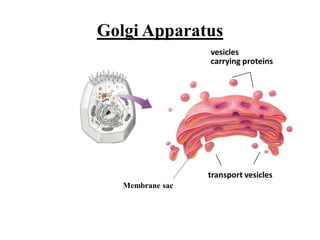
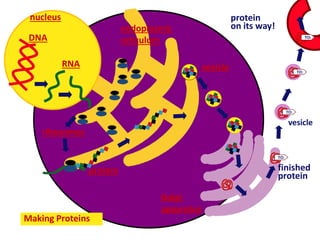
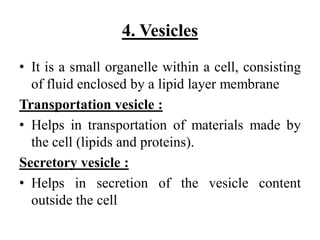
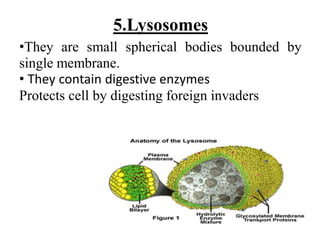
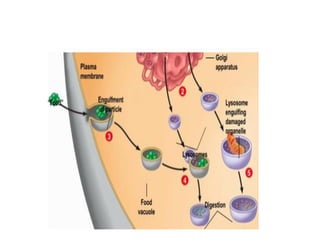
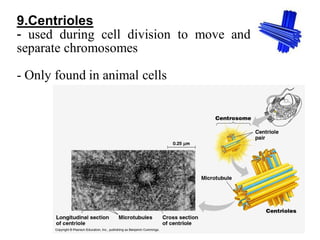
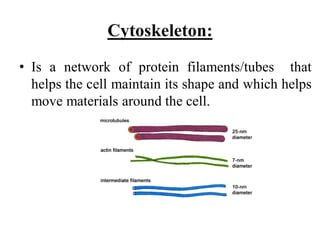
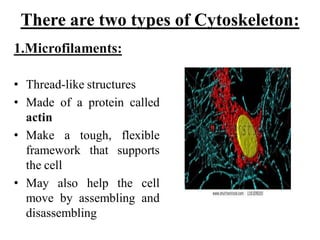
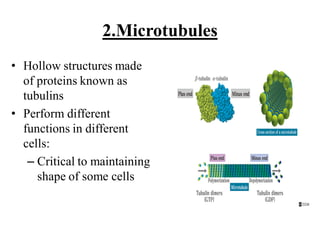
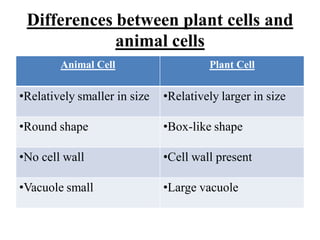
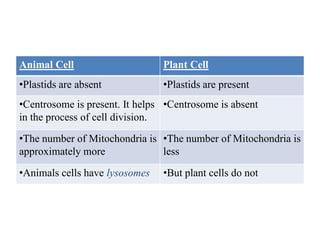
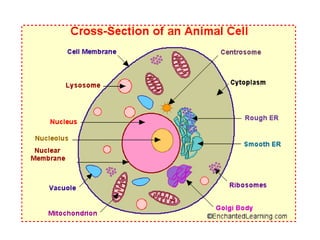
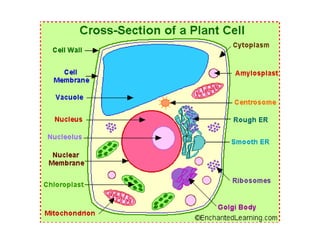
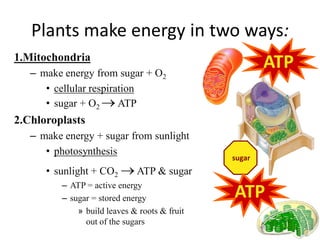
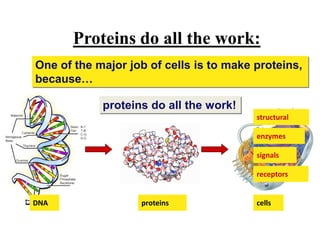
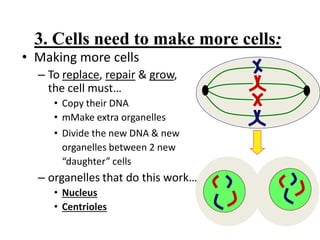
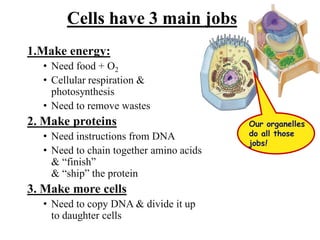
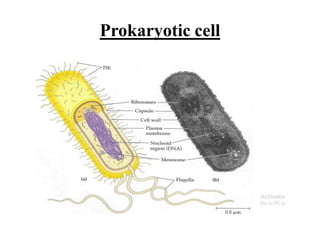
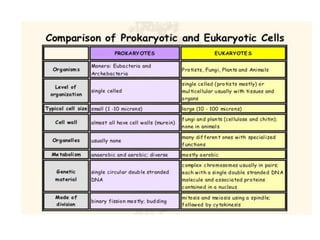
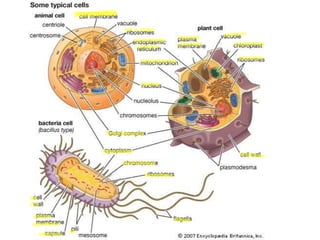
This document provides information on organelles found in eukaryotic cells. It discusses the structure and functions of 9 major organelles - Golgi complex, vesicles, lysosomes, peroxisomes, mitochondria, vacuoles, centrioles, chloroplasts (in plant cells), and plastids (in plant cells). The Golgi complex packages and modifies proteins and lipids, vesicles transport materials within the cell, and lysosomes digest foreign particles and old cell components. Mitochondria generate energy for the cell, while chloroplasts and plastids are involved in photosynthesis and storage in plant cells. The document also compares key differences between plant and animal cells as well as prokaryotic and eukary