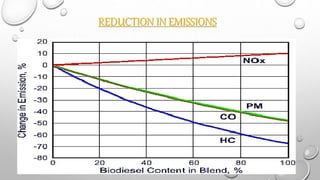
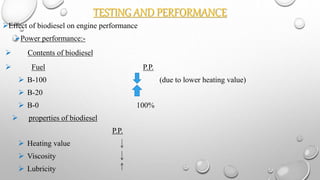
This document discusses biodiesel as an alternative fuel. It defines biodiesel as a fuel produced from organic matter through a process called transesterification. Biodiesel provides environmental benefits such as reduced emissions compared to fossil fuels and can help countries gain energy security. It also has economic benefits and can be used in existing diesel engines when blended with petroleum diesel. However, biodiesel may experience some performance issues at higher concentrations or in cold weather.