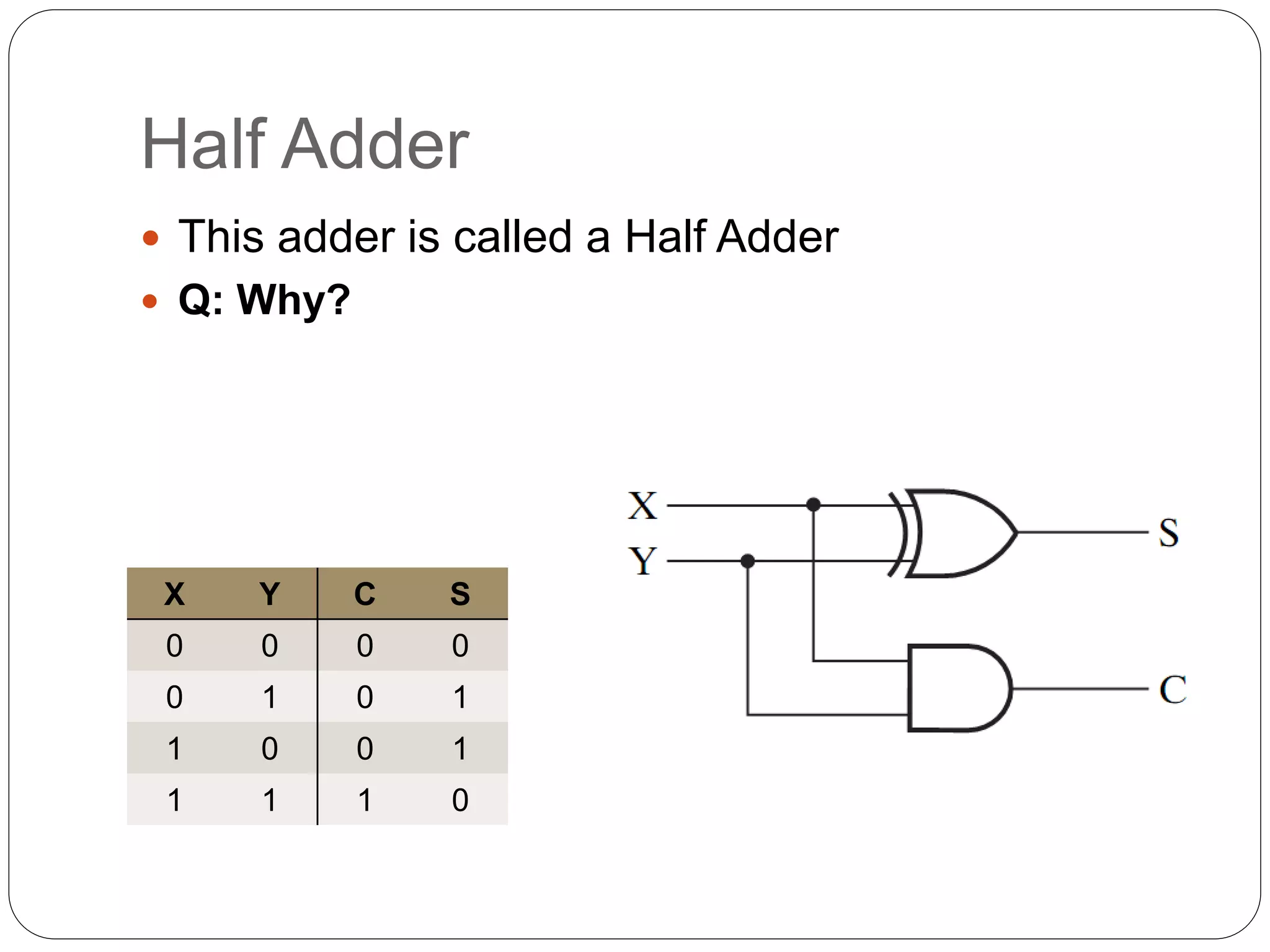
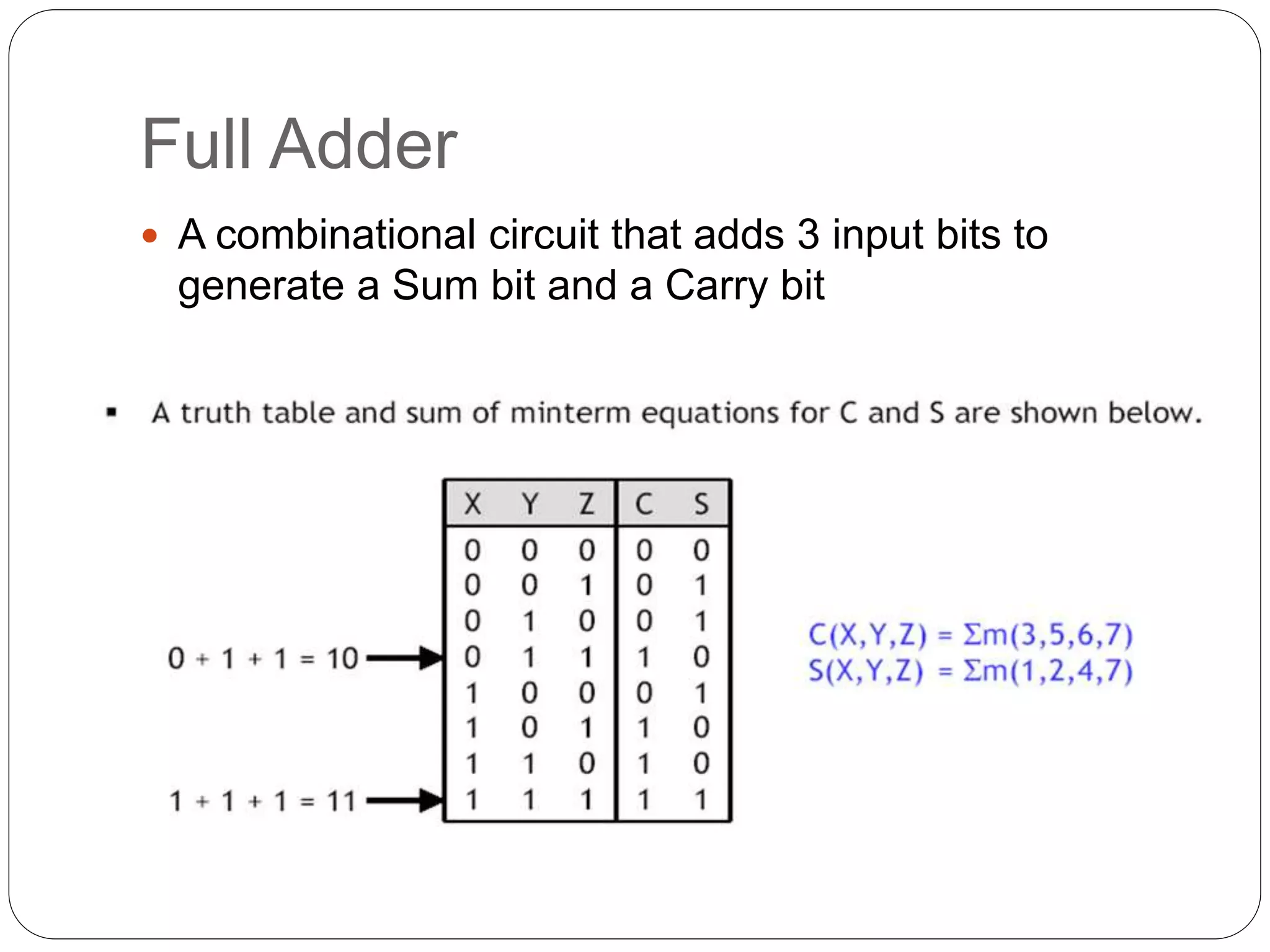
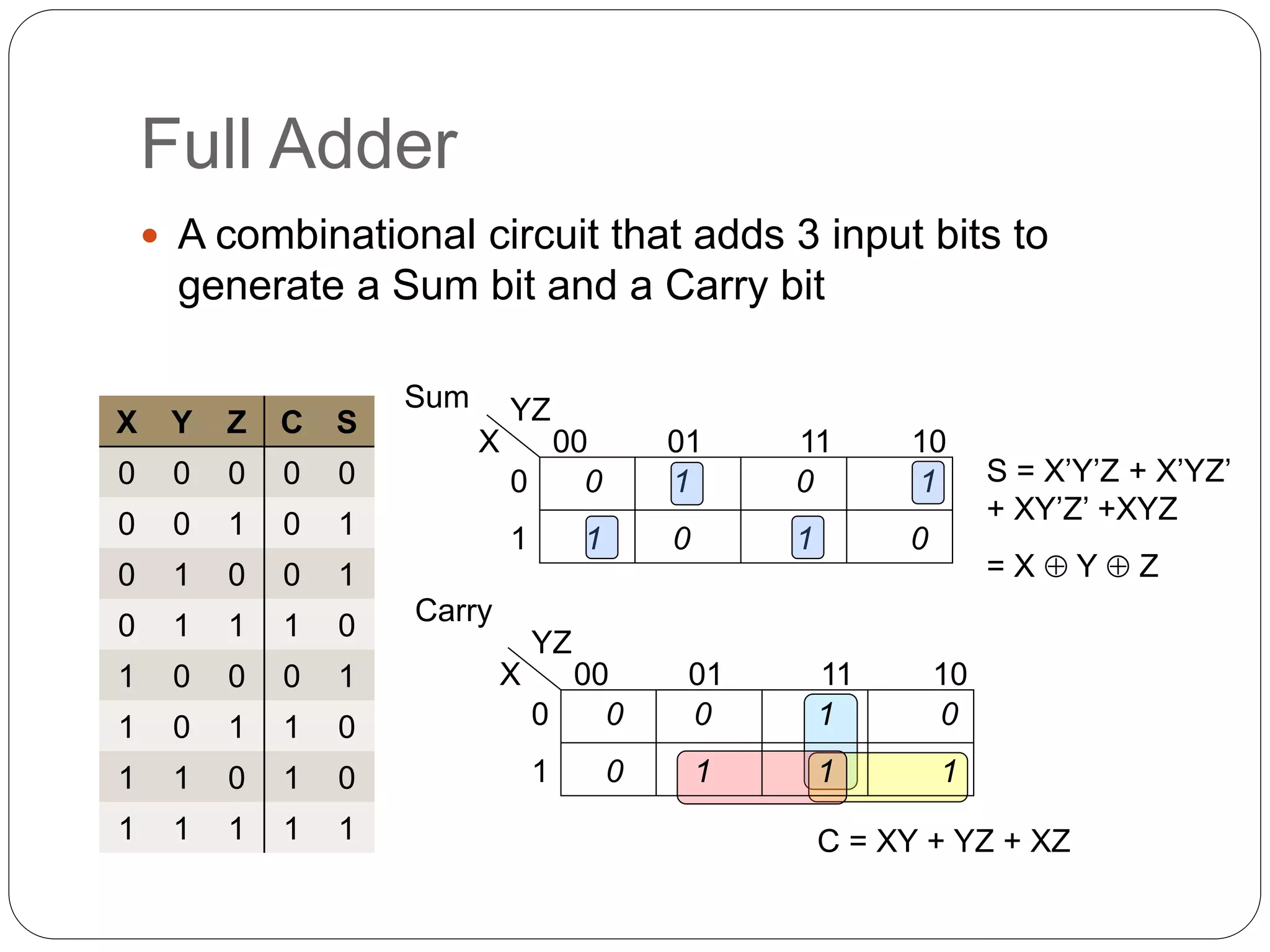
