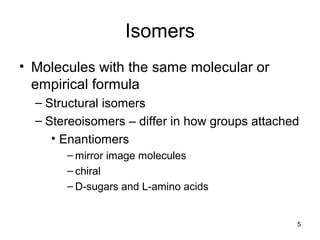
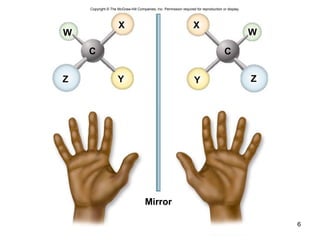
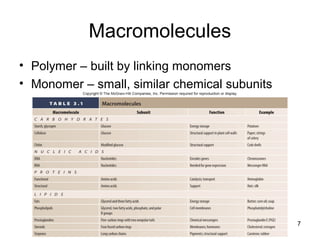
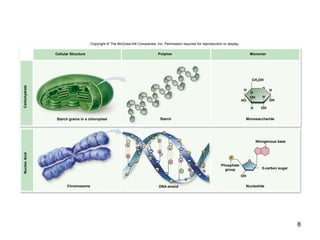
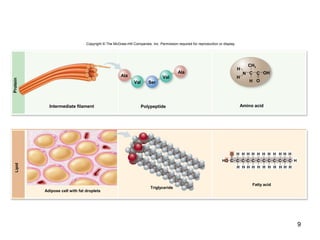
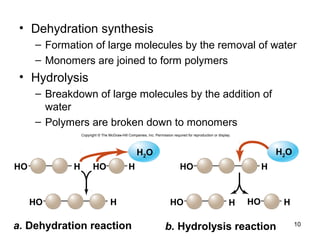
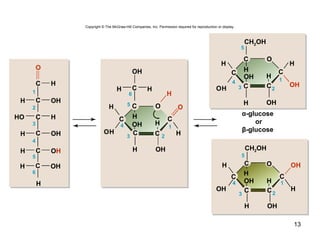
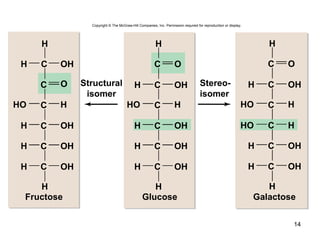
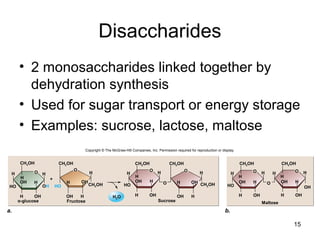
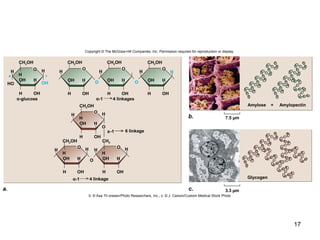
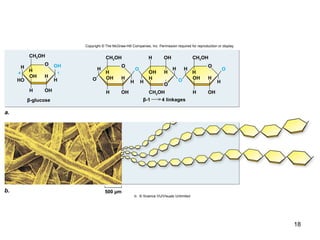
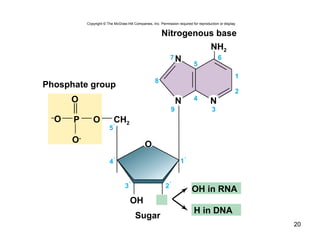
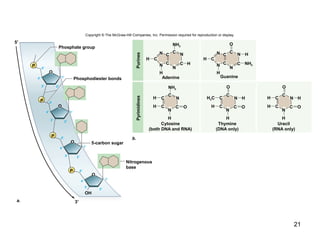
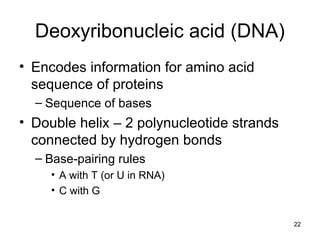
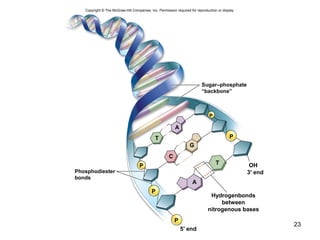
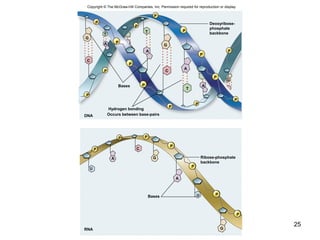
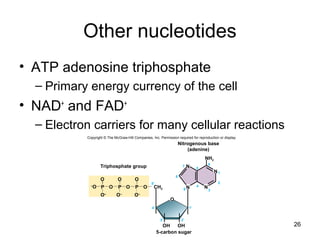
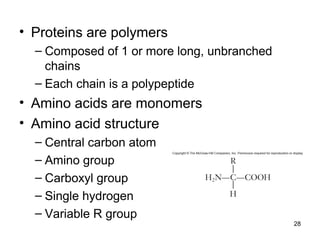
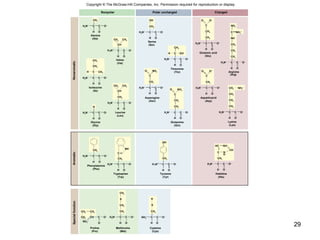
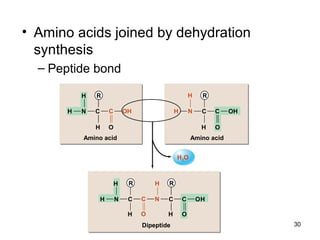
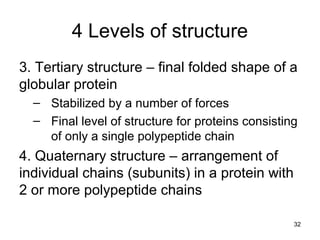
