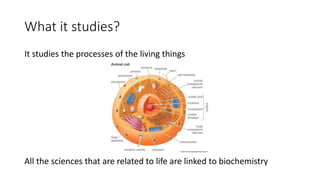
Biochemistry studies the processes of living things at the molecular level. It examines the four main classes of molecules that make up living organisms: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Friedrich Wöhler's synthesis of urea in 1828 demonstrated that organic compounds could be synthesized in a laboratory, challenging the traditional view that vital forces were necessary for the production of organic substances. Monomers like monosaccharides, glycerol and fatty acids, nucleotides, and amino acids link together to form biological polymers including carbohydrates, lipids, DNA and RNA, and proteins.