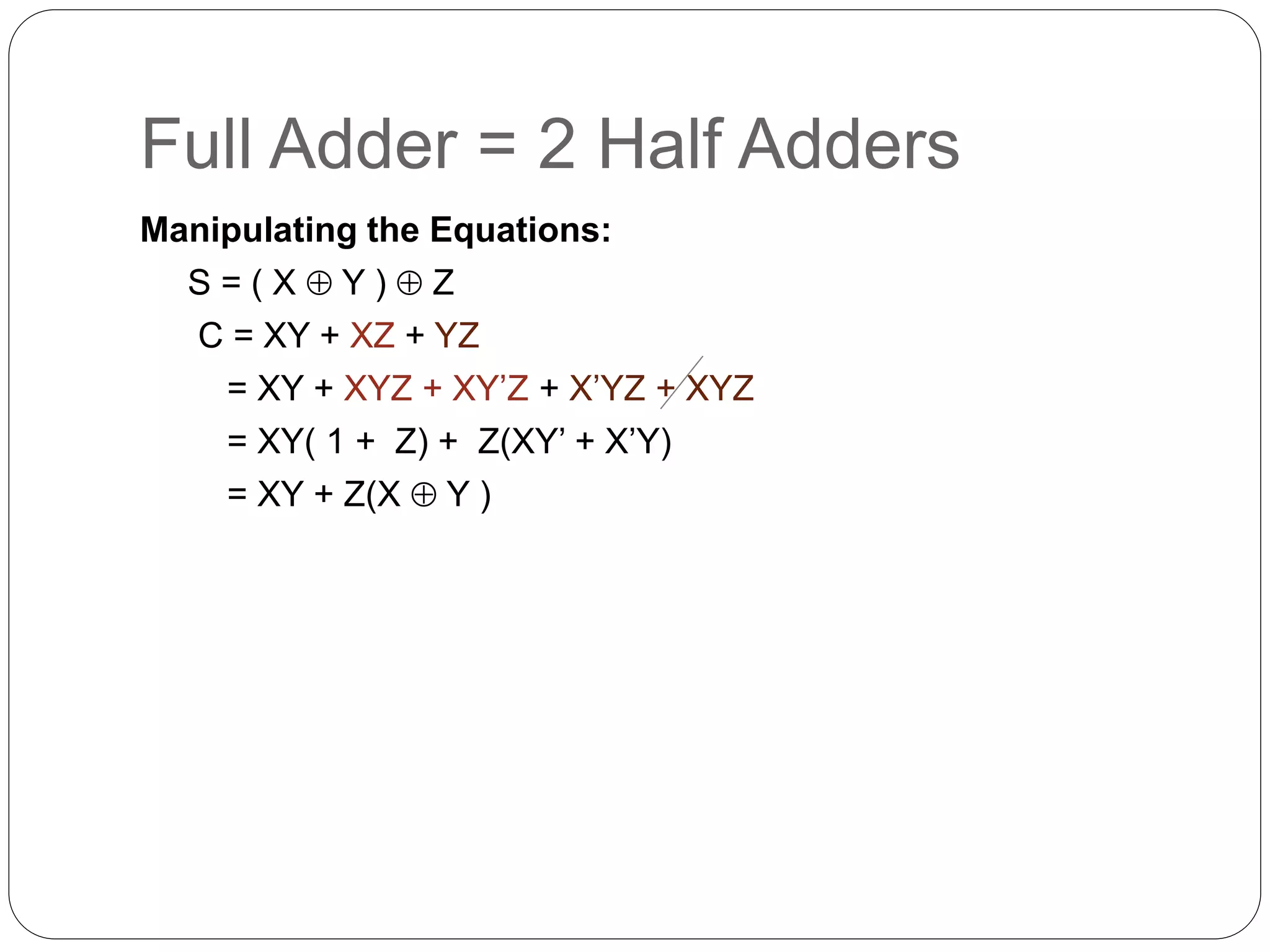
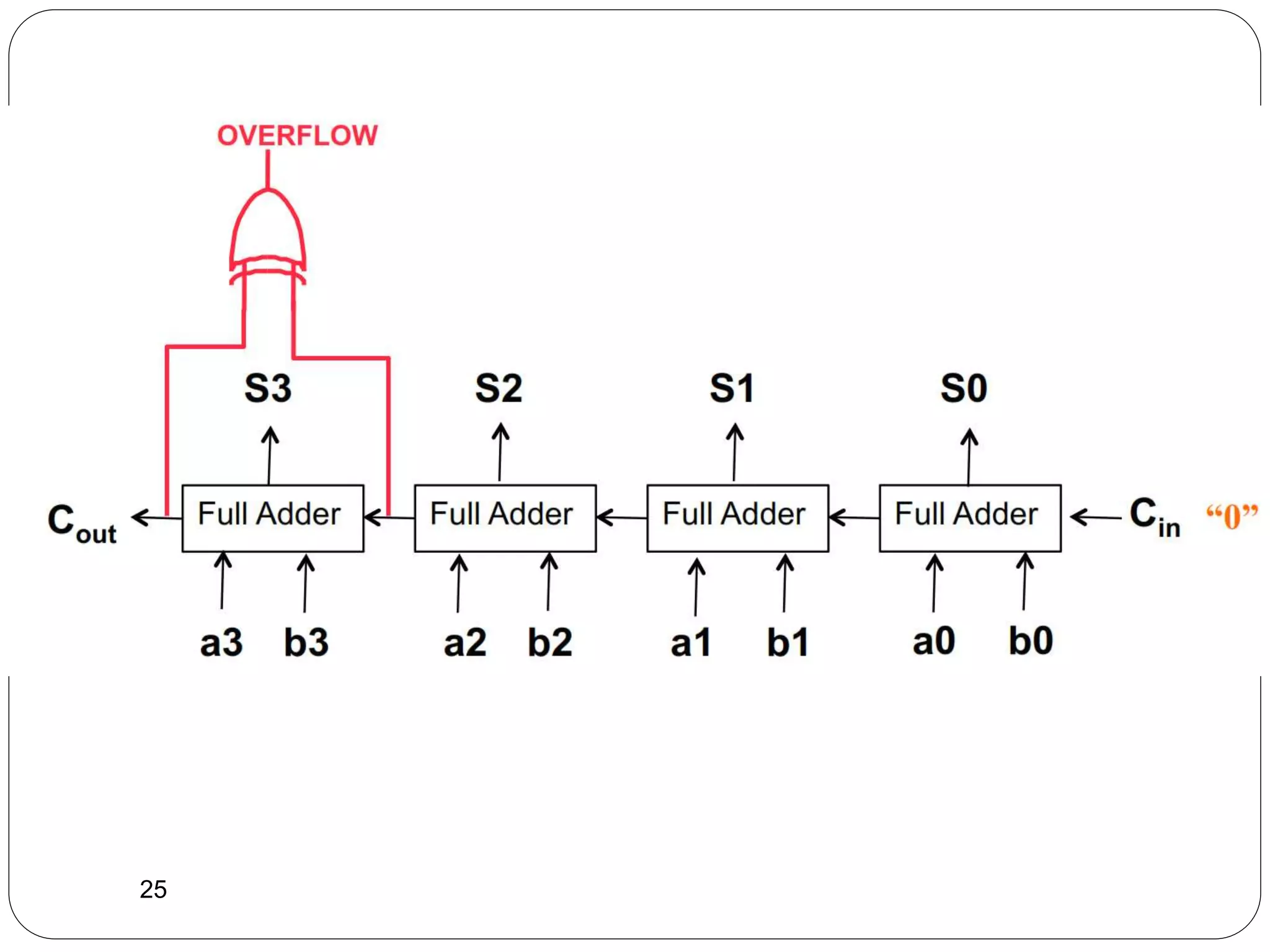
The document summarizes key concepts about