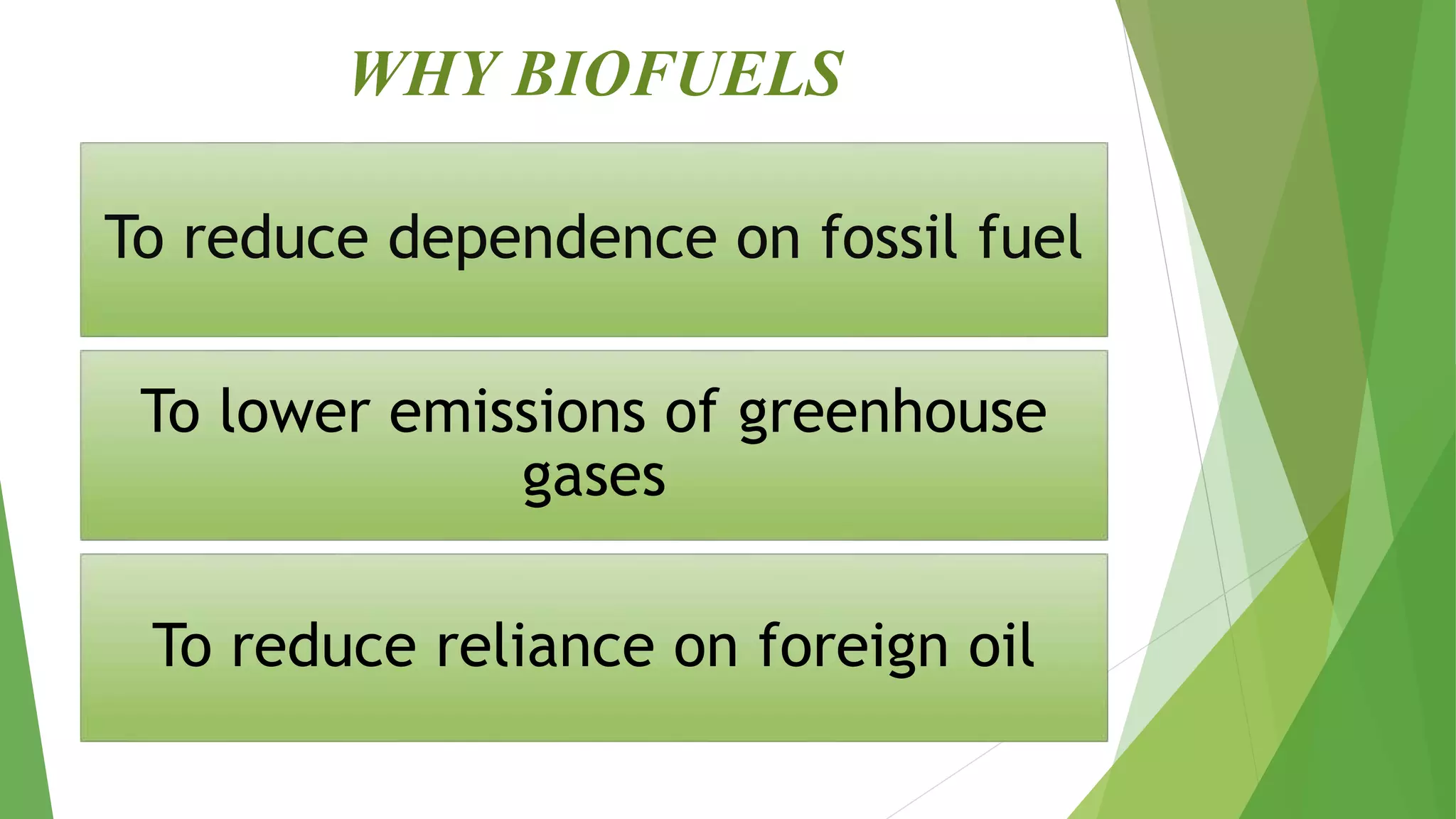
Biofuels are fuels produced from biological sources such as agricultural waste, sugarcane, corn, and algae. They include bioethanol, biodiesel, and biogas. Biofuels offer advantages like reducing dependence on fossil fuels, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and reducing foreign oil reliance. However, they also have disadvantages like potentially higher food prices and shortages if too much cropland is used for fuel production rather than food. Common biofuels include bioethanol from sugar cane or corn fermentation, biodiesel from vegetable or animal fats, and biogas from organic waste digestion.