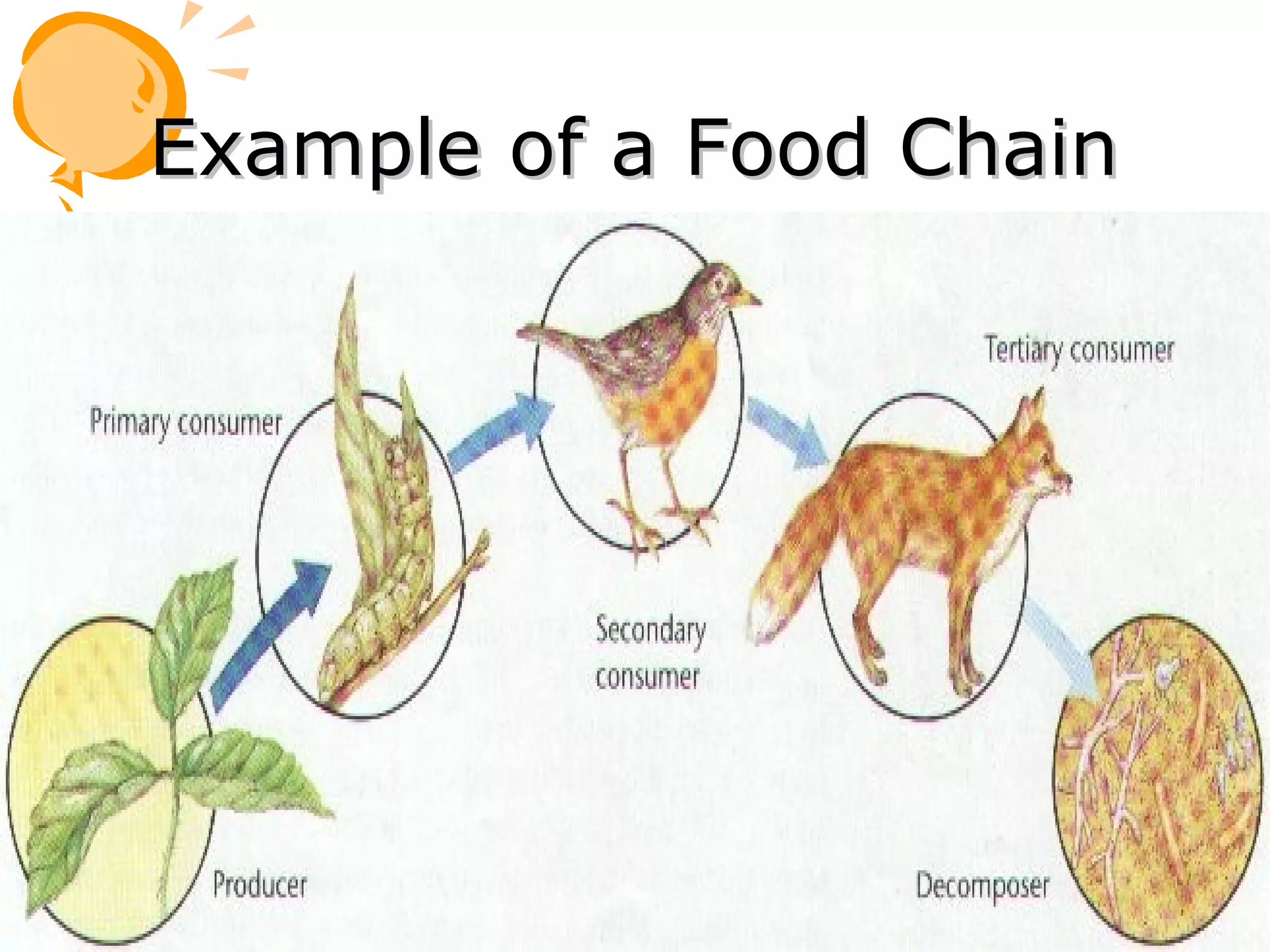
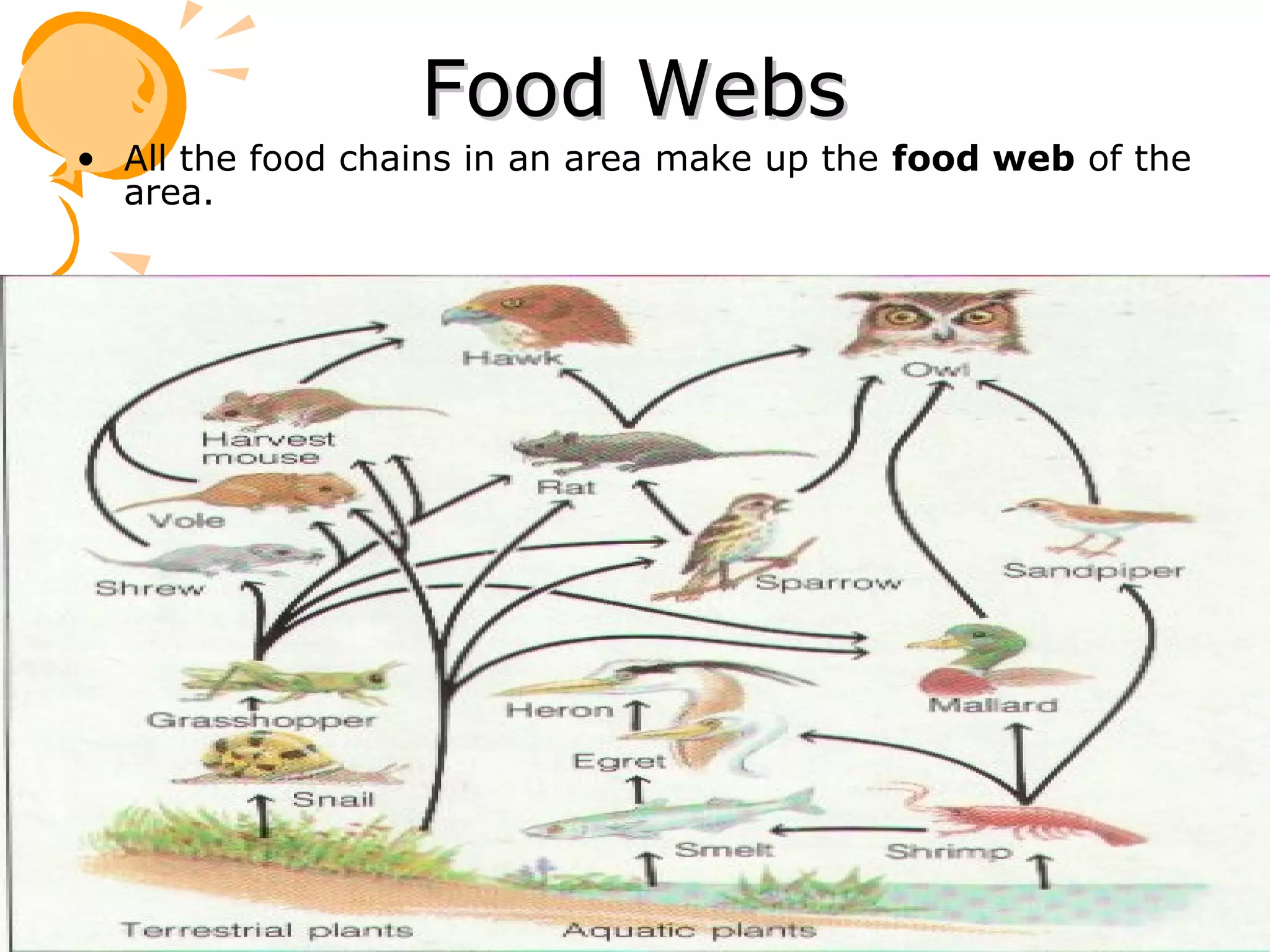
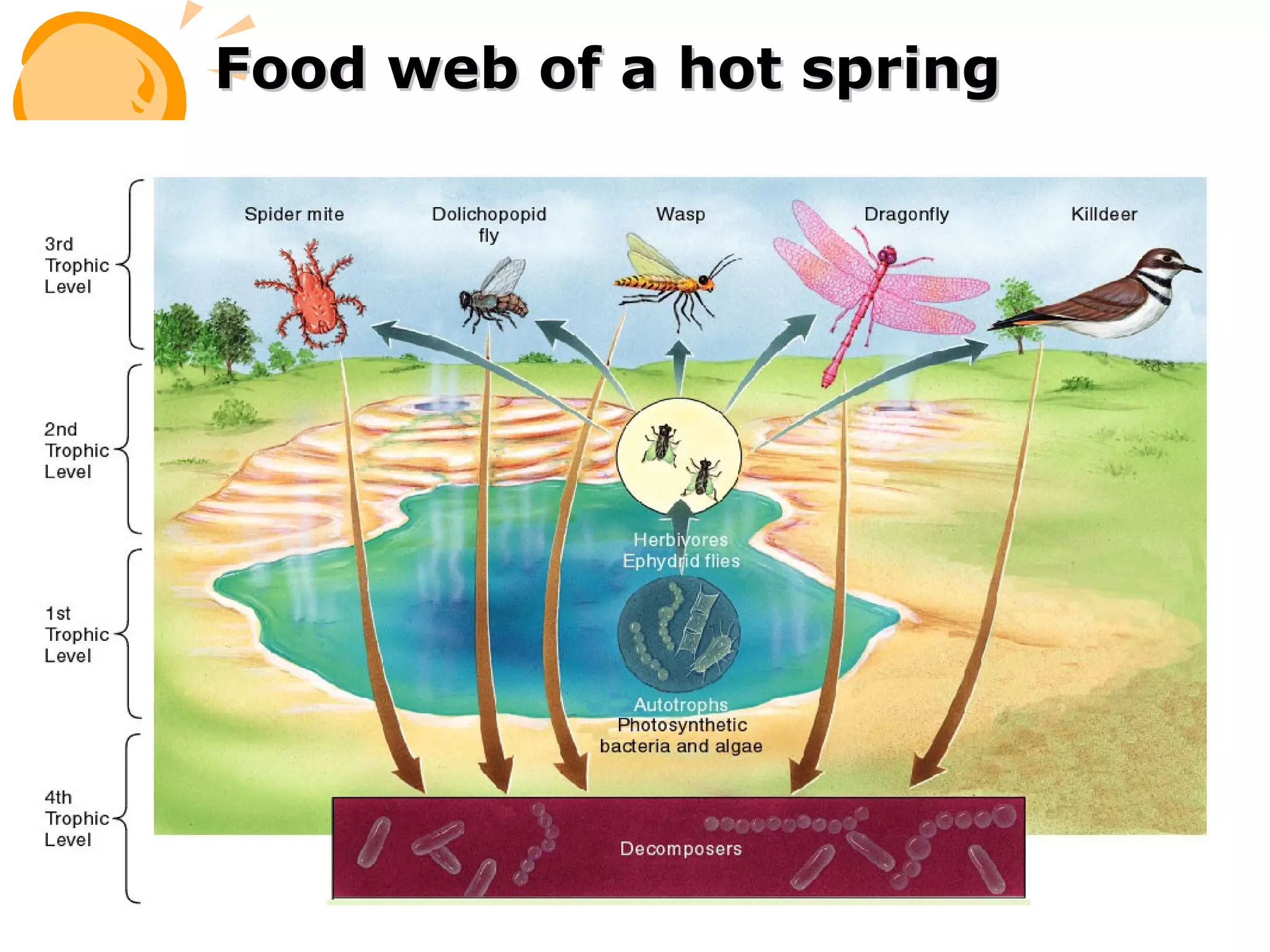