combinational circuits:
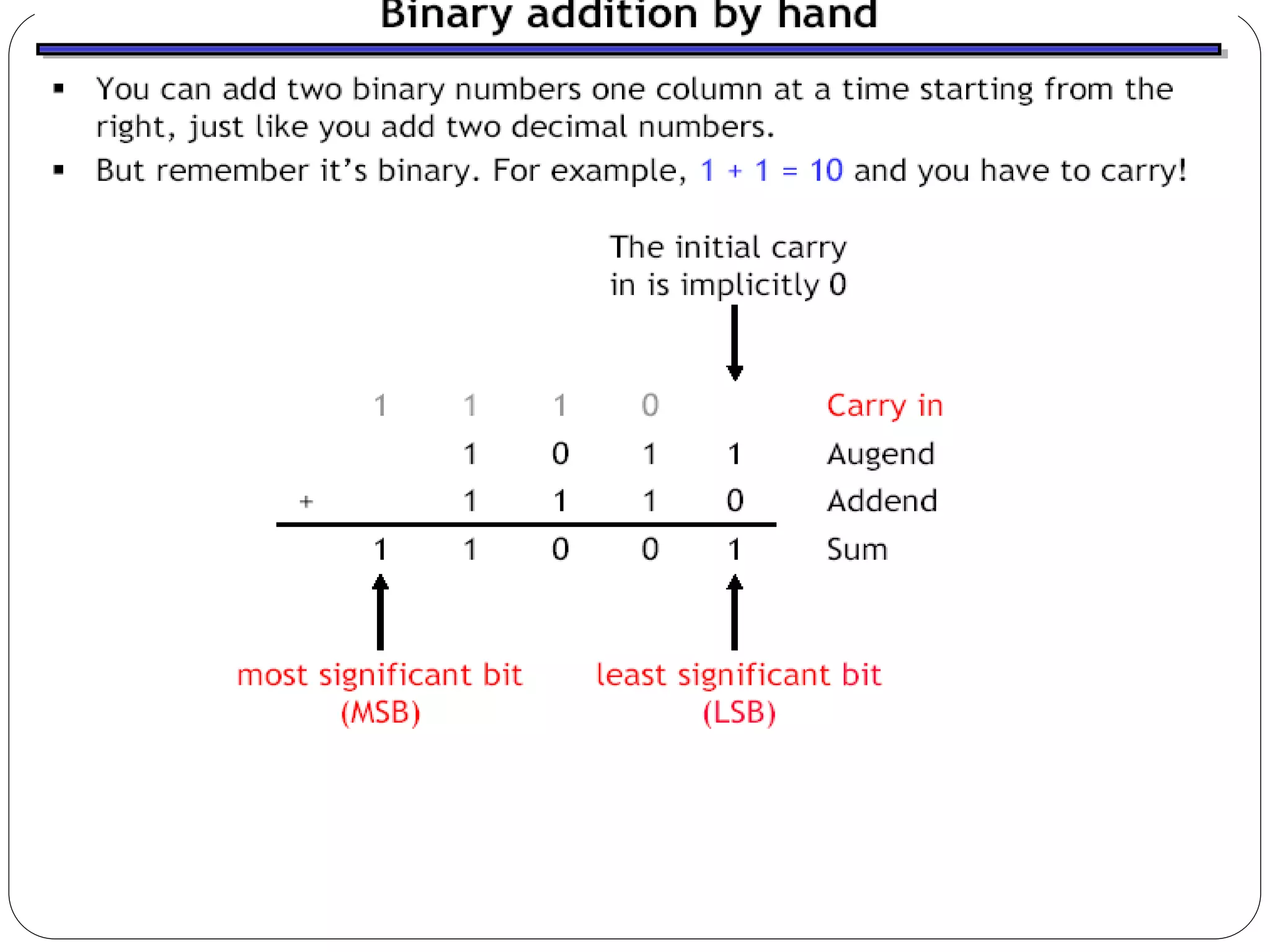
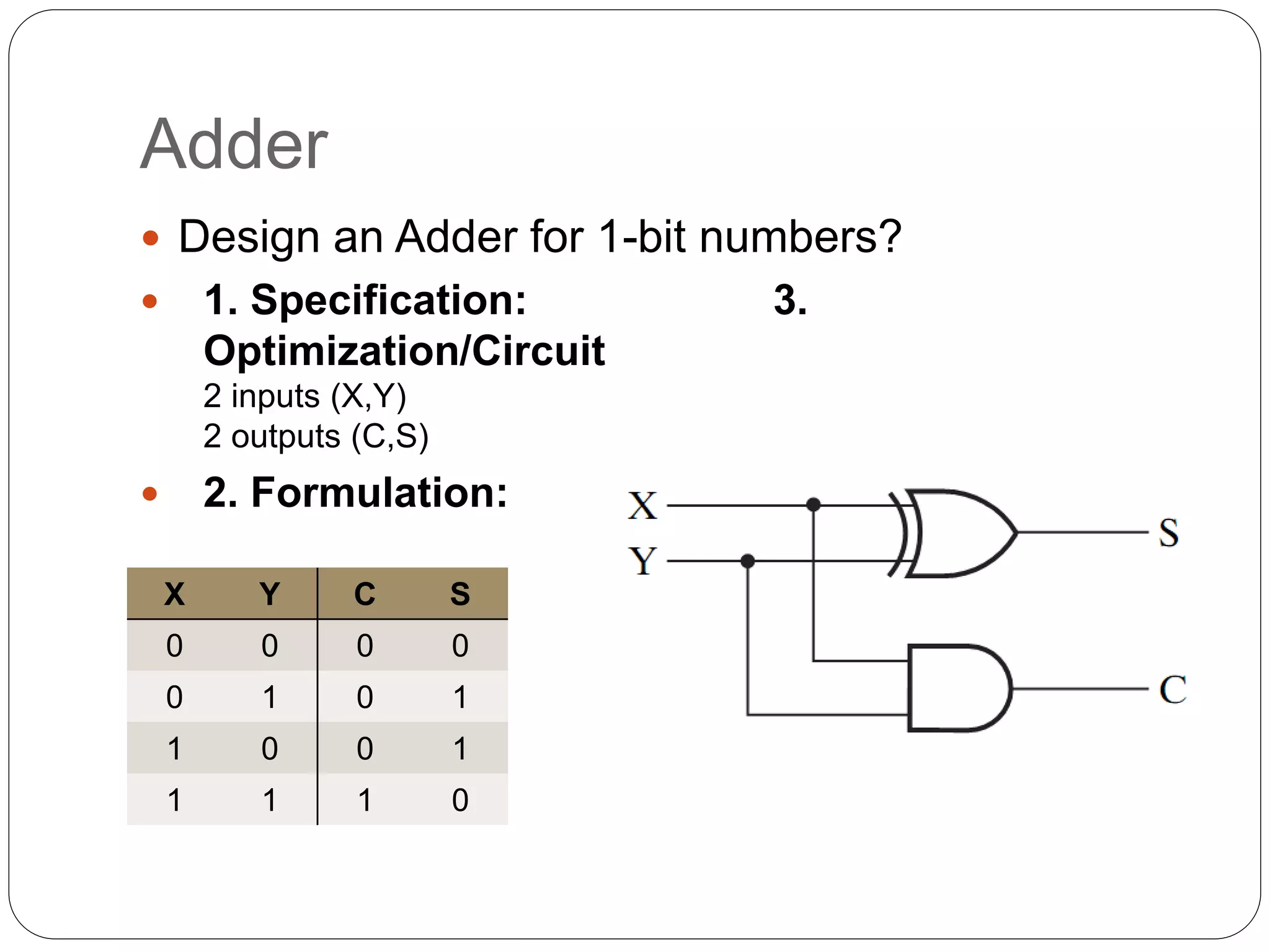
