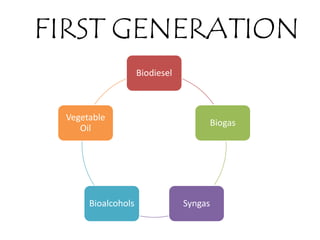
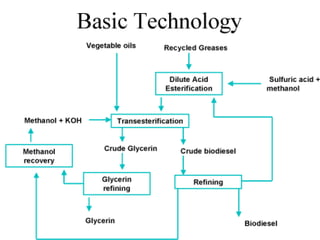
Biofuel is a liquid fuel produced from plant or animal material and used as an alternative to petroleum-based fuels. There are several types of biofuels including biodiesel, bioalcohols like ethanol, and biogas. Biofuels can be produced from feedstocks like palm, coconut, jatropha seeds, rapeseed, and algae. They are produced through fermentation of sugar crops or by heating plant oils. Biofuels are a renewable source and their production can benefit rural development.