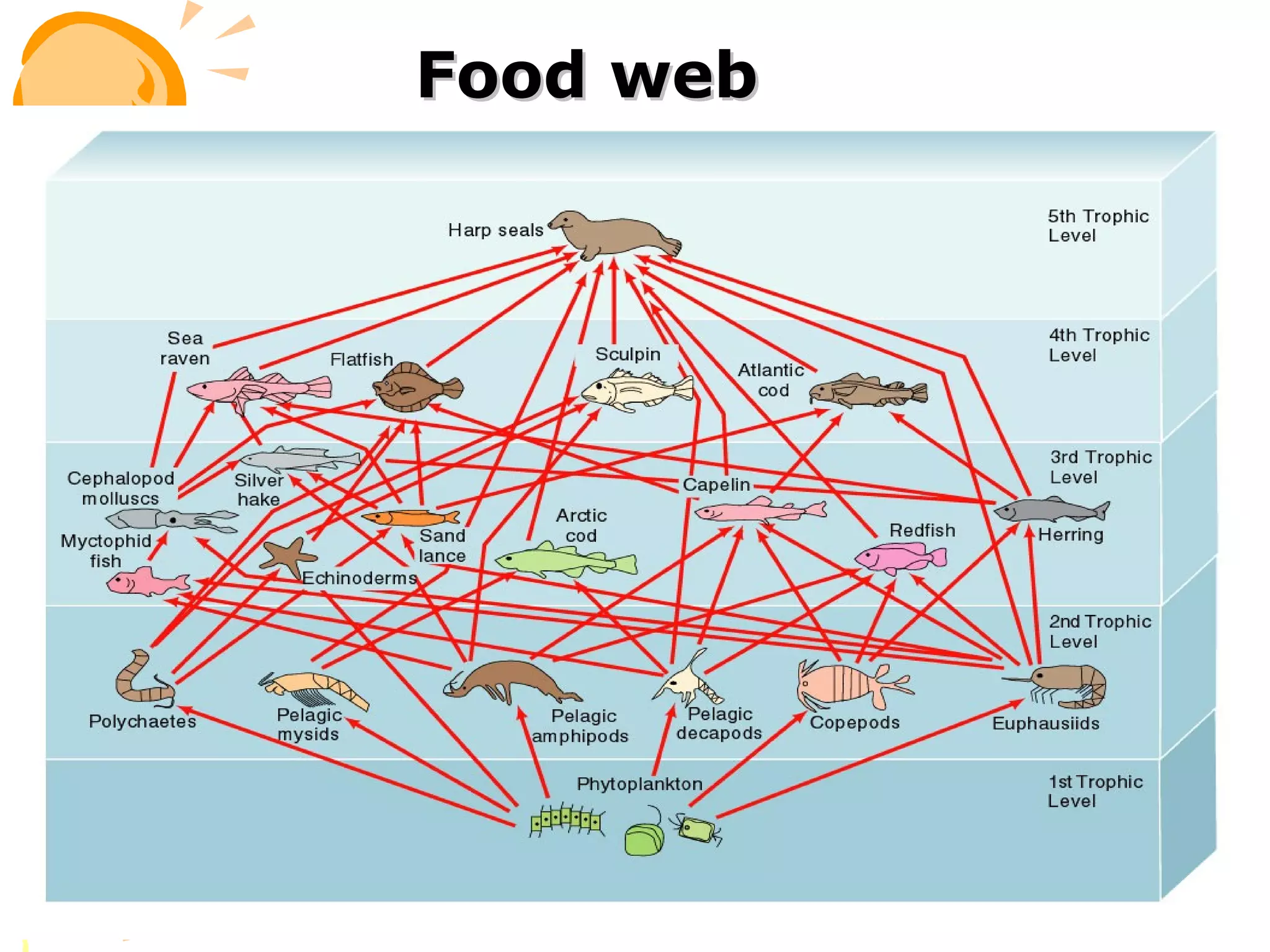
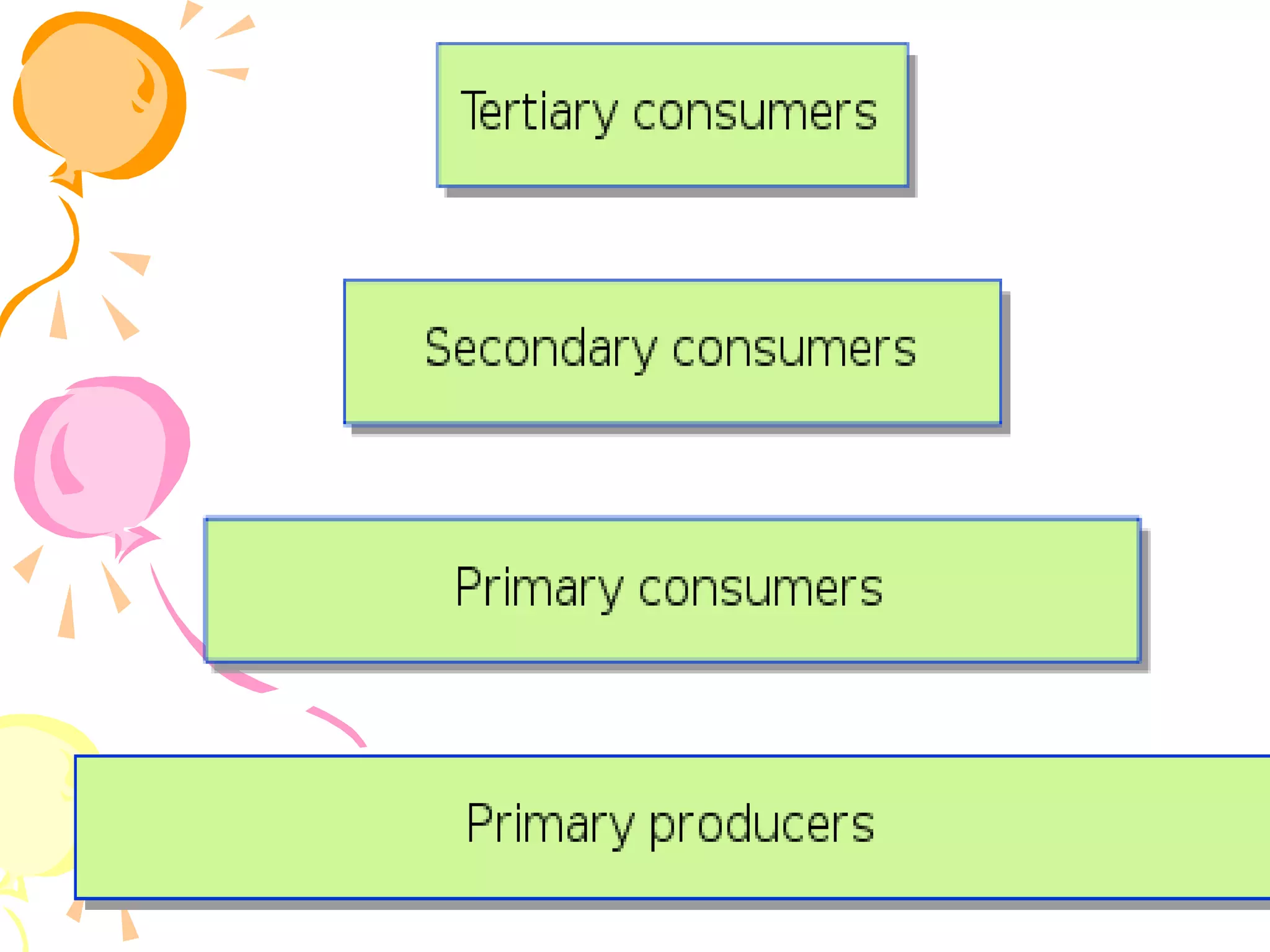