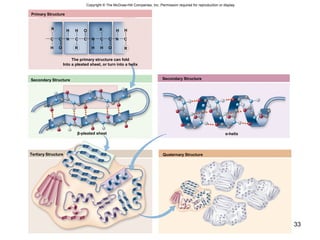
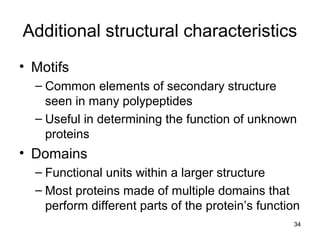
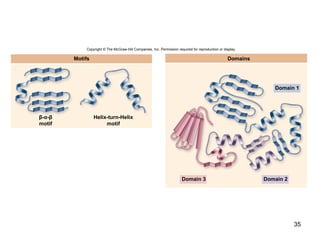
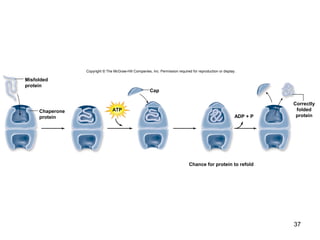
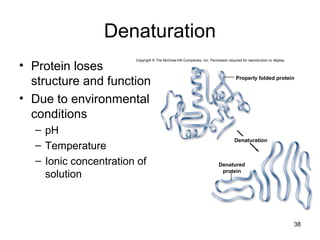
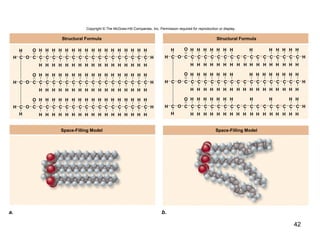
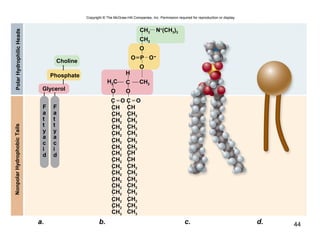
Carbon is the main element that makes up biological molecules. It can form up to four covalent bonds and its ability to do so allows it to form complex structures like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These macromolecules are made through the linking of smaller monomer units like monosaccharides, amino acids, and nucleotides. The three main classes of macromolecules are carbohydrates, which serve structural and energy roles; proteins, which have many functions including enzyme catalysis; and nucleic acids like DNA and RNA, which encode genetic information and direct protein synthesis.