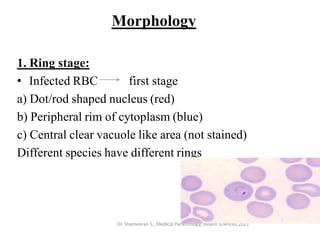
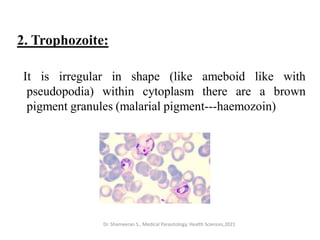
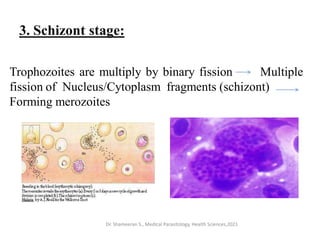
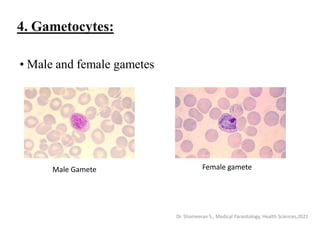
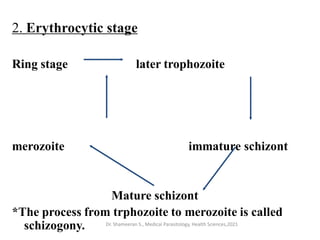
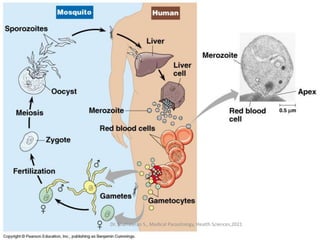
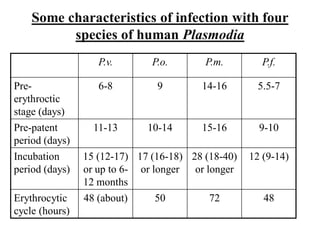
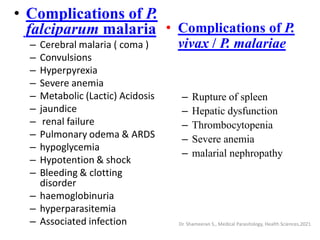
This document provides an overview of malaria and Plasmodium parasites. It discusses the life cycle of Plasmodium, which involves sexual reproduction in mosquitos and asexual replication in humans. Four main species that cause malaria in humans are described: P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae. P. falciparum is the most deadly and can cause complications like cerebral malaria. Symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of malaria are outlined. Vaccine development is mentioned as a future intervention for controlling malaria.