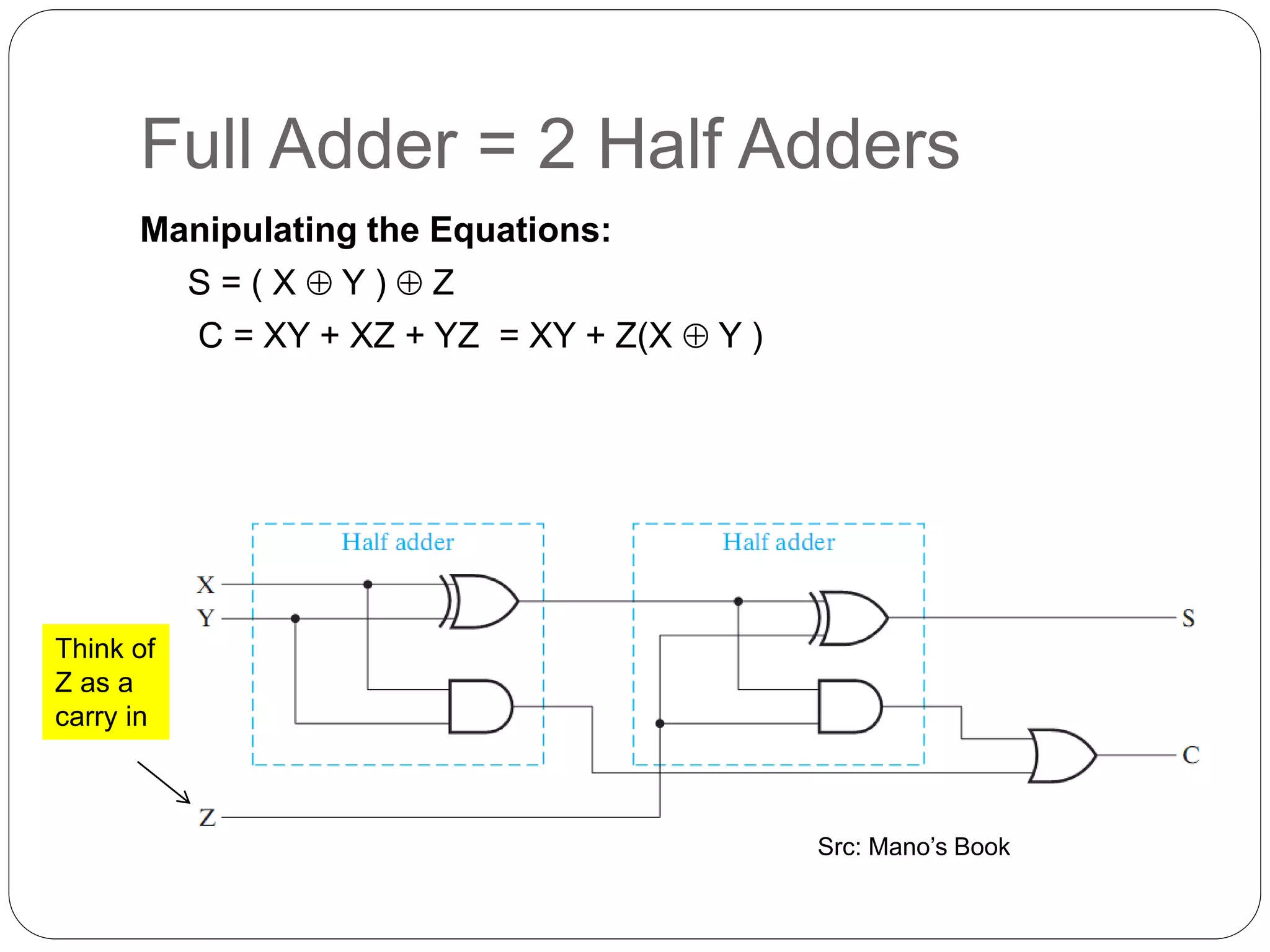
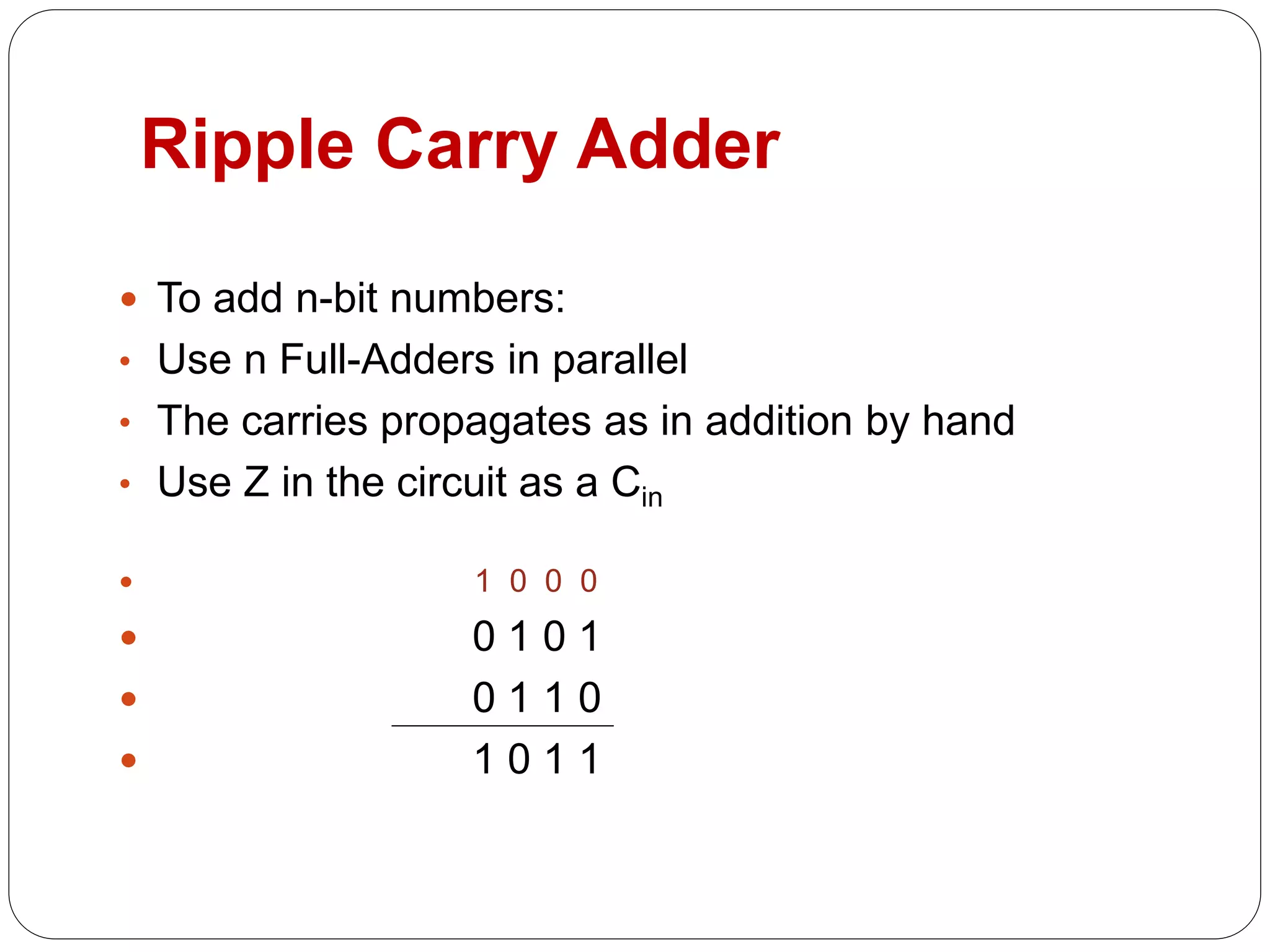
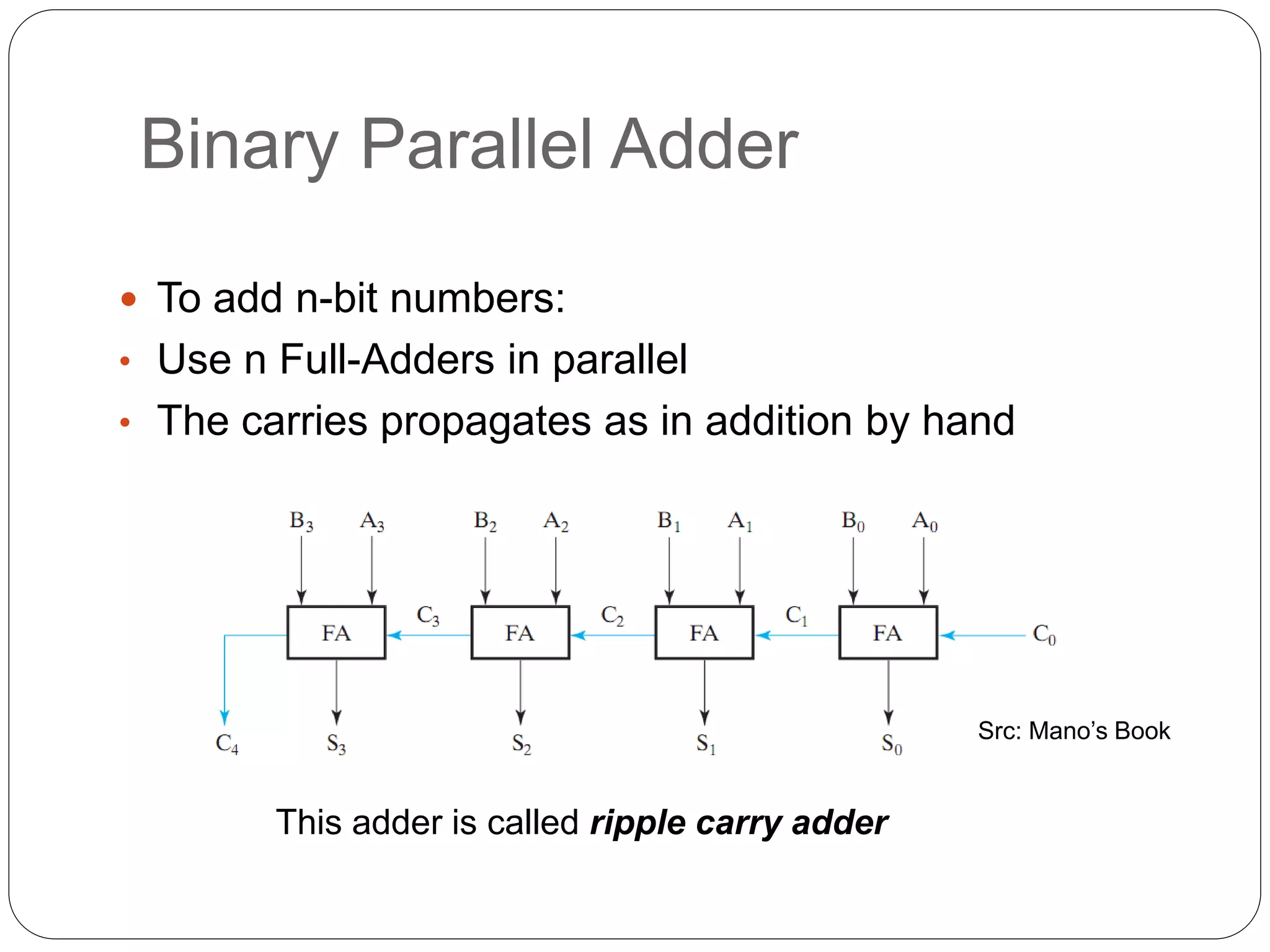