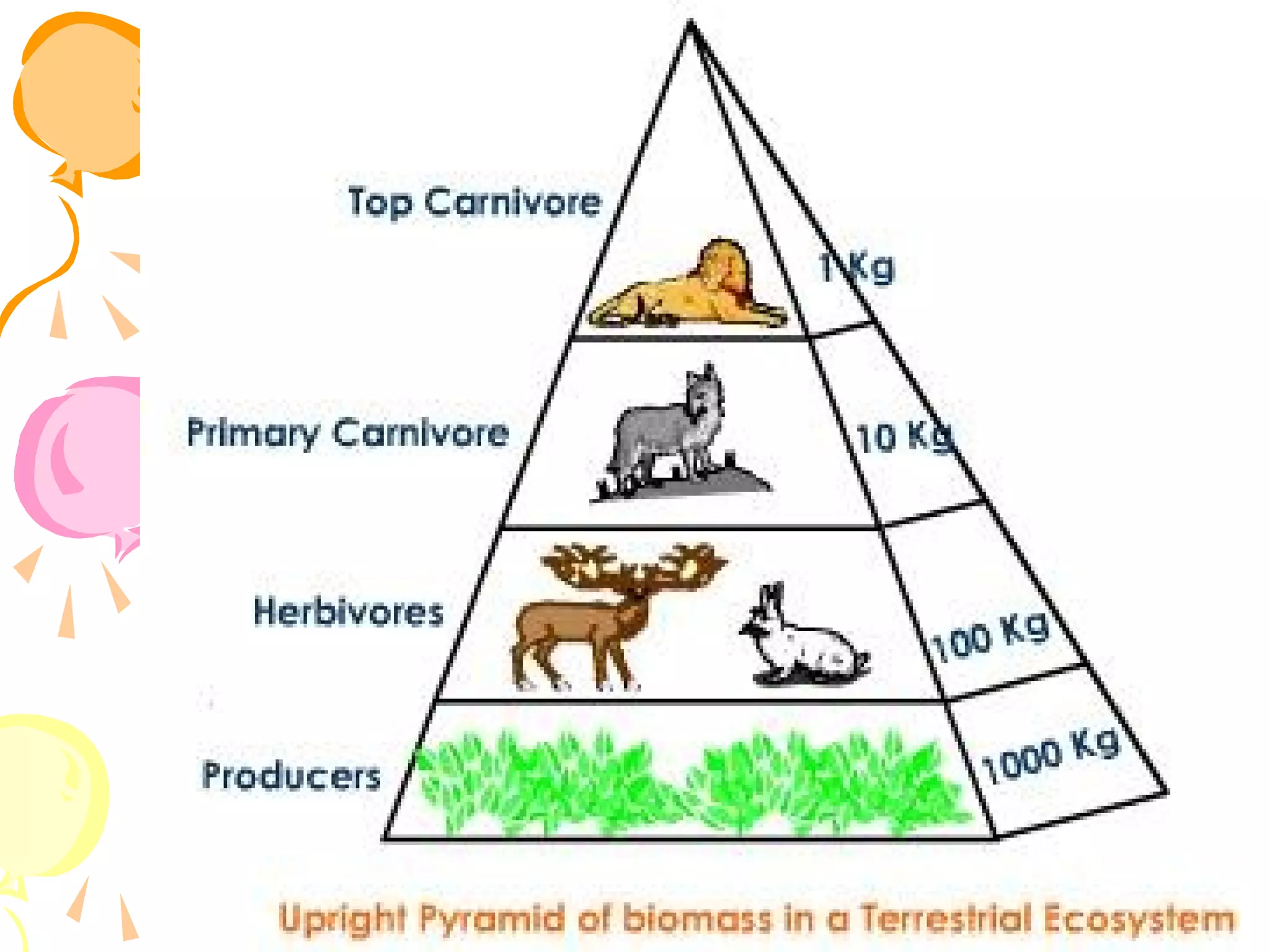
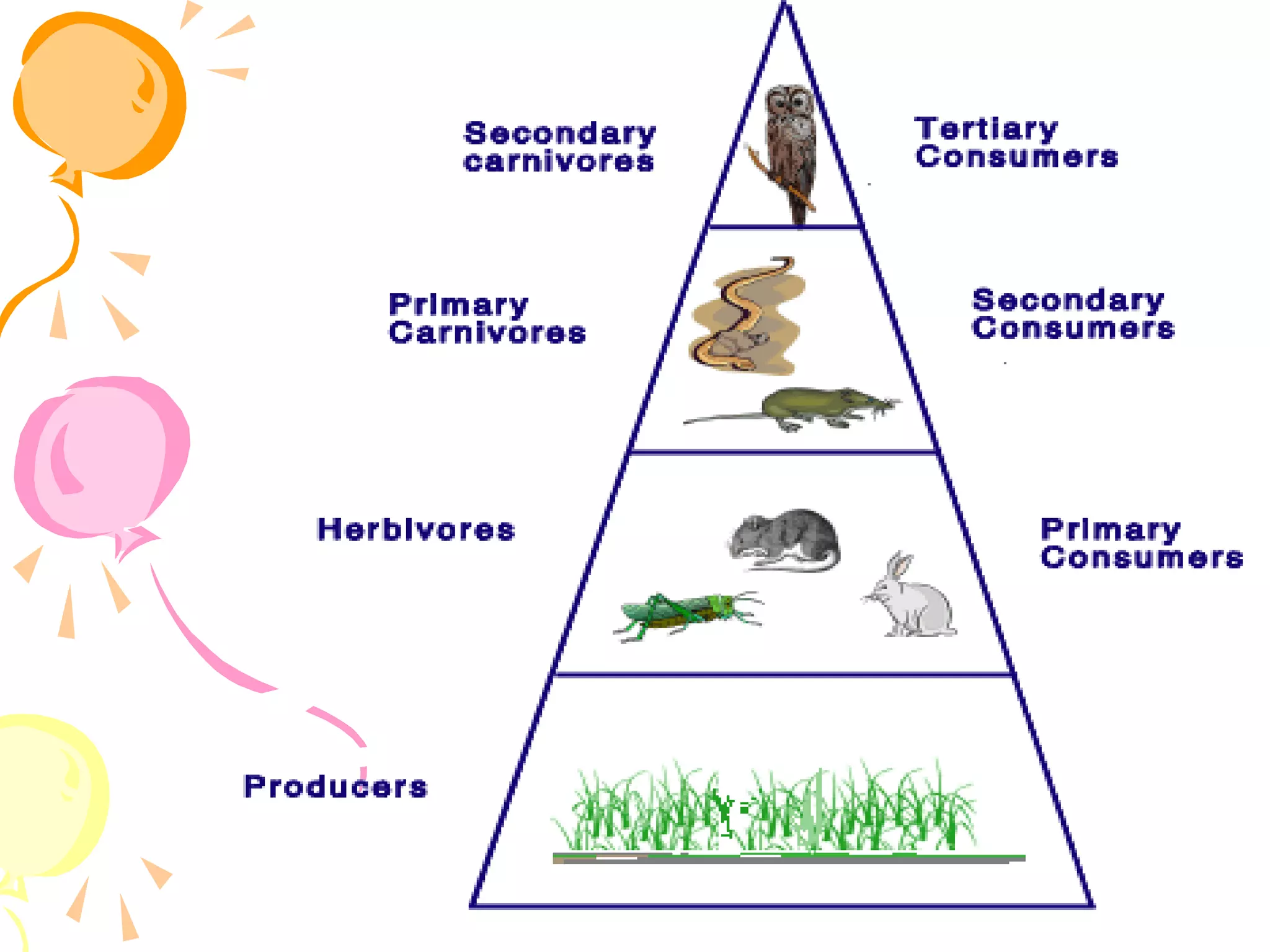
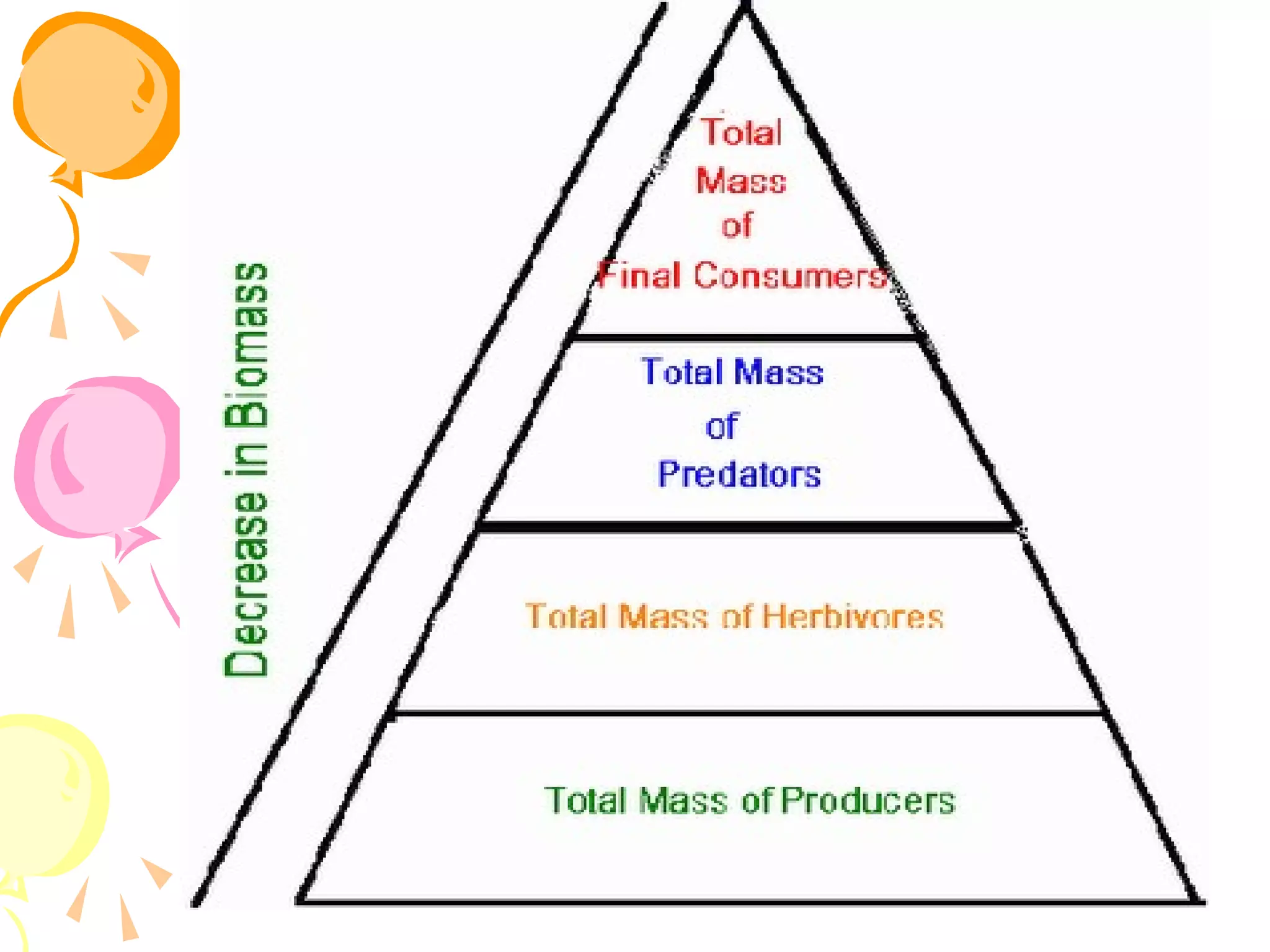
An ecosystem consists of all the living organisms (biotic factors) in an area as well as non-living components (abiotic factors) interacting together. Key abiotic components include climate, soil, sun, water and air. Key biotic components include producers, consumers, and decomposers. Energy enters the ecosystem primarily from the sun and passes through food chains and food webs as organisms consume, and are consumed by, others. Decomposers break down dead organic matter and cycle nutrients back into the soil.