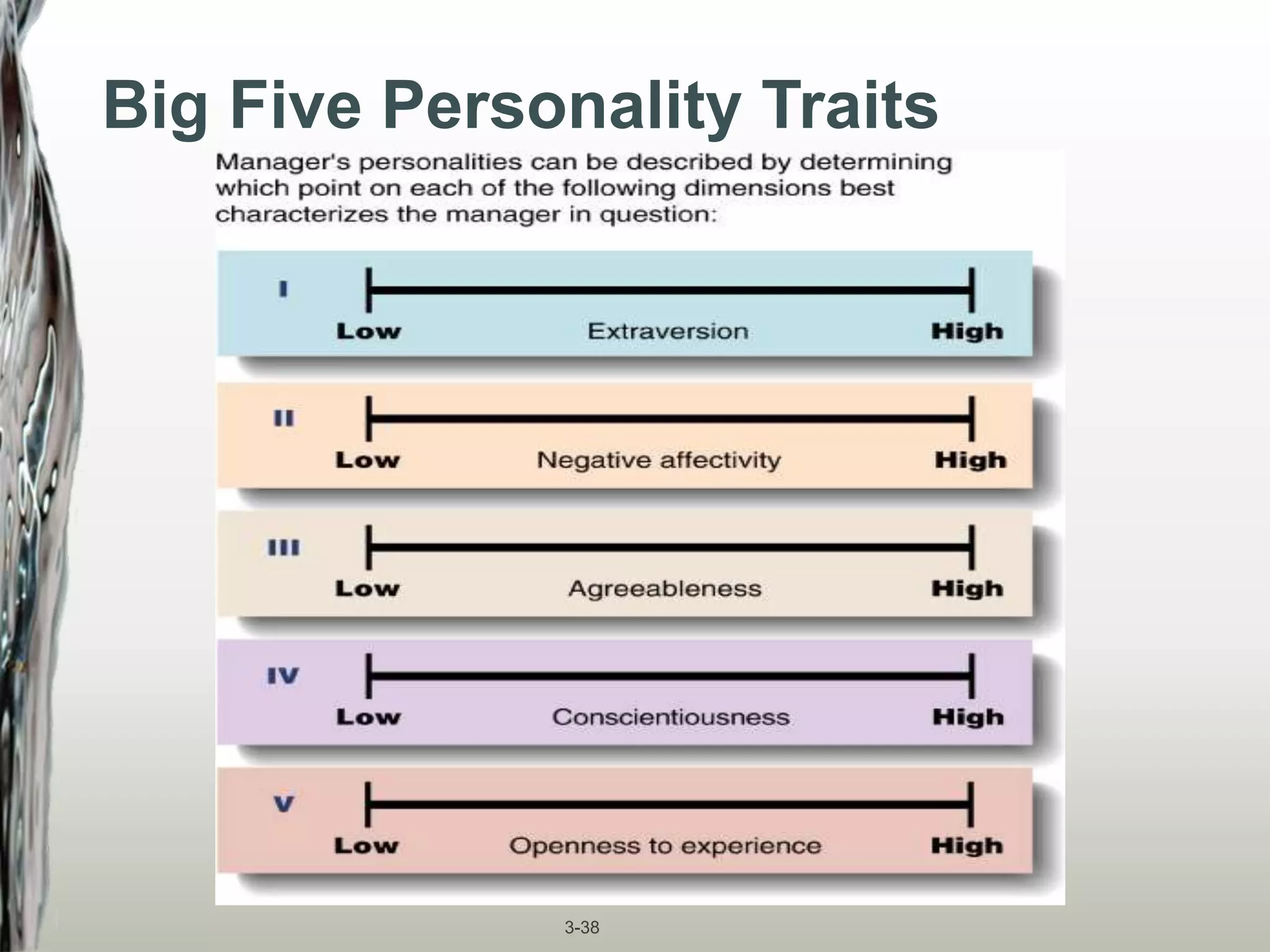
This document discusses personality types and models. It covers the Big Five personality traits of extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and openness. It also discusses Myers-Briggs personality types based on preferences for extraversion/introversion, sensing/intuition, thinking/feeling, and judging/perceiving. Understanding personality types can help managers understand how to interact with different personalities.