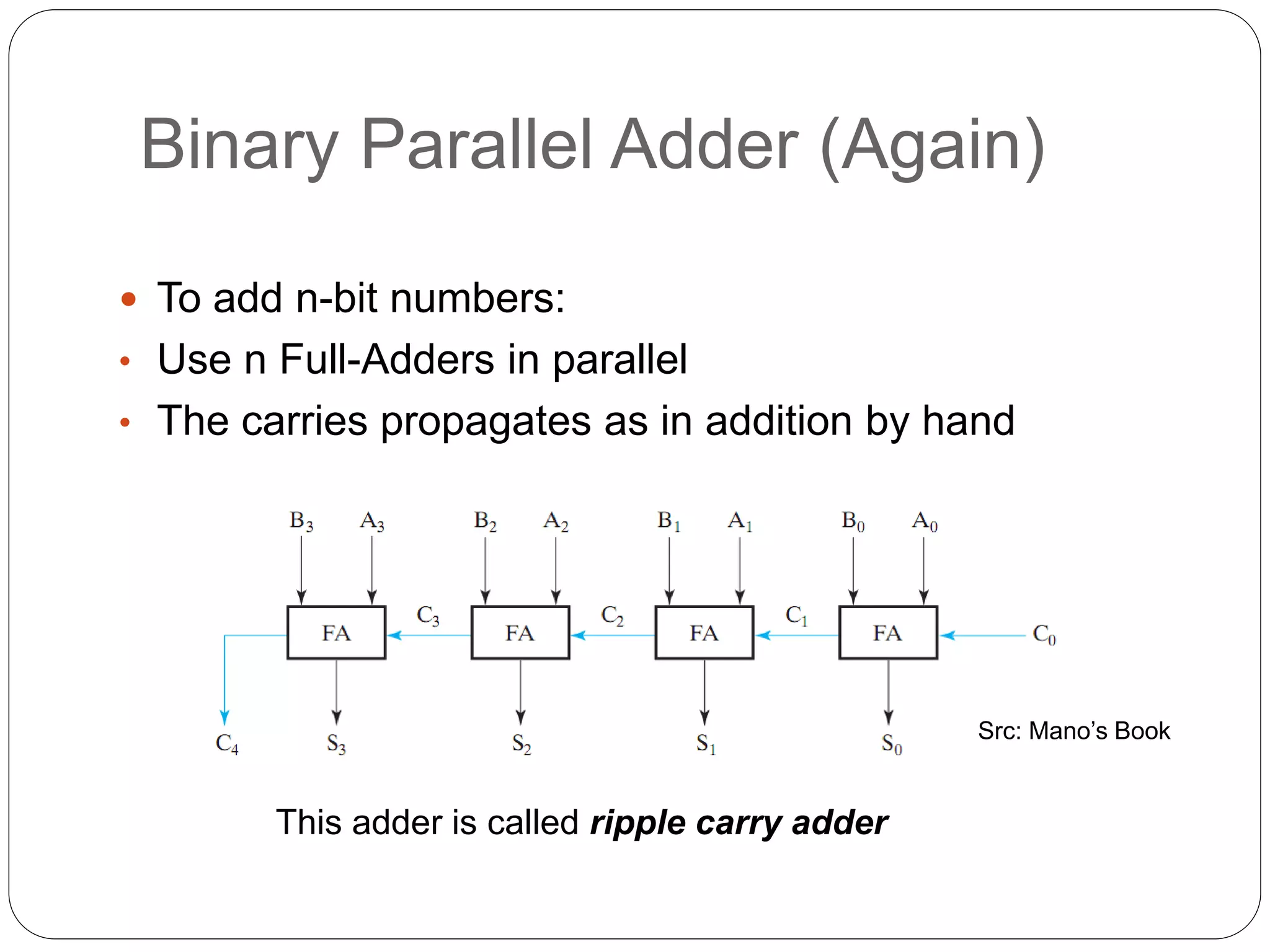
1) It introduces adders, half adders, full adders, and how full adders can be constructed from two half adders. It also explains how ripple carry adders are built by connecting multiple full adders to add n-bit numbers.
