This document provides an introduction to liquid crystals including:
- Their discovery in 1888 by Friedrich Reinitzer who observed two melting points in cholesteryl benzoate.
- Their unique properties between solid and liquid phases termed the "mesogenic state".
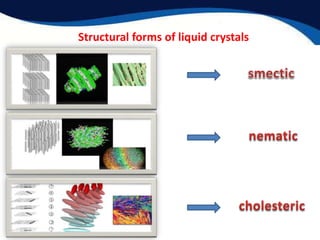
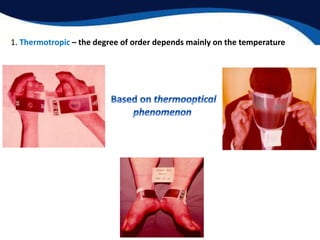
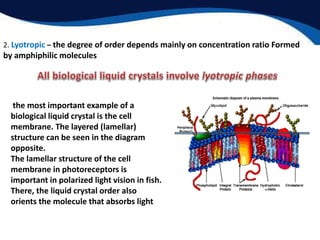
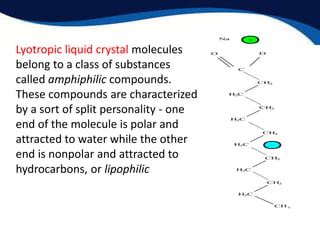
- Two main structural forms: thermotropic which depends on temperature and lyotropic which depends on concentration.
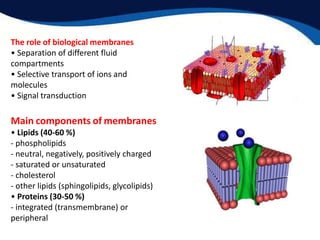
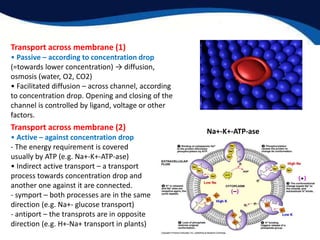
- Examples of liquid crystals in biology like cell membranes, myelin, and spider silk which use liquid crystalline properties.
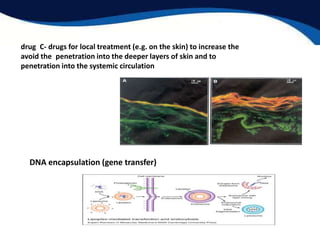
- Potential medical applications of lyotropic liquid crystals like liposomes for targeted drug delivery.