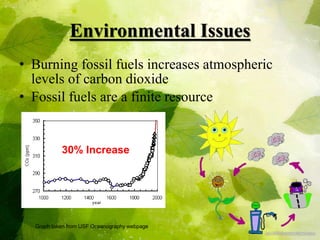
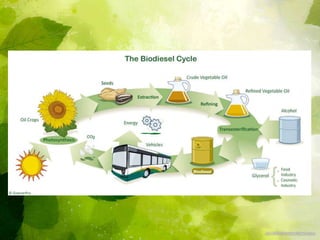
Biodiesel is an alternative fuel made from vegetable oils or animal fats that can be used in diesel engines. It has benefits over petroleum diesel such as being non-toxic, biodegradable, and producing lower emissions. However, biodiesel also faces challenges including limited availability of feedstock for large-scale replacement of petroleum diesel, issues with cold weather operation, and potential engine and emissions optimization. While biodiesel provides short and long-term environmental benefits, issues around fuel stability, transportation costs, and lack of understanding of its full environmental impacts need to be addressed for it to become a primary fuel source.