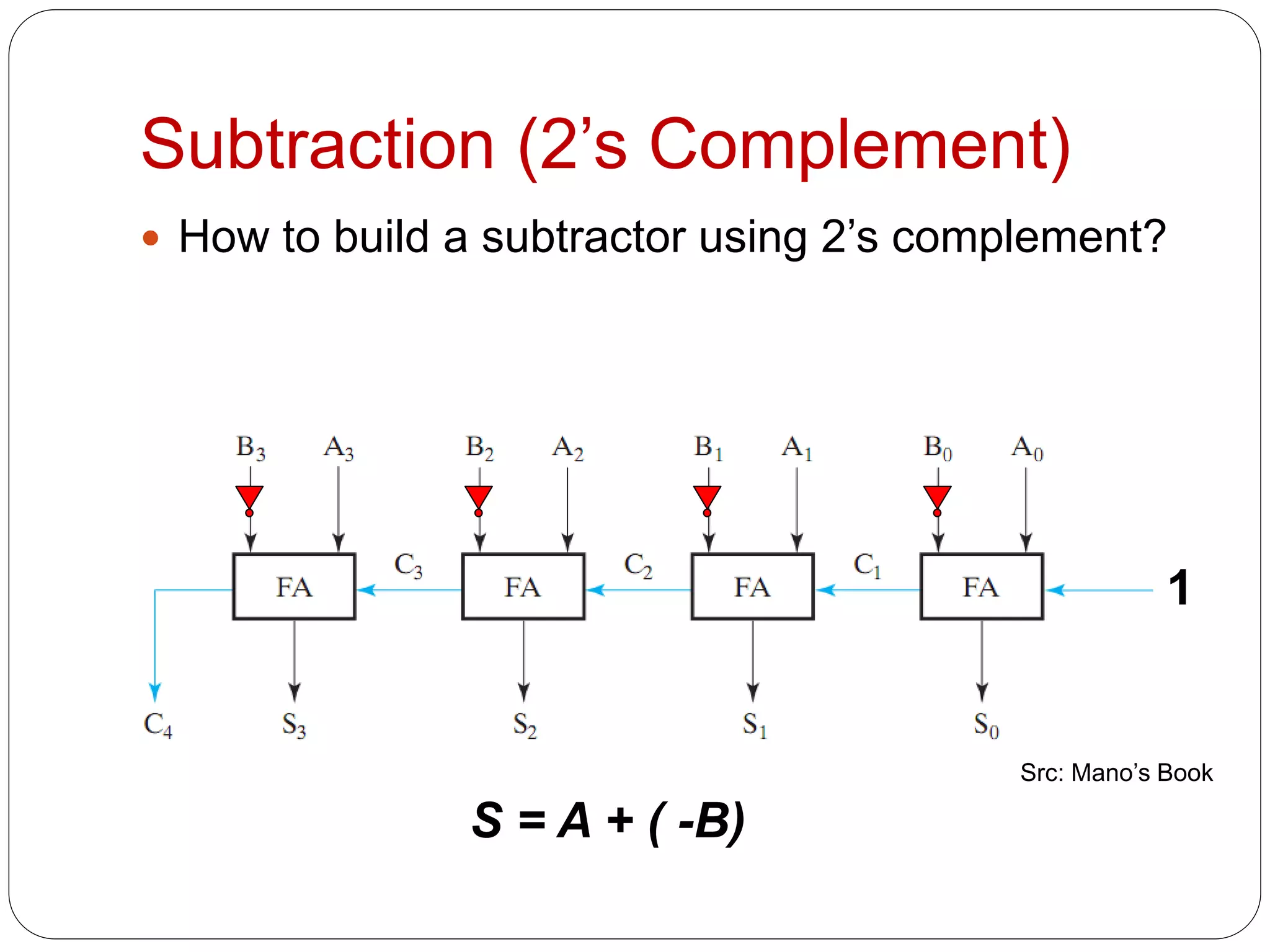
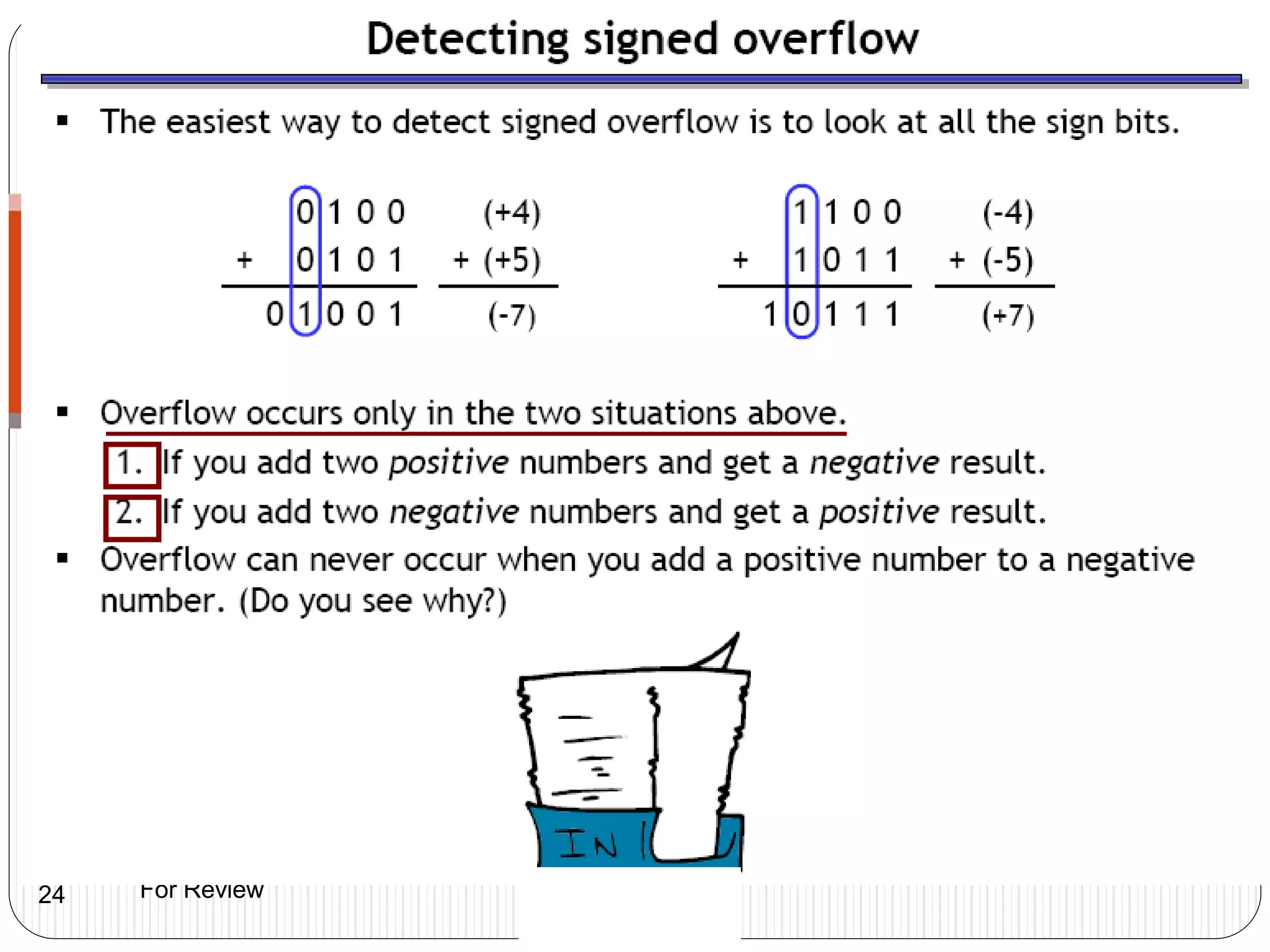
2) It discusses how subtraction can be performed using two's complement representation by adding the minuend and the twos complement of the subtrahend.
