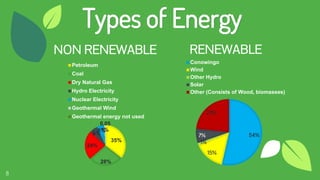
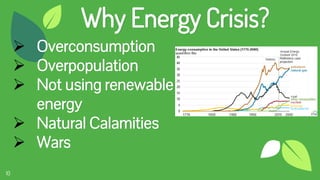
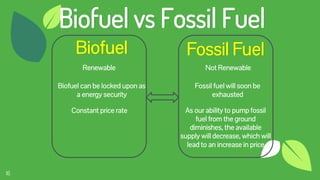
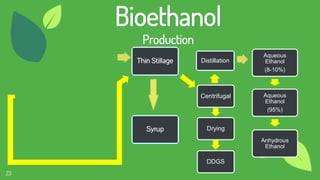
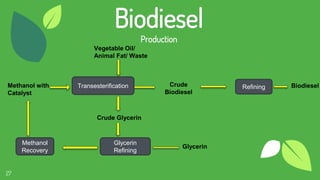
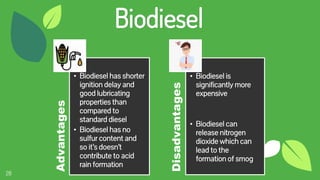
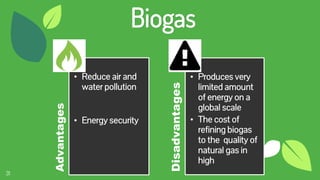
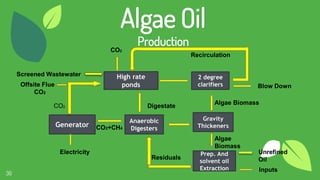
The document discusses the concept of fuels, the global energy crisis fueled by overpopulation and overconsumption, and the importance of transitioning to biofuels. It classifies biofuels into three generations and outlines various types such as bioethanol, biodiesel, biogas, and algae, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. The conclusion emphasizes that while replacing fossil fuels with biofuels is feasible, significant challenges in production costs and political influence must be addressed.