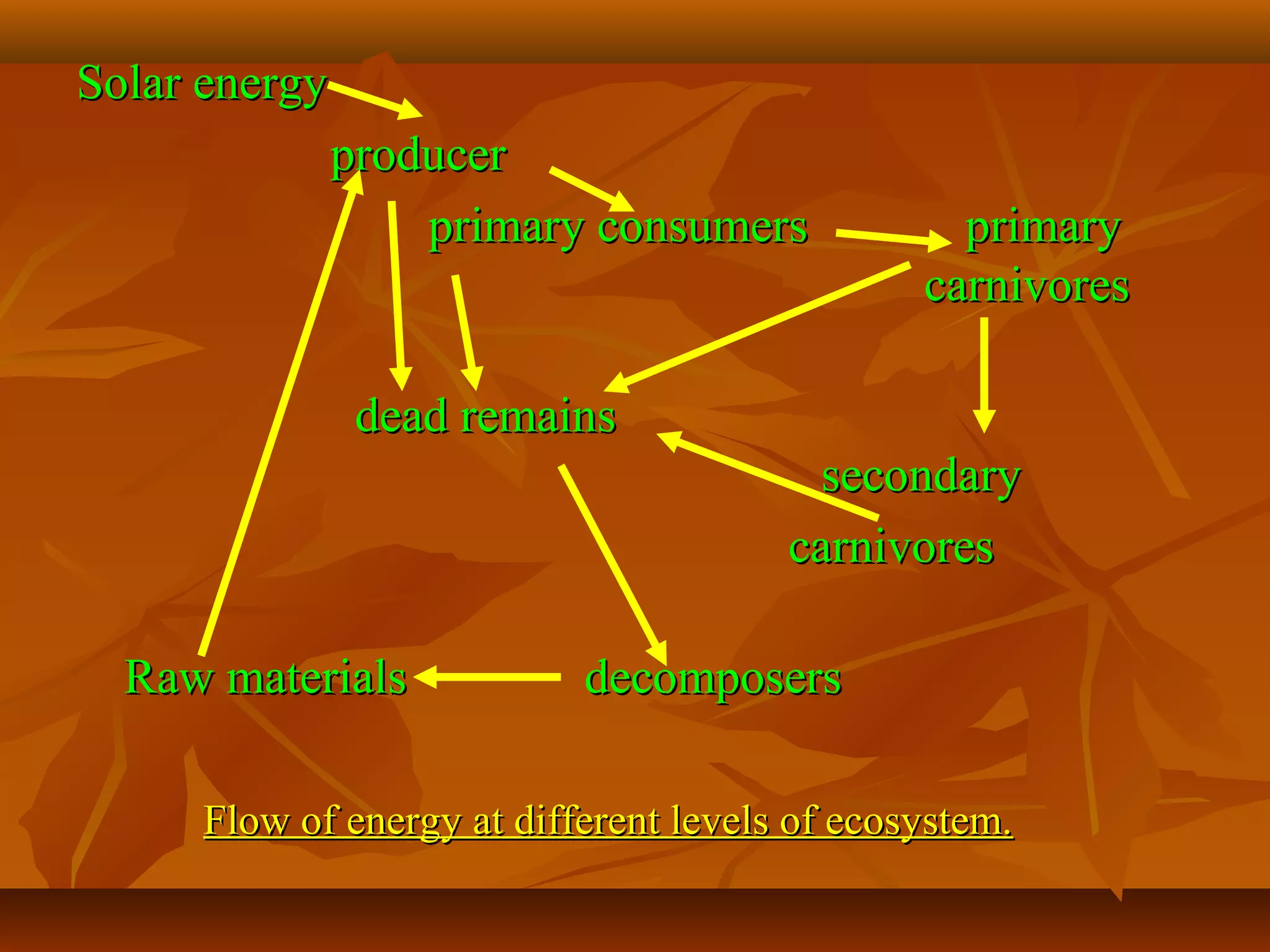
The document discusses the history and structure of ecosystems. It defines an ecosystem as a complex unit of living and non-living things that interact and exchange materials. Ecosystems have biotic components like producers, consumers, and decomposers, as well as abiotic components like soil, water, and nutrients. Producers use photosynthesis to convert sunlight into chemical energy, which consumers then use as food and decomposers break down dead remains, recycling nutrients for producers. Energy and matter flow through the ecosystem via these interactions and components.