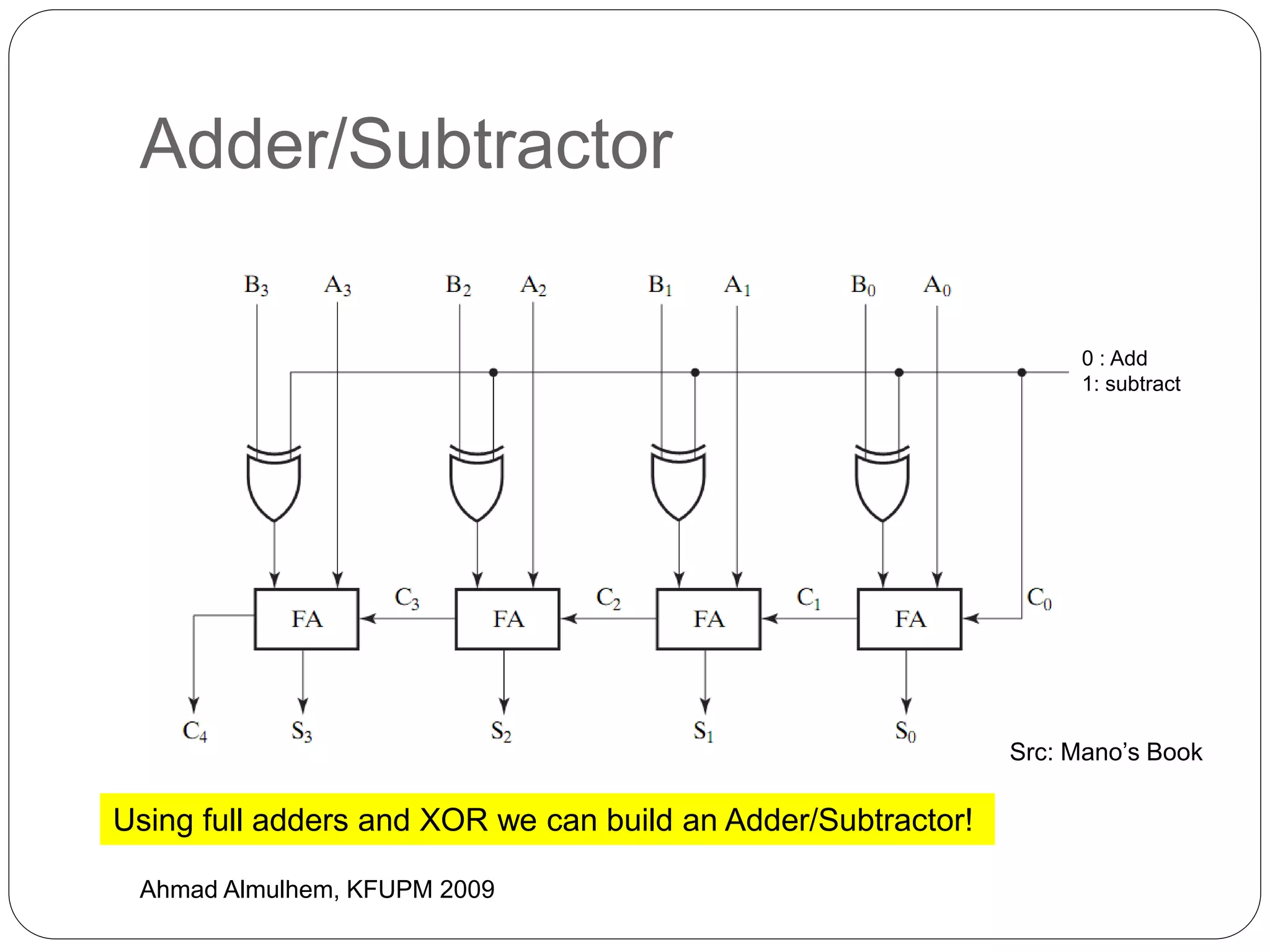
3) It describes how an adder/subtractor circuit can be built using full adders and XOR gates to perform both addition and subtraction operations depending on an additional control input.
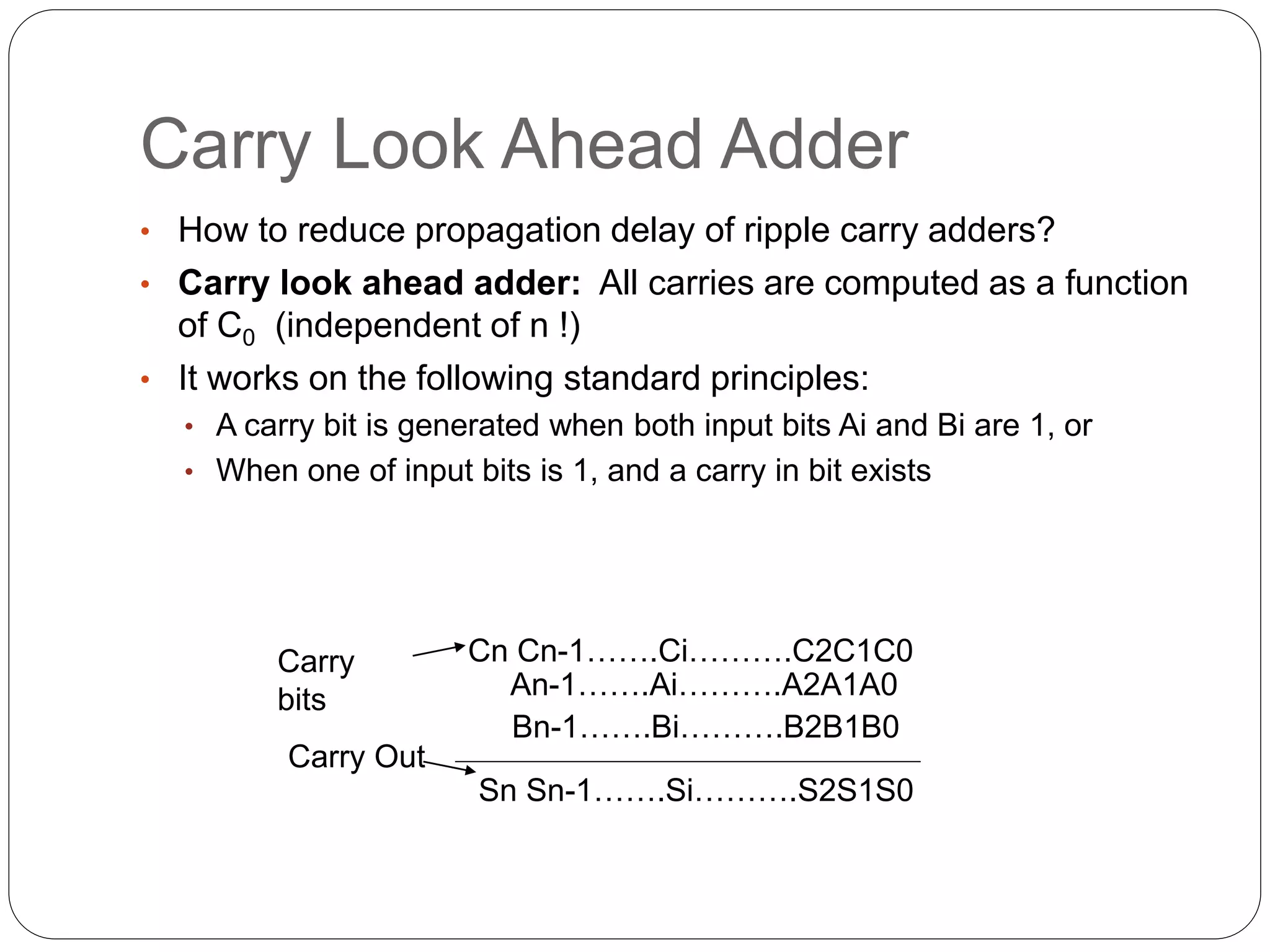
4) It briefly introduces carry look