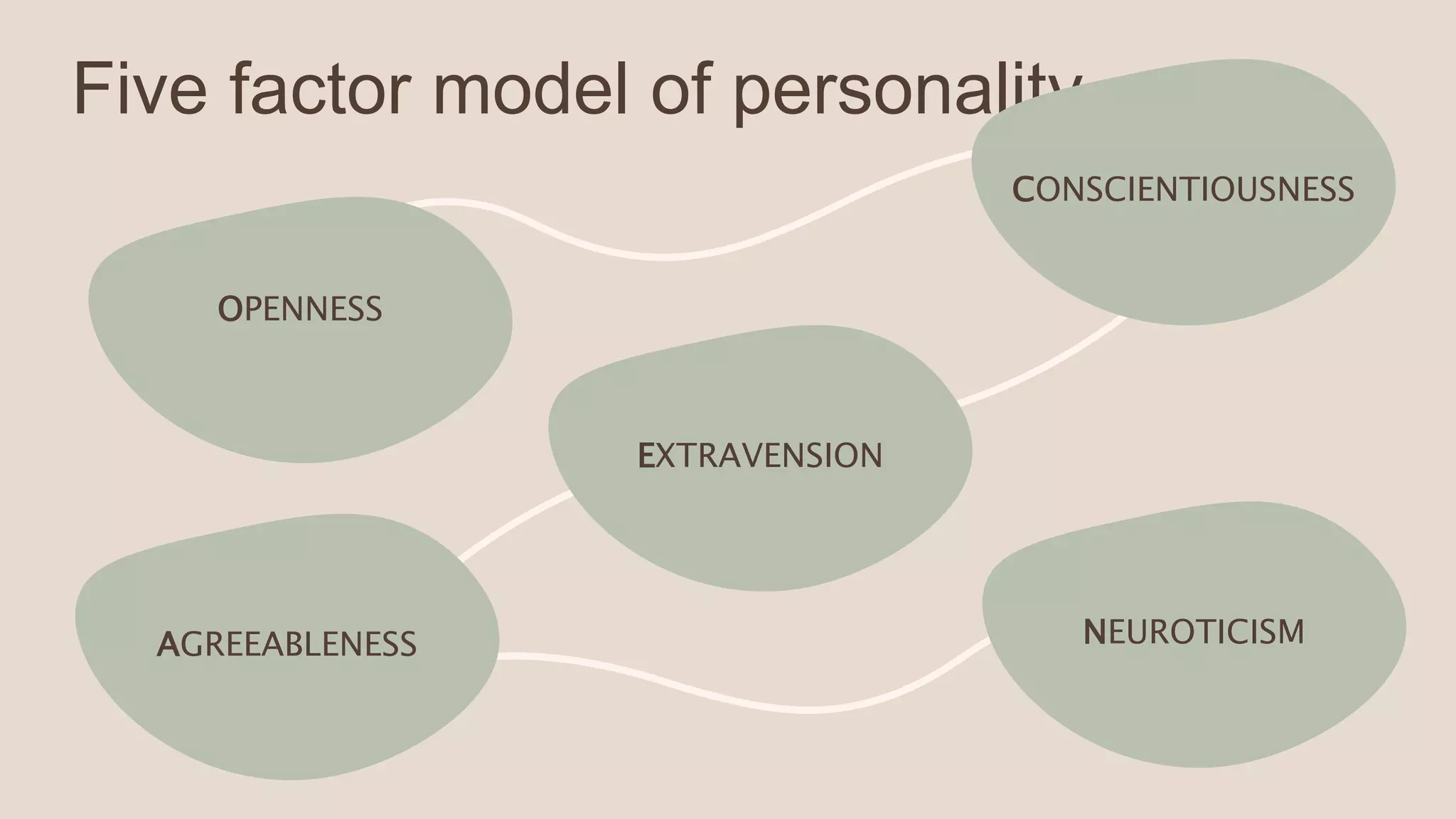
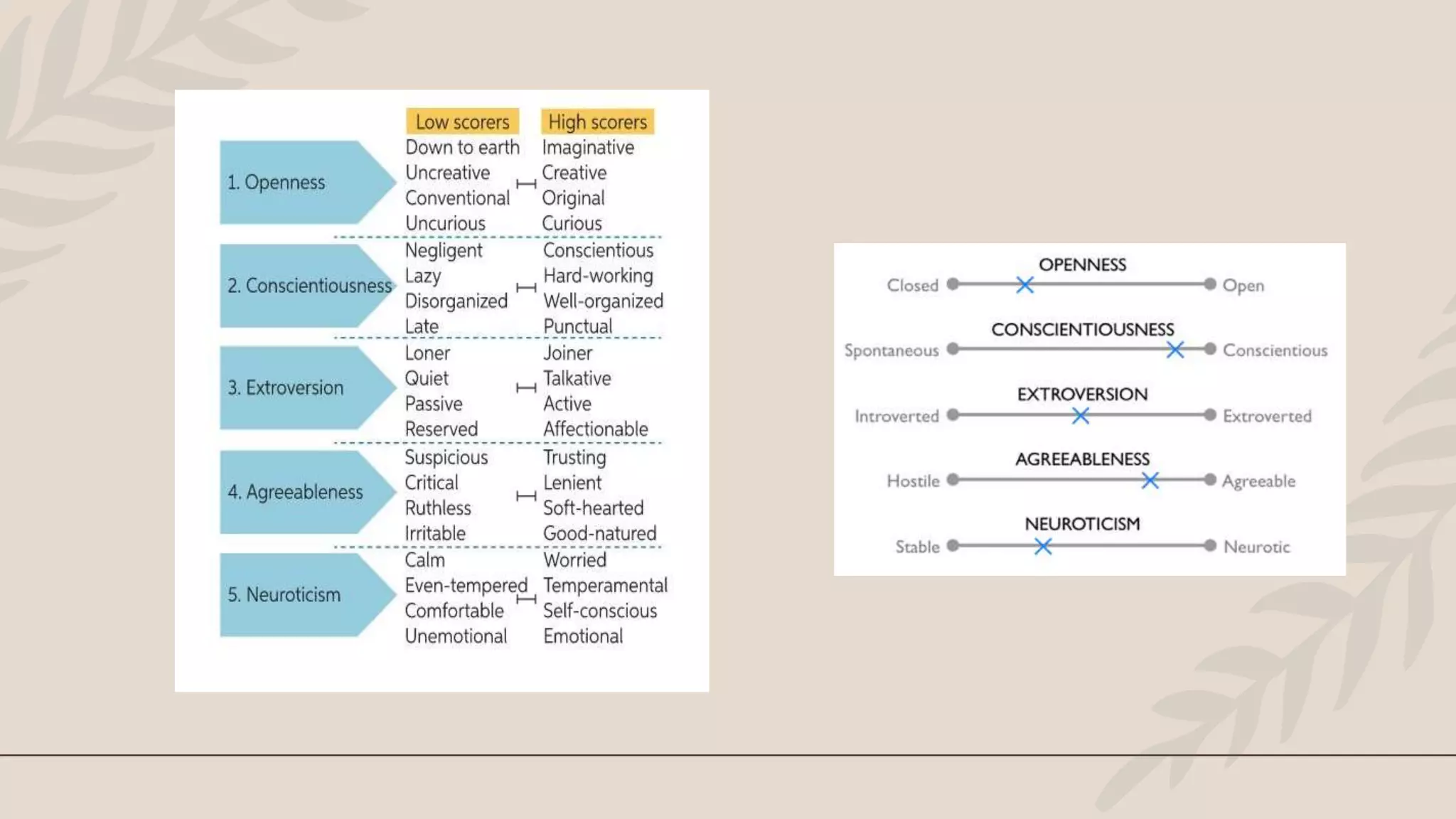
The five-factor model of personality identifies five broad domains or factors of personality: Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism. Researchers including Raymond Cattell, Gordon Allport, Robert McCrae and Paul Costa contributed to the development and validation of this model. Each of the five factors represents a continuum between two extremes. The five-factor model is now widely used to study individual differences in personality and their implications.