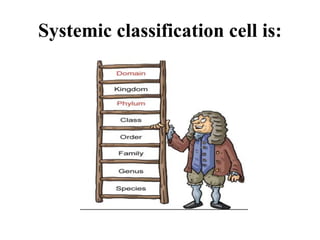
This document provides an introduction to biology, including definitions and key concepts. It discusses biology as the study of living things and describes its main branches as zoology, botany, and microbiology. The importance of biology is explained as helping to understand body functions and use natural resources sustainably. The basic unit of life, the cell, is introduced, along with its history of discovery. The modern cell theory states that all organisms are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function, and new cells arise from existing cells. The main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are outlined.